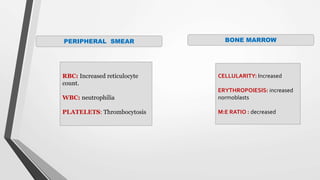
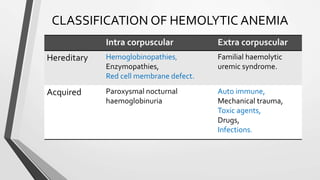
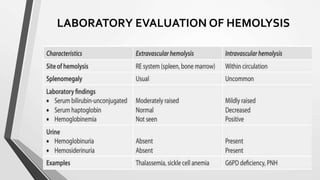
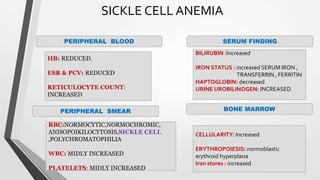
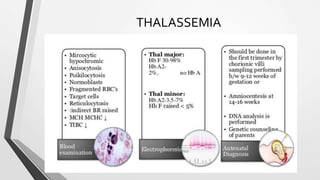
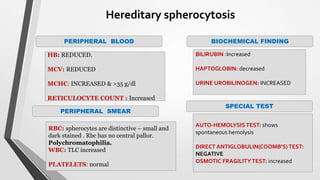
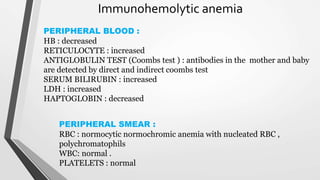
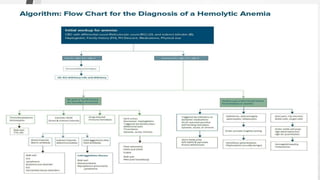
This document discusses the workup and evaluation of hemolytic anemia. Common tests include a complete blood count, peripheral smear, LDH, haptoglobin, and indirect bilirubin. Changes in LDH and low haptoglobin are sensitive indicators of hemolysis. Hemolytic anemias can be hereditary or acquired. The workup depends on the suspected cause and may include hemoglobin electrophoresis, Coombs testing, and flow cytometry to identify the specific type of hemolytic anemia.


![GENERAL FEATURES
OF HEMOLYTIC DISORDERS
GENERAL EXAMINATION - JAUNDICE, PALLOR
BOSSING OF SKULL
PHYSICAL FINDINGS - ENLARGED SPLEEN
HEMOGLOBIN - FROM NORMAL TO SEVERELY REDUCED
MCV - USUALLY INCREASED
RETICULOCYTES - INCREASED
BILIRUBIN - INCREASED[MOSTLY UNCONJUGATED]
LDH - INCREASED
HAPTOGLOBULIN - REDUCED TO ABSENT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesu-161210151447/85/lab-work-up-for-hemolytic-anemia-3-320.jpg)