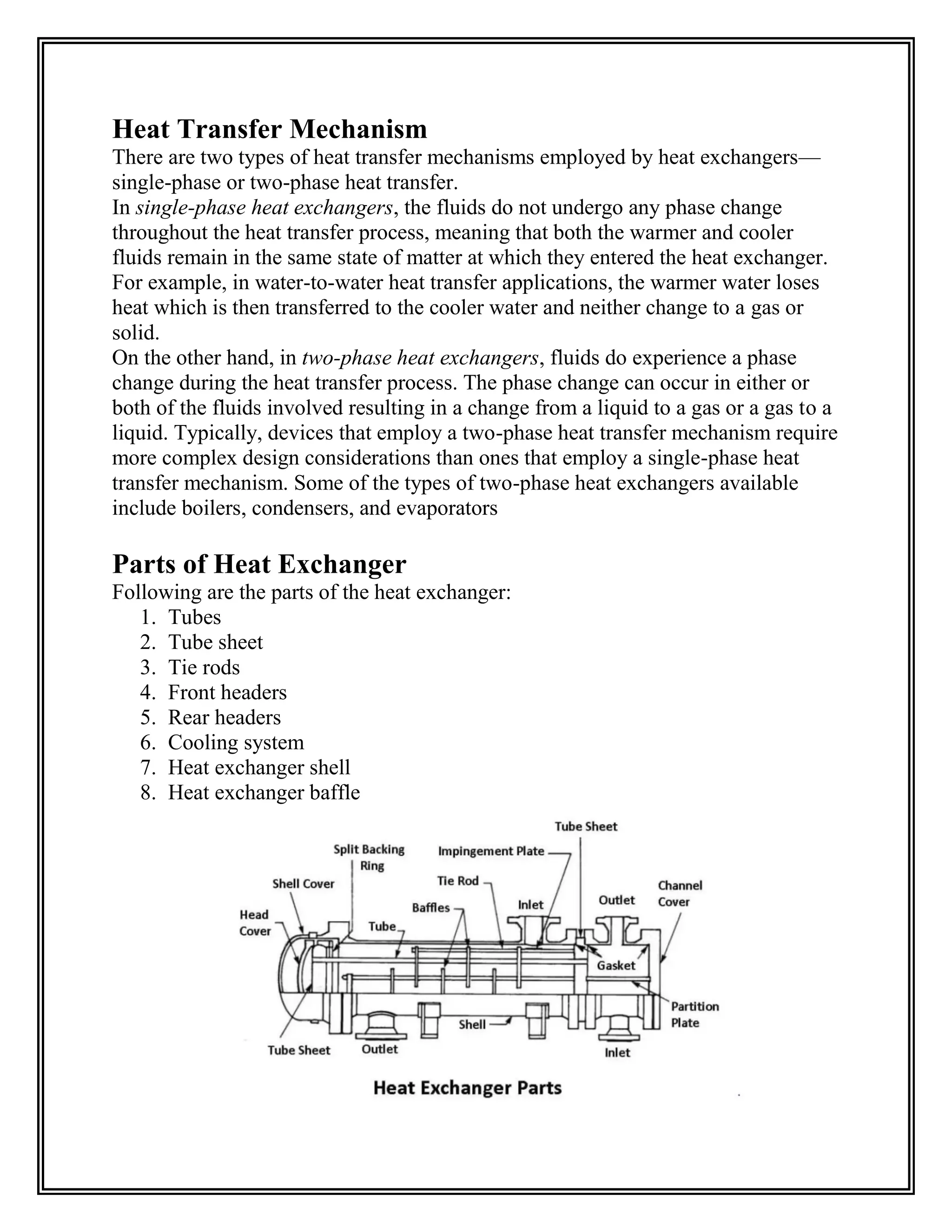
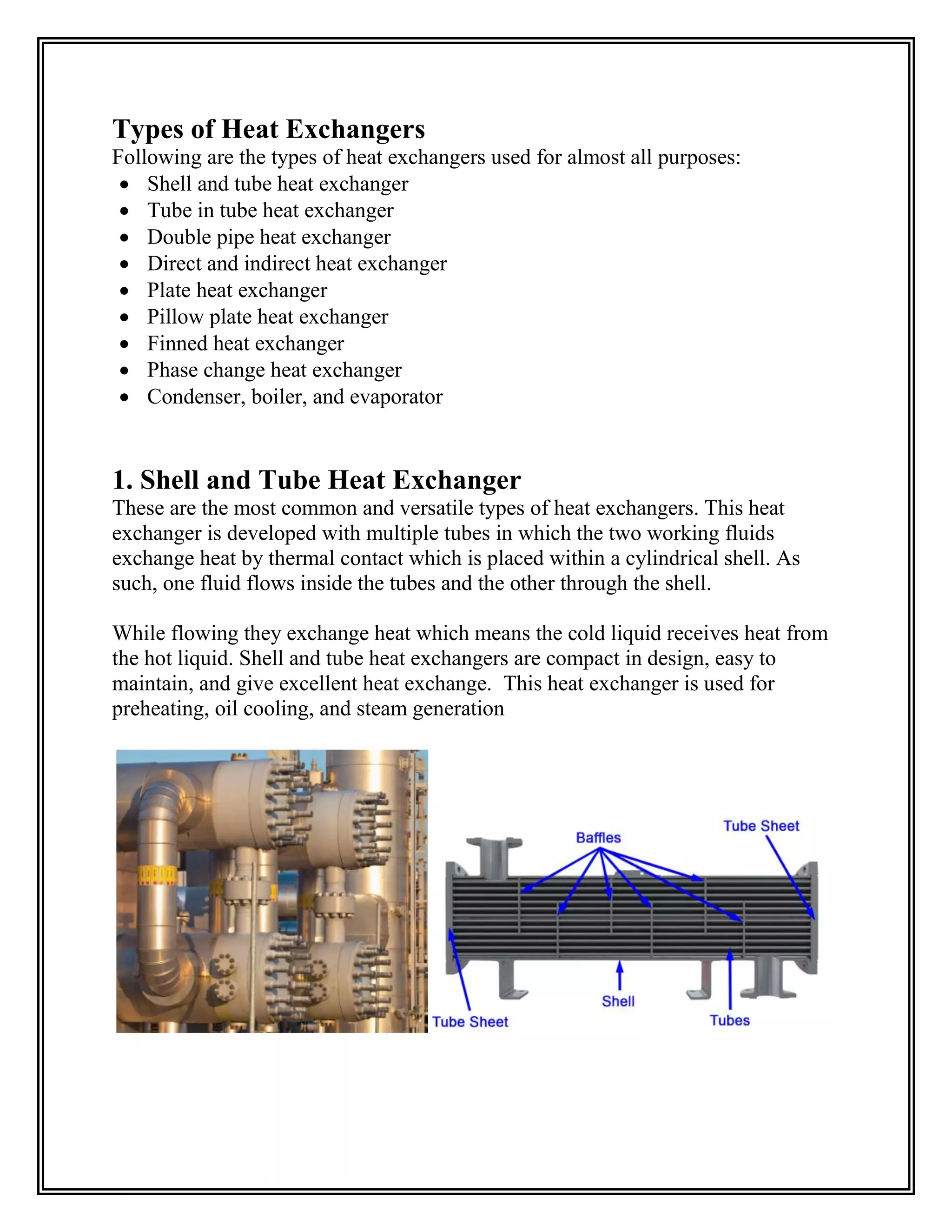
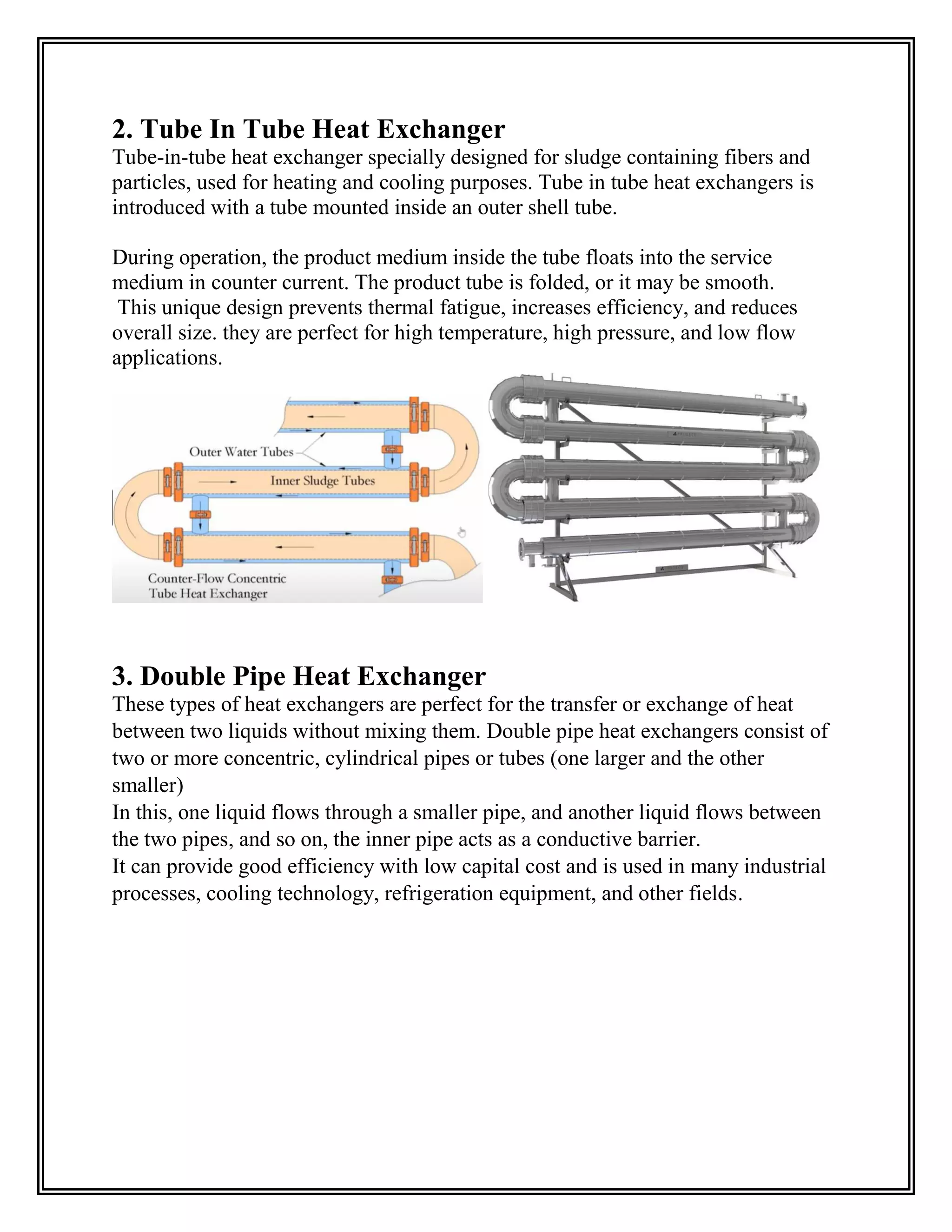
