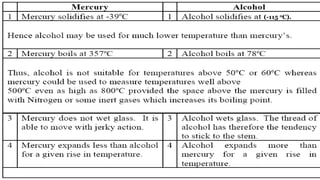
1. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a sample of matter. Thermometers are devices used to define and measure temperature.
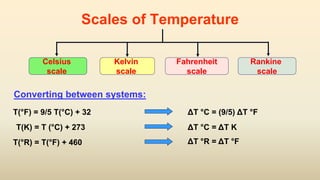
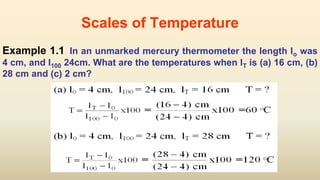
2. Thermometers work by exploiting a physical property, like length or resistance, that changes uniformly with temperature. They require fixed points like freezing and boiling points to define a temperature scale.
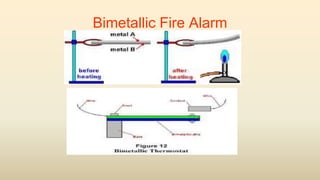
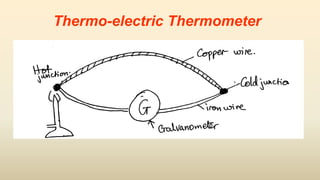
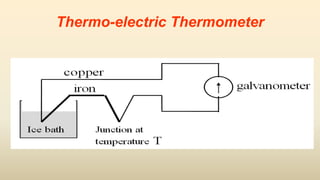
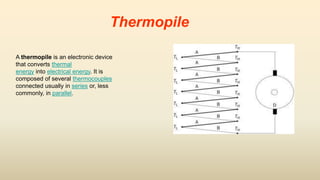
3. Common thermometers include liquid-in-glass, bimetallic, resistance, and thermoelectric types. Each exploits a different temperature-sensitive physical property and has advantages like accuracy, range, or response time.













![Fill in the blanks
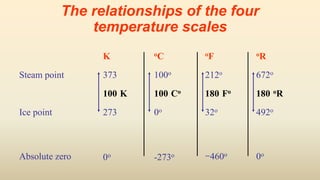
ice
steam 100
273 32
212
-40
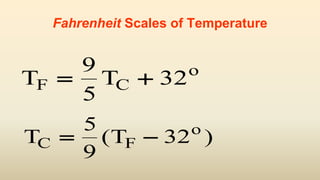
= (5/9)[TF-32] = (5/9) (-72) = - 40T TC F
o
5
9
32( )
233](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/22-200601153200/85/heat-18-320.jpg)