1) The document defines temperature and different ways of measuring it, including various temperature scales like Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
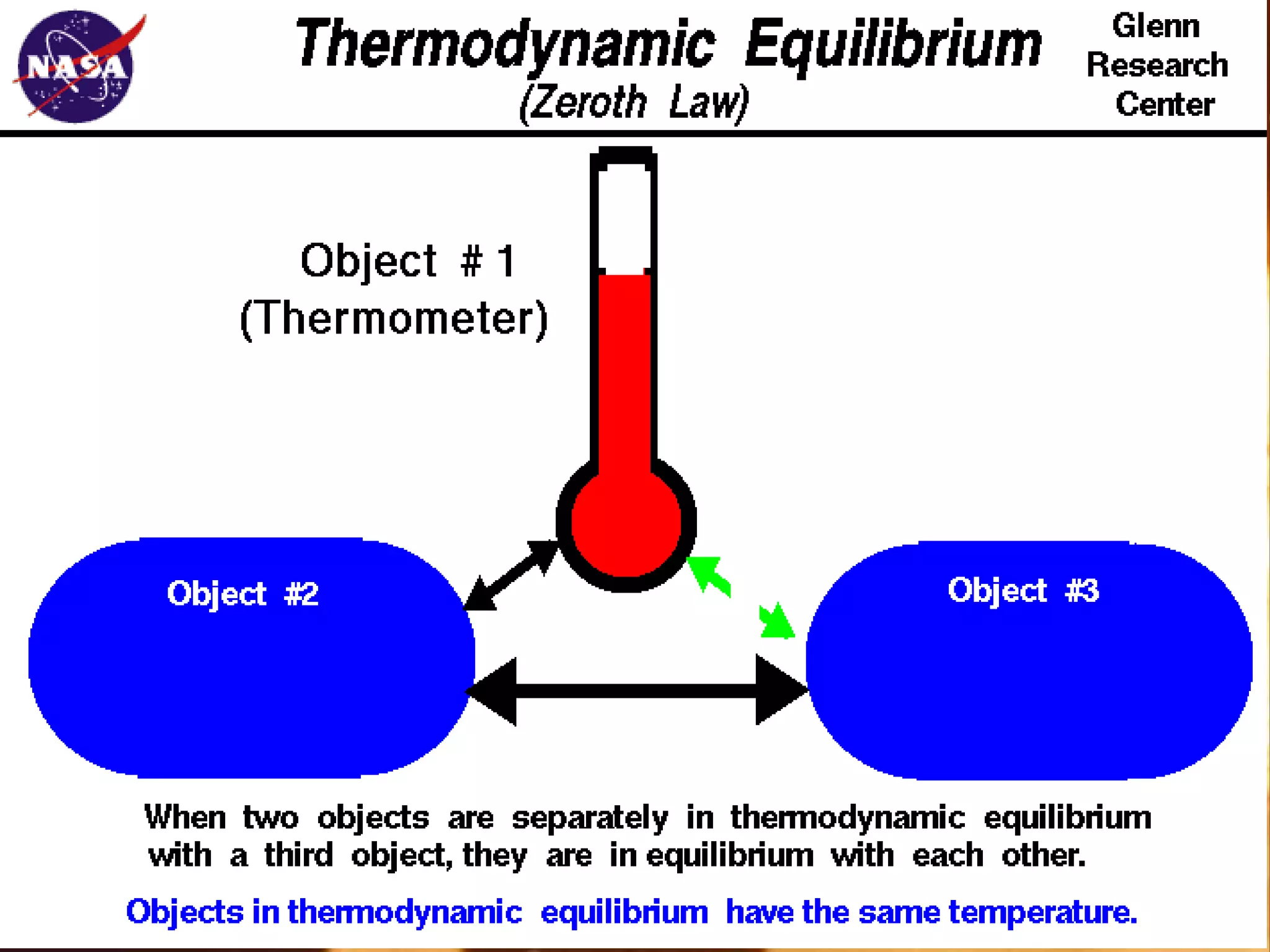
2) Methods of temperature measurement are discussed, including thermometers, thermocouples, and pyrometers. Conversion formulas between temperature scales are also provided.
