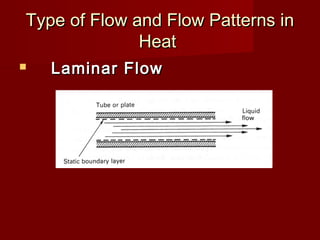
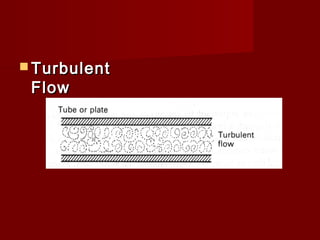
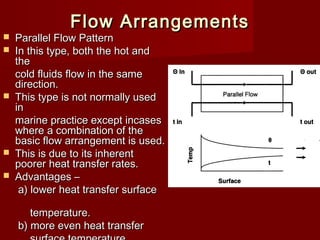
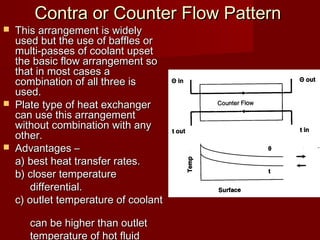
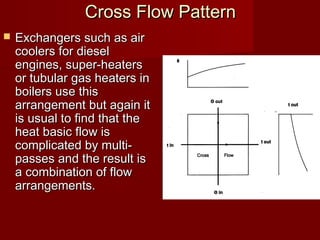
Heat exchangers transfer heat from one medium to another and come in various types. They consist of channels that separate the mediums but allow heat transfer between them. Common examples include coolers that use sea water to cool engine fluids, and heaters that use steam to heat fuels. Tubular heat exchangers are most widely used and can accommodate a variety of temperatures and pressures. Heat exchangers effectively transfer heat through processes like cooling, heating, condensing, and evaporating.