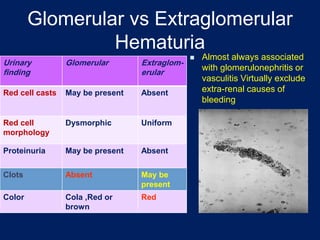
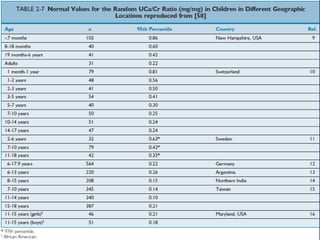
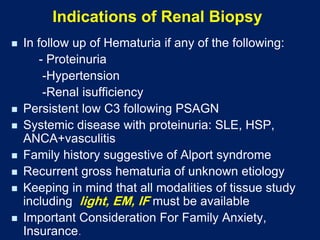
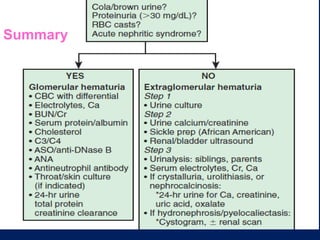
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is a common reason children are referred to pediatricians and nephrologists. While sometimes transient and insignificant, hematuria can also be a sign of serious renal disease. The document outlines the evaluation and workup of hematuria in children, noting that urinalysis, history, and physical exam usually guide the cause. For isolated microscopic hematuria, repeat testing and minimal workup can rule out significant disease in most cases. However, if hematuria presents with proteinuria, rising creatinine, failure to thrive, or hypertension, it increases the likelihood of an underlying serious renal condition requiring further evaluation.