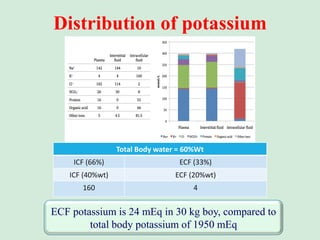
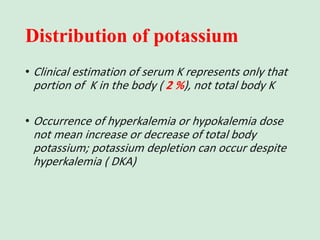
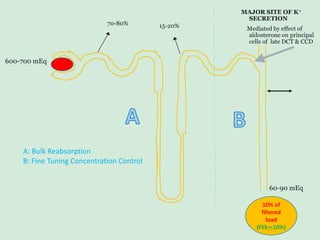
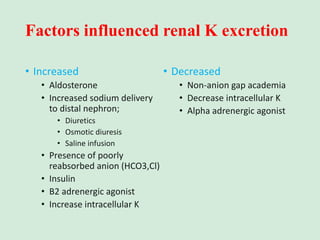
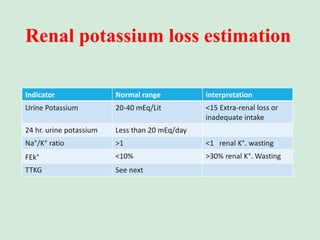
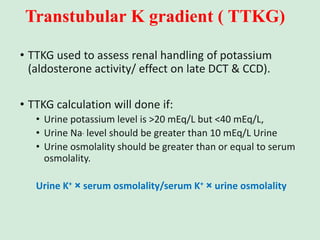
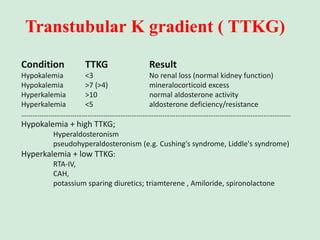
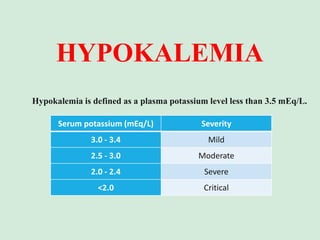
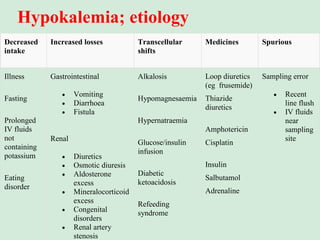
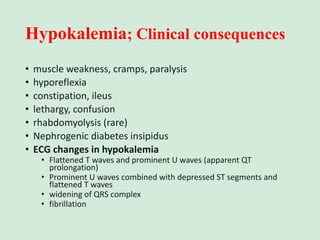
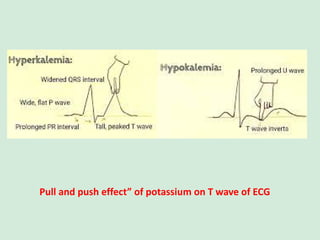
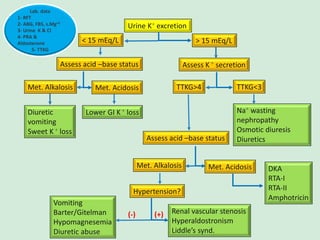
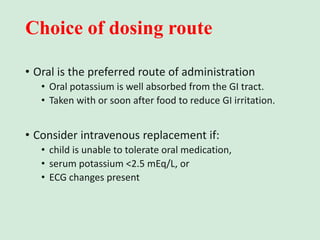
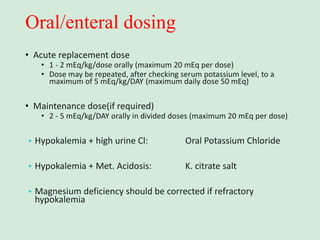
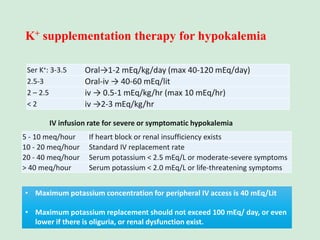
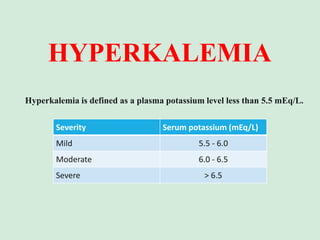
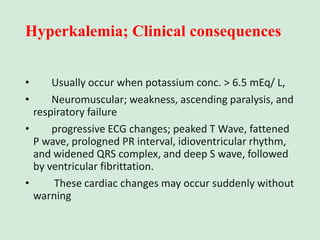
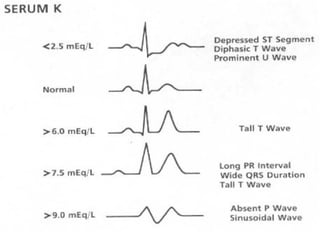
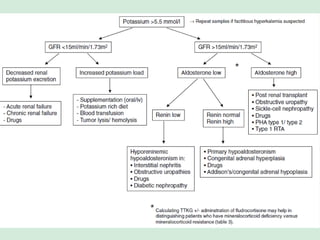
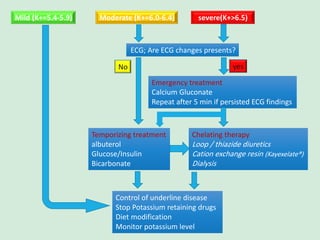
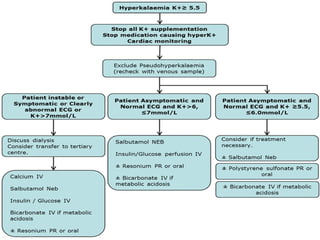
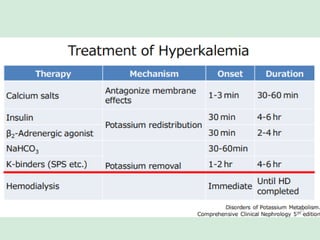
This document discusses potassium balance and disorders of potassium levels. It begins by outlining the vital functions of potassium ions in the body and factors that influence potassium balance. It then details the causes, clinical features, diagnostic approaches, and therapies for hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. For hypokalemia, it discusses etiologies such as decreased intake, increased losses, and transcellular shifts. It outlines clinical consequences, diagnostic testing, and management including oral or IV potassium replacement. For hyperkalemia it similarly discusses etiologies, clinical consequences, and emergency, temporizing, and chelating therapy approaches.