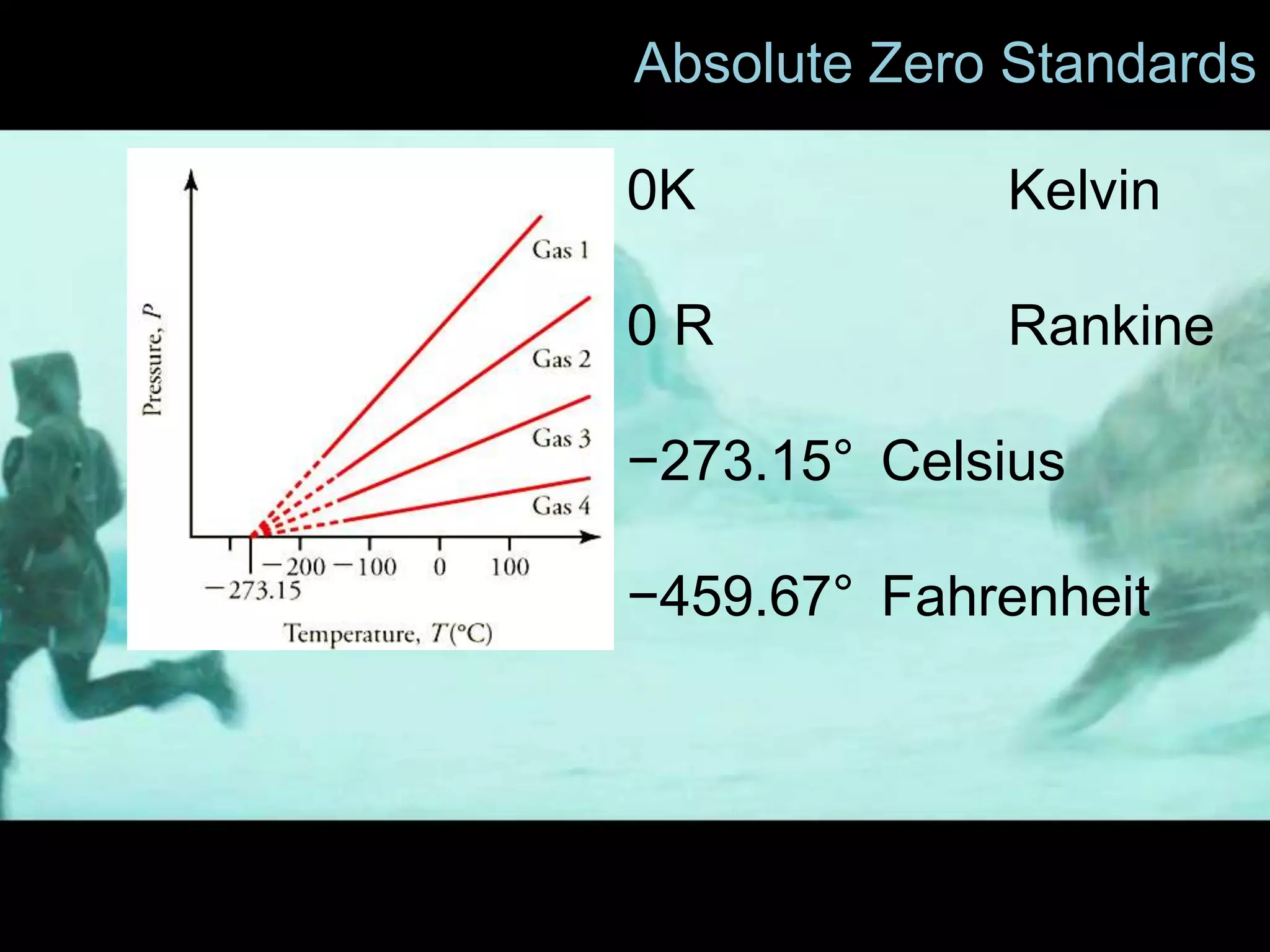
3) Several problems are presented involving converting temperatures between Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin scales and calculating temperature changes. Absolute zero is defined as the lowest possible temperature where entropy reaches its minimum value.