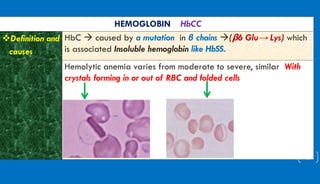
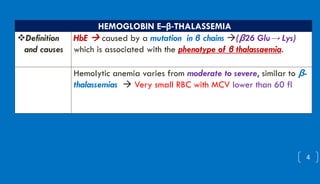
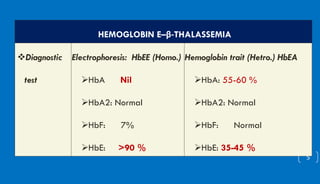
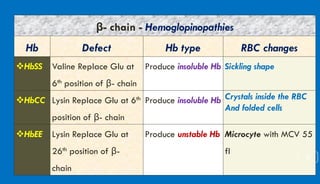
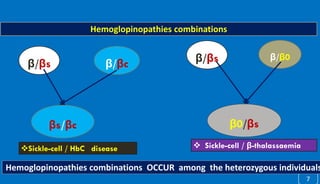
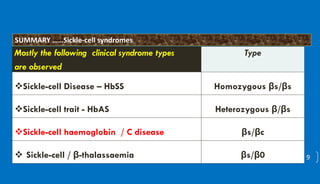
This document discusses different hemoglobinopathies including HbCC, HbEE, and their combinations. HbCC is caused by a mutation in the beta chains and results in insoluble hemoglobin and hemolytic anemia of varying severity due to crystal formation inside or outside red blood cells. HbEE also results from a beta chain mutation and causes unstable hemoglobin and microcytic anemia similar to beta-thalassemia. Electrophoresis can be used to diagnose HbCC and HbEE homozygous and heterozygous states. Common sickle cell syndromes include sickle cell disease (HbSS), sickle cell trait (HbAS), sickle cell hemoglobin C disease (HbSC), and sick