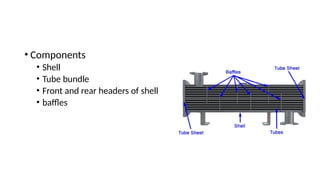
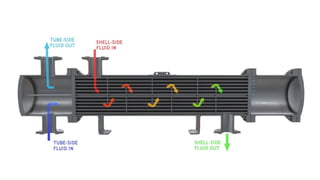
A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of a bundle of tubes inside a cylindrical shell, allowing one fluid to flow inside the tubes and another over them. While it is cheaper and easier to maintain than plate heat exchangers, it is less efficient and requires more space for maintenance. The design allows for thermal expansion and has measures to reduce leakage risks, but it cannot increase cooling capacity as effectively as plate heat exchangers.