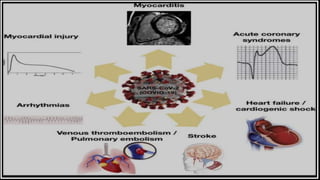
Common postoperative cardiovascular complications include myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias, hypotension, and deep vein thrombosis. Signs and symptoms of complications involve palpitations, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Treatment includes monitoring cardiac rhythm, administering antiarrhythmic medications to stabilize rhythm, intravenous fluids to raise blood pressure, and blood thinners to prevent clot formation. Nursing interventions focus on close monitoring of vital signs and cardiovascular status, encouraging mobility to prevent deep vein thrombosis, and proper use of compression devices.