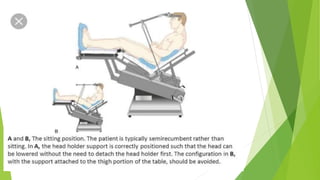
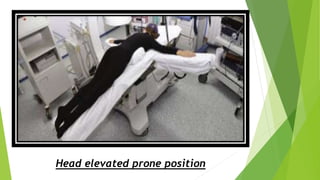
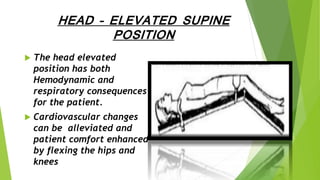
This document discusses various head elevated positions used in surgery and their purposes. It describes the low sitting position, used for neck dissection and dental procedures, where the torso is elevated about half as much as a standard sitting position. The sitting position is most frequently used and elevates the head above the heart to improve drainage during neurosurgery. The head elevated prone position, also called the concorde position, is used for posterior fossa neurosurgery with the head elevated slightly above the heart. The head elevated supine position elevates the head and moves the abdominal contents downwards, providing better exposure for procedures like laparoscopic cholecystectomy.