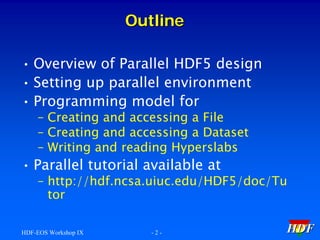
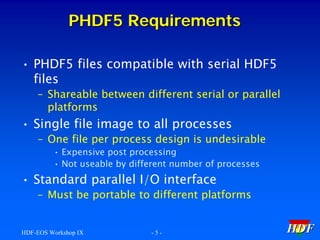
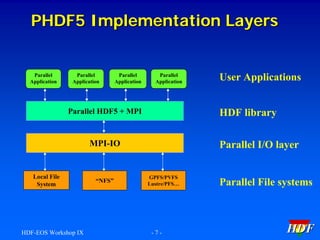
This document provides an introductory tutorial on Parallel HDF5 within the context of the HDF and HDF-EOS Workshop IX. It covers topics such as the design and requirements of Parallel HDF5, programming models for file and dataset access, the differences between collective and independent calls, and examples of using the API for creating and accessing data. Key aspects include the necessity of using MPI for parallel processing and the importance of setting up parallel file access properties.
















![C Example
Parallel Dataset Create
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
file_id = H5Fcreate(…);
/*
* Create the dataspace for the dataset.
*/
dimsf[0] = NX;
dimsf[1] = NY;
filespace = H5Screate_simple(RANK, dimsf, NULL);
70
71
72
73
74
H5Dclose(dset_id);
/*
* Close the file.
*/
H5Fclose(file_id);
/*
* Create the dataset with default properties collective.
*/
dset_id = H5Dcreate(file_id, “dataset1”, H5T_NATIVE_INT,
filespace, H5P_DEFAULT);
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
- 20 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-20-320.jpg)








![Example 1
Writing dataset by rows
File
P1 (memory space)
offset[1]
count[1]
count[0]
offset[0]
count[0] = dimsf[0]/mpi_size
count[1] = dimsf[1];
offset[0] = mpi_rank * count[0];
offset[1] = 0;
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
- 29 -
/* = 2 */
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-29-320.jpg)
![C Example 1
71 /*
72
* Each process defines dataset in memory and
* writes it to the hyperslab
73
* in the file.
74
*/
75
count[0] = dimsf[0]/mpi_size;
76
count[1] = dimsf[1];
77
offset[0] = mpi_rank * count[0];
78
offset[1] = 0;
79
memspace = H5Screate_simple(RANK,count,NULL);
80
81 /*
82
* Select hyperslab in the file.
83
*/
84
filespace = H5Dget_space(dset_id);
85
H5Sselect_hyperslab(filespace,
H5S_SELECT_SET,offset,NULL,count,NULL);
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
- 30 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-30-320.jpg)
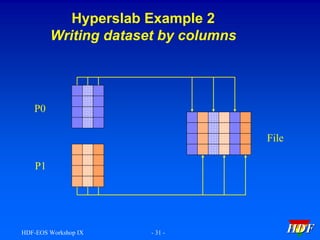

![Example 2
Writing Dataset by Column
Memory
P0 offset[1]
block[0]
P0
dimsm[0]
dimsm[1]
File
P1 offset[1]
block[1]
stride[1]
P1
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
- 33 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-33-320.jpg)
![C Example 2
85
86
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
/*
* Each process defines hyperslab in
* the file
*/
count[0] = 1;
count[1] = dimsm[1];
offset[0] = 0;
offset[1] = mpi_rank;
stride[0] = 1;
stride[1] = 2;
block[0] = dimsf[0];
block[1] = 1;
/*
* Each process selects hyperslab.
*/
filespace = H5Dget_space(dset_id);
H5Sselect_hyperslab(filespace,
H5S_SELECT_SET, offset, stride,
count, block);
- 34 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-34-320.jpg)


![Example 3
Writing dataset by pattern
Memory
File
stride[1]
P2
stride[0]
count[1]
offset[0] = 0;
offset[1] = 1;
count[0] = 4;
count[1] = 2;
stride[0] = 2;
stride[1] = 2;
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
offset[1]
- 37 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-37-320.jpg)
![C Example 3: Writing by
pattern
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
/* Each process defines dataset in memory and
* writes it to the hyperslab
* in the file.
*/
count[0] = 4;
count[1] = 2;
stride[0] = 2;
stride[1] = 2;
if(mpi_rank == 0) {
offset[0] = 0;
offset[1] = 0;
}
if(mpi_rank == 1) {
offset[0] = 1;
offset[1] = 0;
}
if(mpi_rank == 2) {
offset[0] = 0;
offset[1] = 1;
}
if(mpi_rank == 3) {
offset[0] = 1;
offset[1] = 1;
}
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
- 38 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-38-320.jpg)


![Example 4
Writing dataset by chunks
File
Memory
P2
offset[1]
chunk_dims[1]
offset[0]
chunk_dims[0]
block[0]
block[0] = chunk_dims[0];
block[1] = chunk_dims[1];
offset[0] = chunk_dims[0];
offset[1] = 0;
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
block[1]
- 41 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-41-320.jpg)
![C Example 4
Writing by chunks
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
HDF-EOS Workshop IX
count[0] = 1;
count[1] = 1 ;
stride[0] = 1;
stride[1] = 1;
block[0] = chunk_dims[0];
block[1] = chunk_dims[1];
if(mpi_rank == 0) {
offset[0] = 0;
offset[1] = 0;
}
if(mpi_rank == 1) {
offset[0] = 0;
offset[1] = chunk_dims[1];
}
if(mpi_rank == 2) {
offset[0] = chunk_dims[0];
offset[1] = 0;
}
if(mpi_rank == 3) {
offset[0] = chunk_dims[0];
offset[1] = chunk_dims[1];
}
- 42 -
HDF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phdf5tutorial1-cheng-140218130839-phpapp01/85/Parallel-HDF5-Introductory-Tutorial-42-320.jpg)

