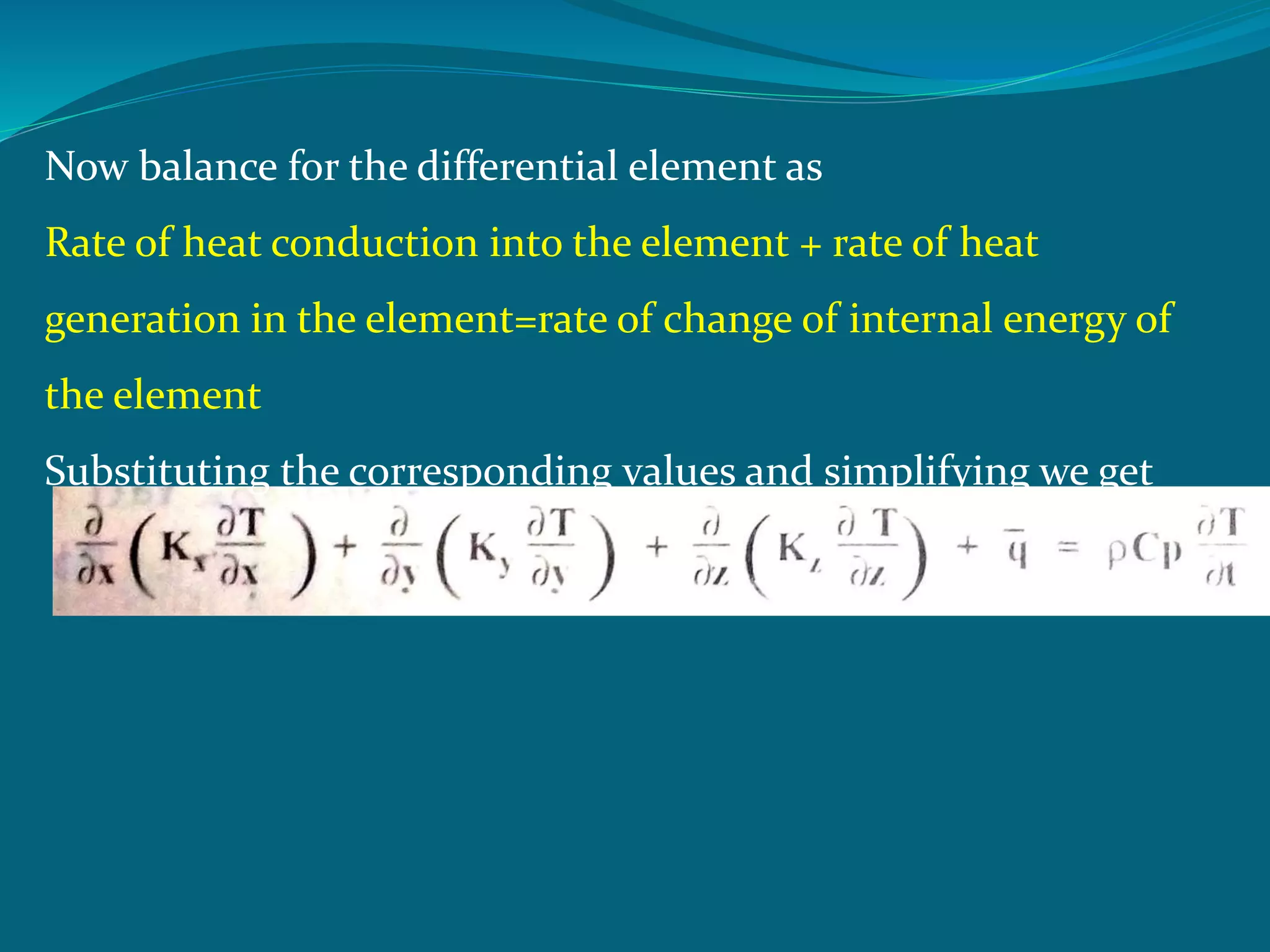
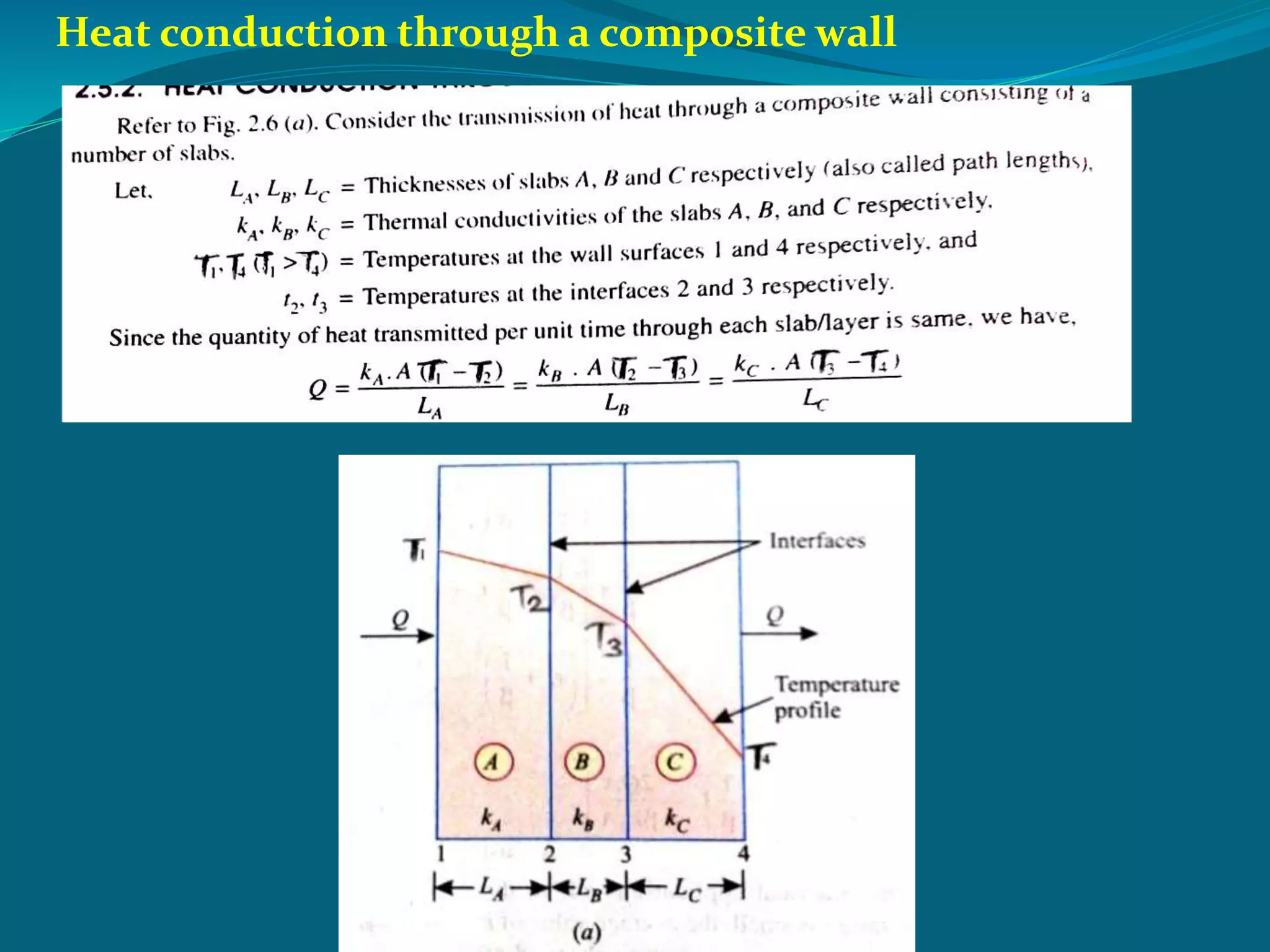
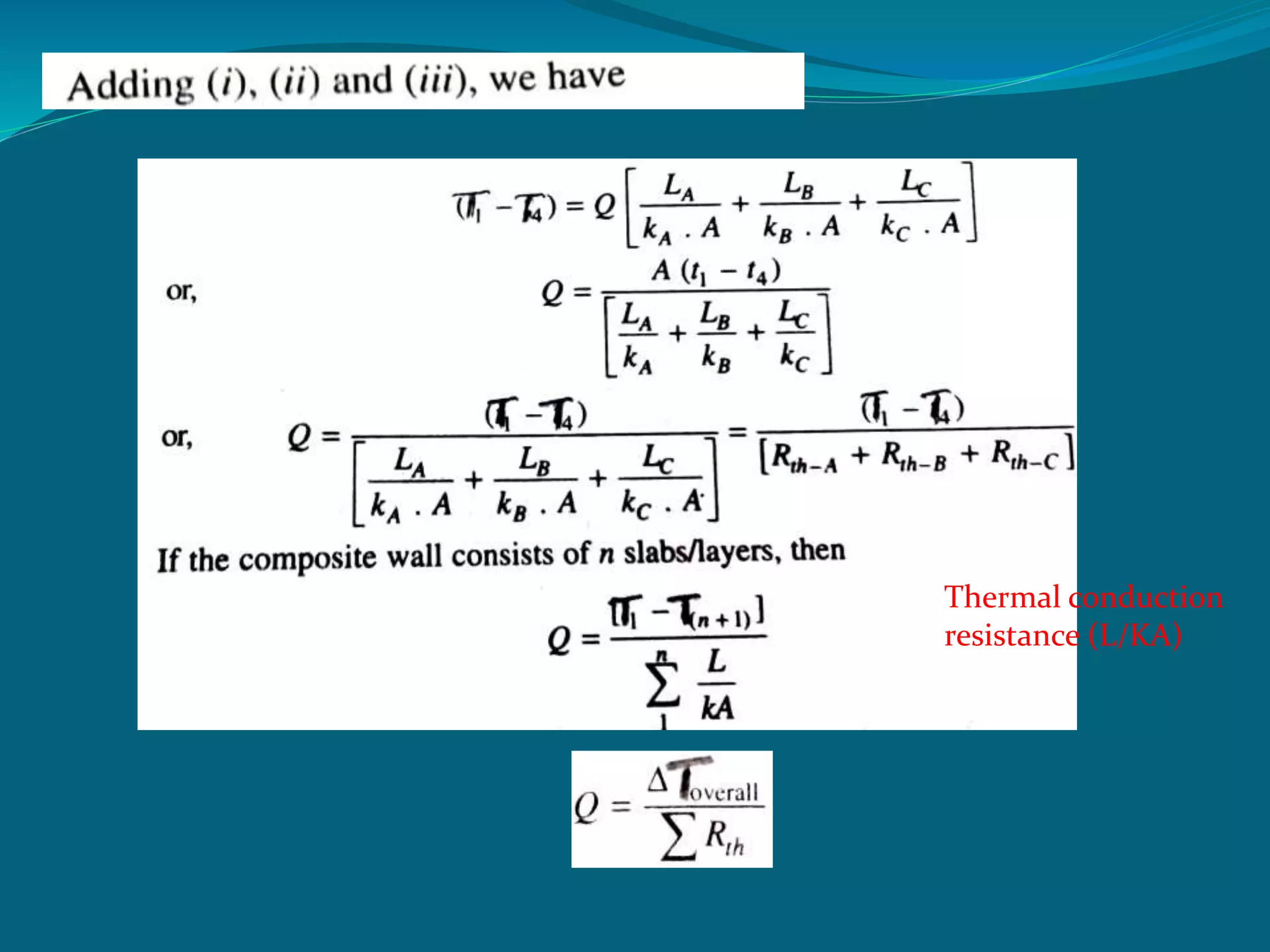
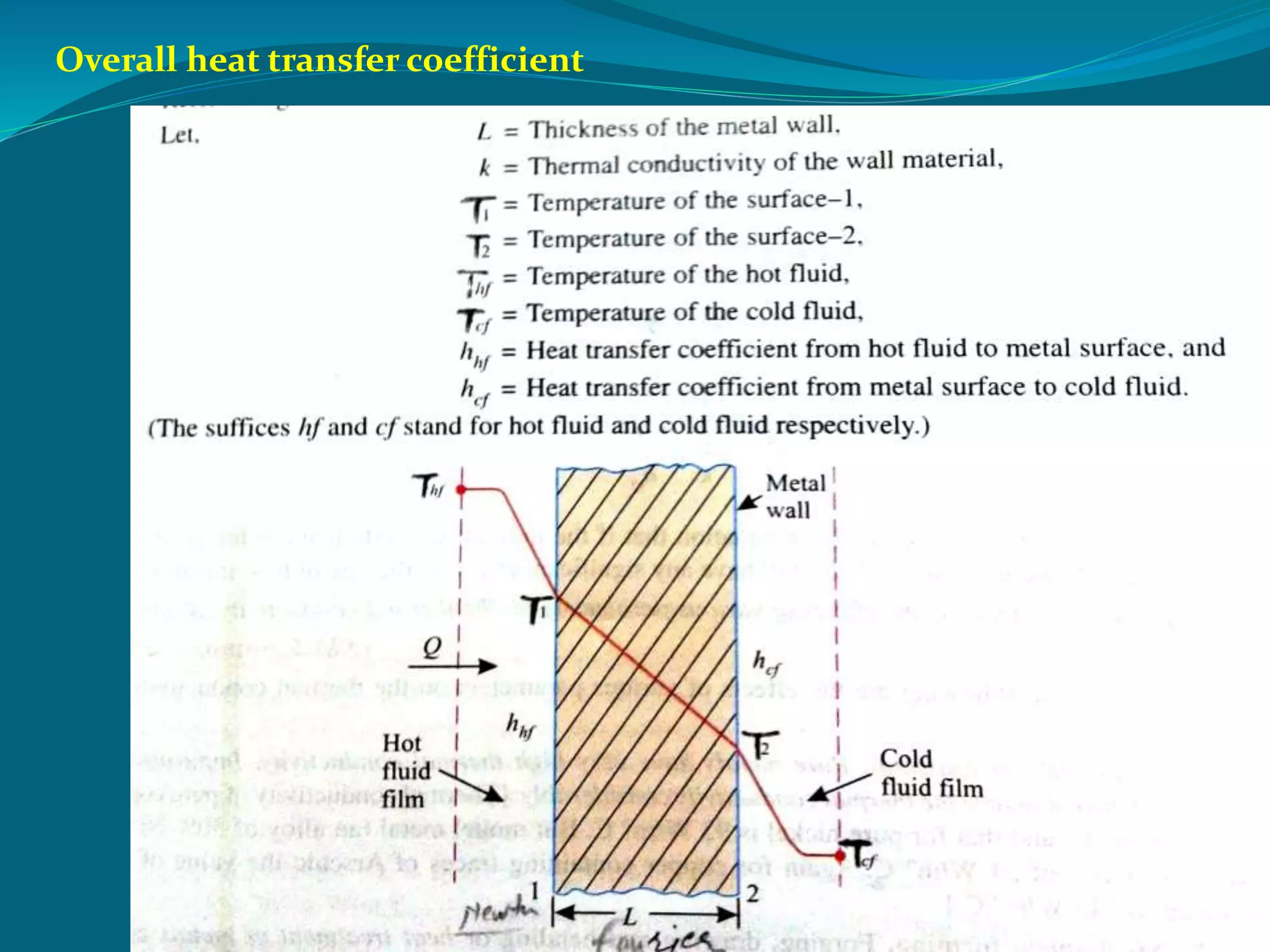
This document discusses heat conduction and the differential equation of heat conduction. It introduces the concept of using a differential element to model heat transfer in the x, y, and z directions. The rate of heat conduction into and out of the element is equated to the rate of heat generation and change in internal energy of the element to derive the general heat conduction equation. The document also discusses thermal diffusivity and its relationship to thermal conductivity and heat capacity, as well as heat conduction through composite walls.