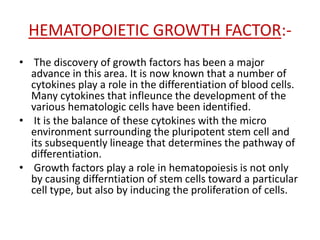
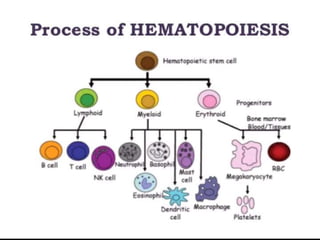
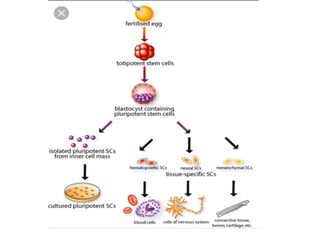
Hematopoiesis is the formation of blood cellular components from hematopoietic stem cells. Hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into red blood cells, lymphocytes, or non-lymphocyte white blood cells. In fetal development, hematopoiesis occurs in the yolk sac and liver before shifting to the bone marrow in adults. Stem cells are capable of self-renewal and differentiation into various blood cell types. Growth factors play an important role in hematopoiesis by influencing the differentiation and proliferation of blood cell lineages from hematopoietic stem cells.

![IN FETAL DEVELOPMENT:-
-- Yolk sac, and then liver as body matures.
IN ADULTS:- RBCs and Platelets are made in
the bone marrow.
-- WBCs are made in lymph tissue [ more on that
later].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hematopoesis-200916185749/85/Hematopoesis-4-320.jpg)

![HALLMARKS OS HSCs:-
• SELF- RENEWAL:- Ability to make copies the
same or very similar potential.
• DIFFERENTIATION:- Differentiation into several
different cellular components pf blood.
• MIGRATION:- Occurs at specific times during
development [ i.e. seeding of fetal liver, spleen,
and eventually bone marrow] and certain
condition [ e.g. Cytokine induced mobilization ]
later in life.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hematopoesis-200916185749/85/Hematopoesis-9-320.jpg)

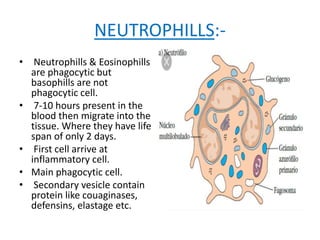
![GRANULOCYTIC CELL:-
• Neutrophils from the
major part of the white
blood carpules [ 40- 75%]
they are mostly short
lived cells with multilobed
nucleus.
• The cytoplasmic contain
granules which do not
take up acidic or basic
stains strongly and hence
named Neutrophils.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hematopoesis-200916185749/85/Hematopoesis-12-320.jpg)
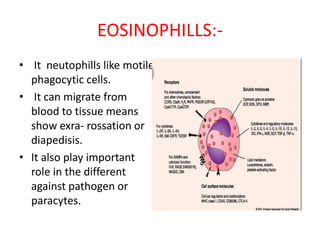
![BASOPHILLS:-
• Non- phagocytic granulocytes.
• vesicle having various signal
molecule like Histamins,
protaglanibins, [ response for
inflammation or pain] and inter- lucin
1.
• Degranulation to contain release
outside.
• immunoglobulin E receptor
recognise FC region immunoglobulin
E.
• Designaline molecules causes in
flammantory response.
• It creates hyper sensitivity type 1.
like Allergy, pollen dust, perform.
• epethelial tissue of respiratory
,genital urinary tract, digestive tracts
also have mast cells.
• IgE mediated response is mediated
by both [ basophills, mast cell].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hematopoesis-200916185749/85/Hematopoesis-14-320.jpg)

![DENDRITIC CELL:-
• Most active antigen prenting
cell[ ATC].
• It having long membranous
projections.
• It look like dendrites of
neuron.
• It have low surface area due
to presence of projetions.
• It express MHC class II With
antigen.
• It activates T- Helper cella
• Originated from both Myeloid
and lymohoid progeniter cell.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hematopoesis-200916185749/85/Hematopoesis-17-320.jpg)