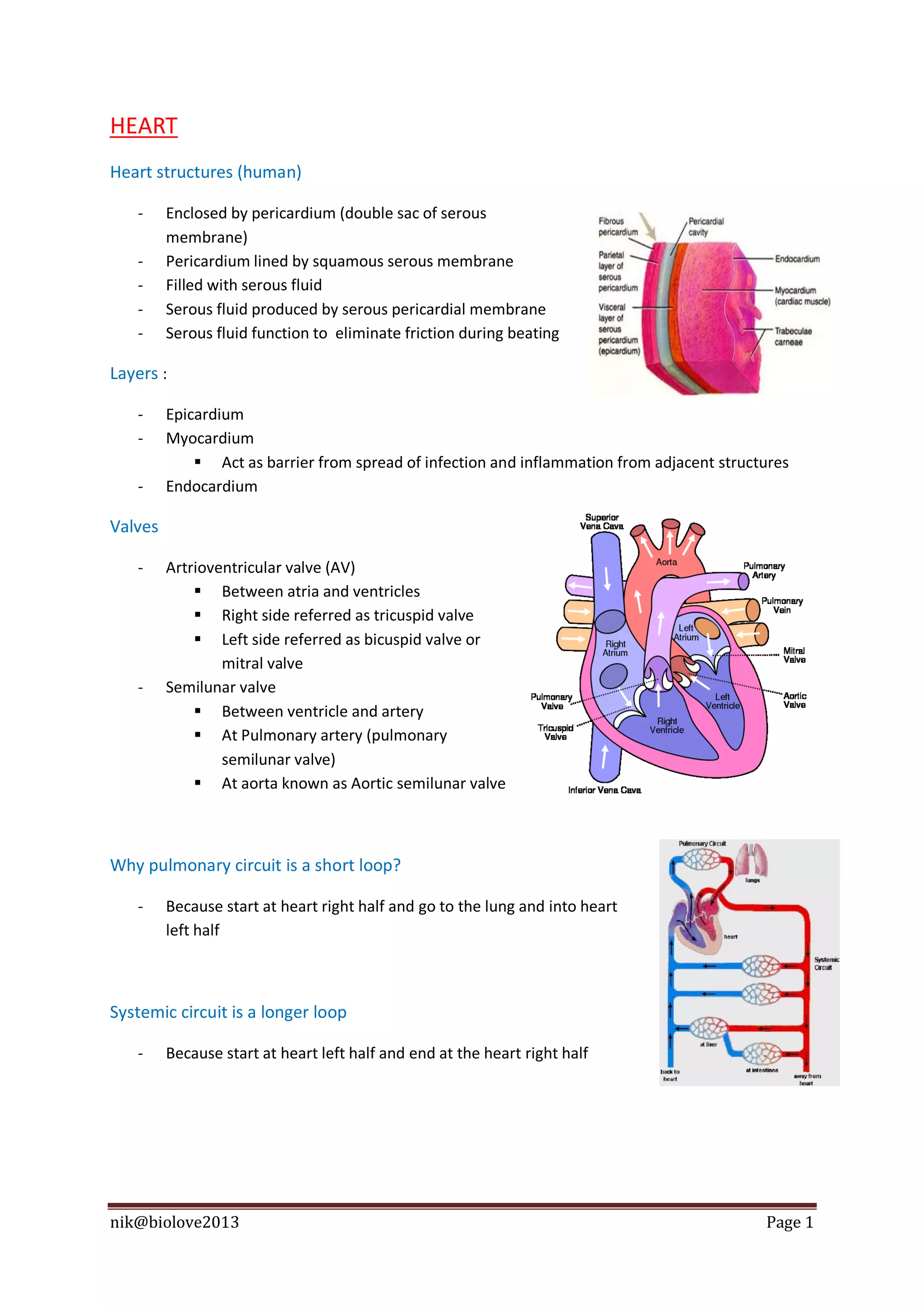
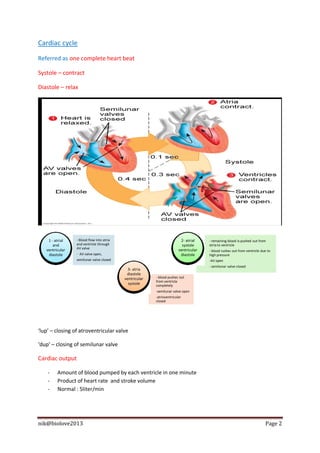
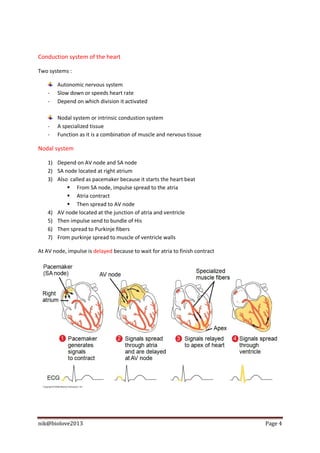
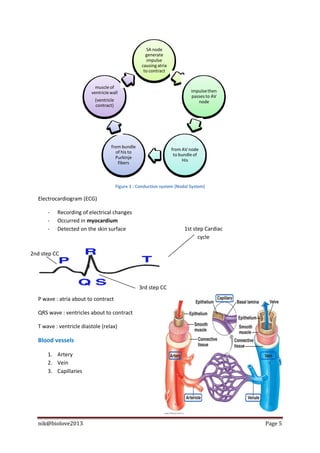
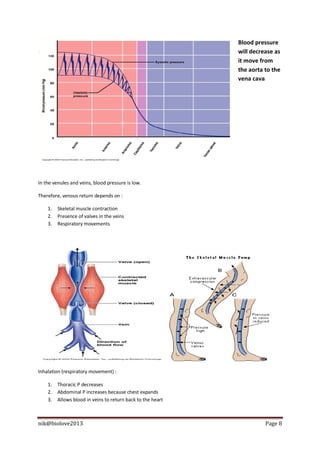
The document describes the structure and function of the human heart. It discusses the layers of the heart, including the epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium. It also describes the heart valves, cardiac cycle, conduction system, regulation of heart rate, and blood vessels. In summary, the document provides an overview of the anatomy and physiology of the heart and circulatory system.