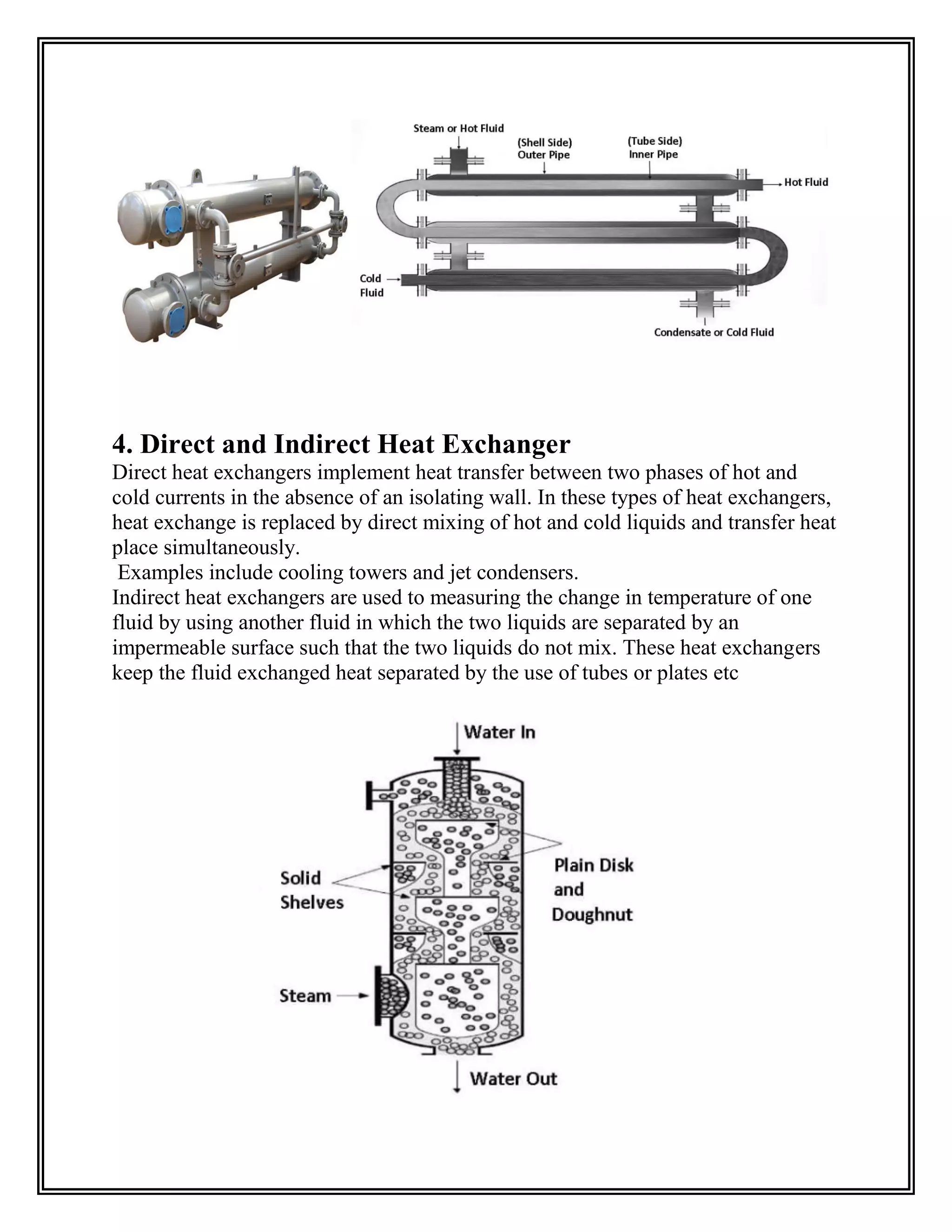
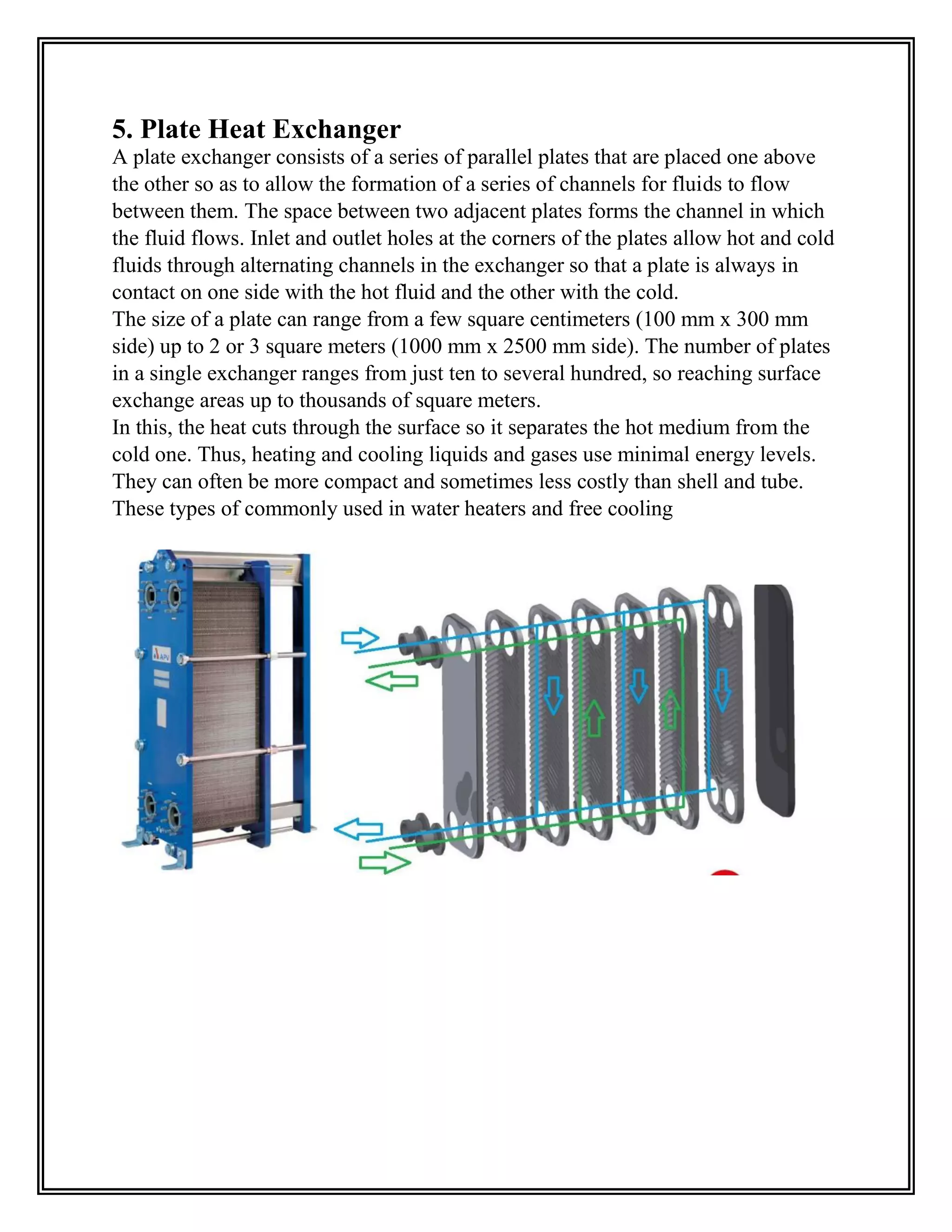
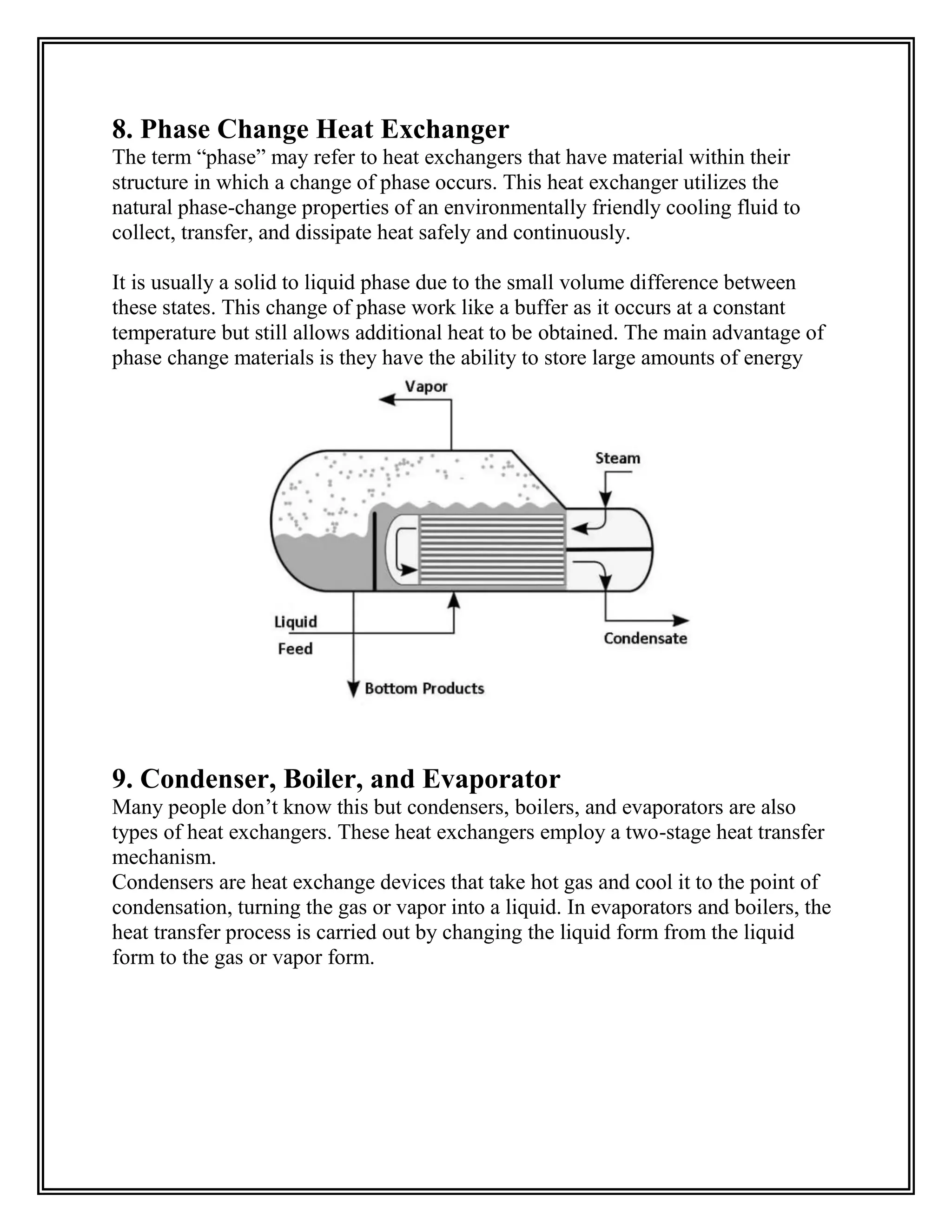
Heat exchangers transfer heat from one medium to another without the two ever mixing. They are used for cooling and heating in applications like air conditioning, refrigeration, and power plants. The document discusses the main types of heat exchangers like shell and tube, plate, and finned tube heat exchangers. It explains how each works and provides examples of their applications.