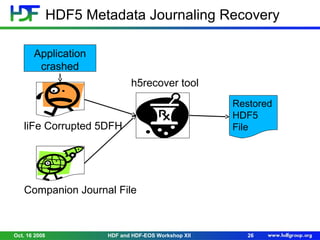
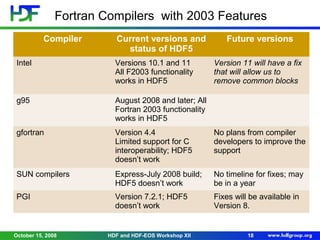
The document discusses enhancements and new features in HDF5 as of October 2008, including performance improvements, Fortran 2003 support, and a metadata journaling system for crash recovery. It highlights improvements in I/O performance and memory usage, along with new functionalities aimed at improving file management and data handling. Limitations of the Fortran API are also detailed, particularly around data type support and interoperability with C, while future enhancements are proposed for further improvements.







![Example
HDF5 "SDScompound.h5" {
GROUP "/" {
DATASET "ArrayOfStructures" {
DATATYPE H5T_COMPOUND {
H5T_ARRAY { [13] H5T_STRING {
STRSIZE 1;
STRPAD H5T_STR_SPACEPAD;
CSET H5T_CSET_ASCII;
CTYPE H5T_C_S1;
} } "chr_name";
H5T_STD_I8LE "a_name";
H5T_IEEE_F64LE "c_name";
H5T_IEEE_F32LE "b_name";
}
…..
October 15, 2008
HDF and HDF-EOS Workshop XII
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exp3-140217140448-phpapp01/85/What-will-be-new-in-HDF5-21-320.jpg)