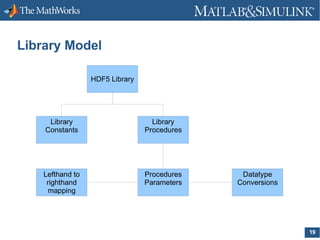
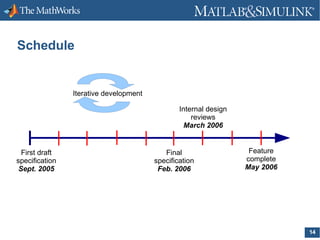
The document discusses the implementation of HDF5 in MATLAB, detailing customer requests for high-level functions, the functionality of various HDF5-related functions like hdf5read, hdf5write, and hdf5info, and the iterative development schedule for these features. It outlines use cases highlighting the need for improved data handling capabilities and the ability to utilize complex data types without MATLAB's overhead. The document also emphasizes future enhancements, including support for large arrays and parallel I/O.












![Use Cases
Use a variety of esoteric HDF5 features at once:
“I'm trying to use HDF5 files [with] grouping
features like compound data types, group links,
and reference data types.”
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5inmatlab-140218121024-phpapp02/85/Implementing-HDF5-in-MATLAB-13-320.jpg)
![MATLAB is not C
Hmm . . . I might
throw an error.
MATLAB
[out1, out2] = function(in1, in2);
C
status = function(in1, in2, &out1, &out2);
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5inmatlab-140218121024-phpapp02/85/Implementing-HDF5-in-MATLAB-15-320.jpg)
![MATLAB is not C
mxArray
void * p_real
void * p_complex
size_t dims[]
size_t ndims
mxCLASS_ID type
...
...
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdf5inmatlab-140218121024-phpapp02/85/Implementing-HDF5-in-MATLAB-16-320.jpg)