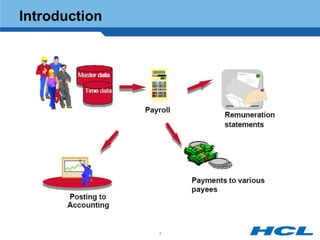
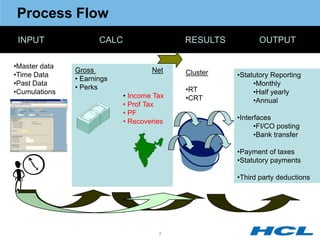
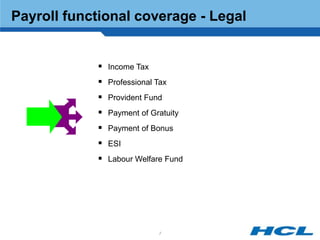
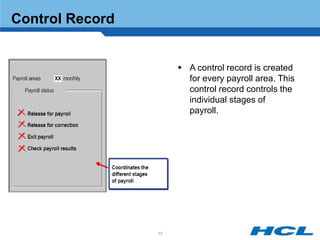
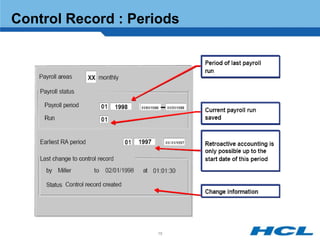
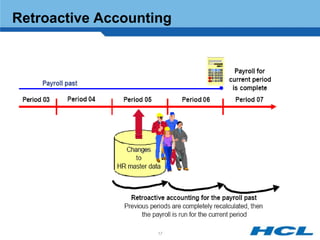
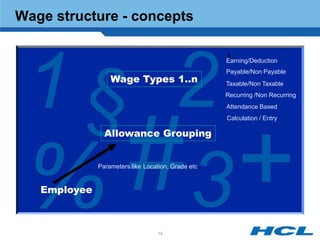
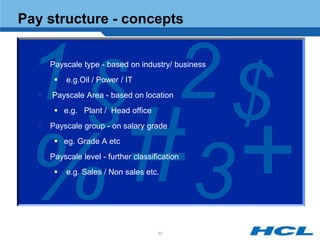
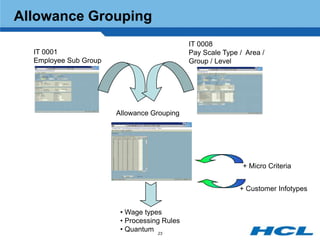
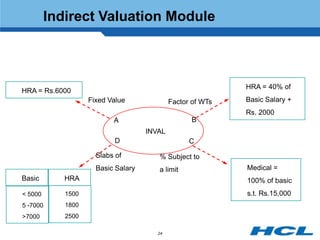
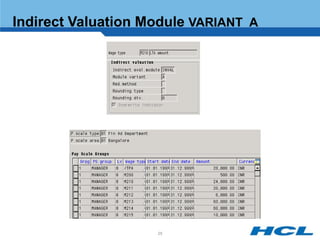
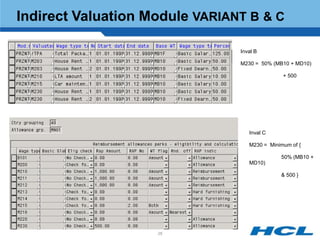
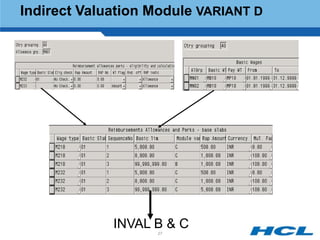
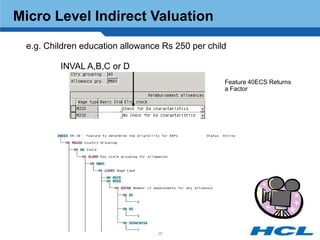
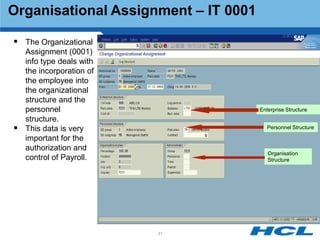
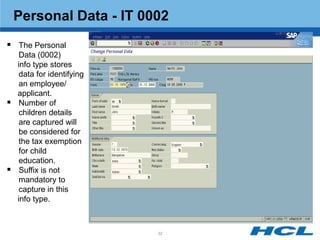
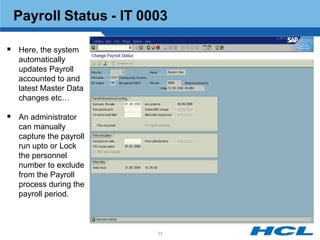
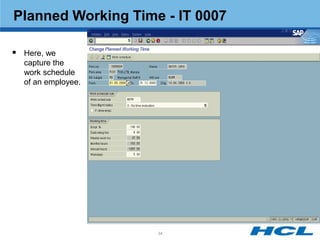
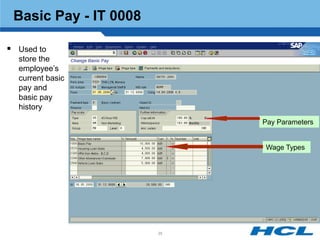
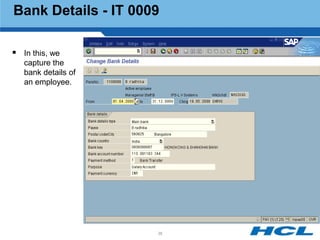
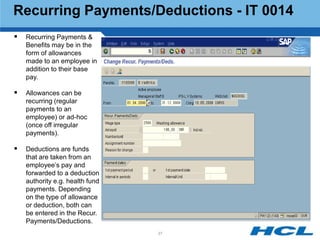
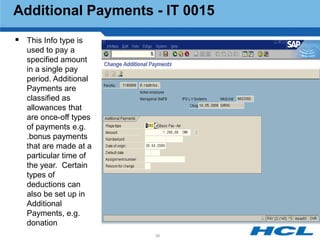
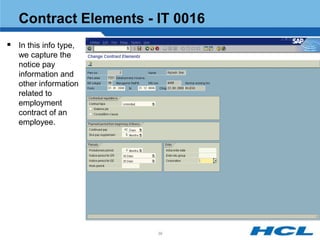
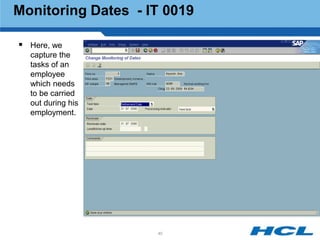
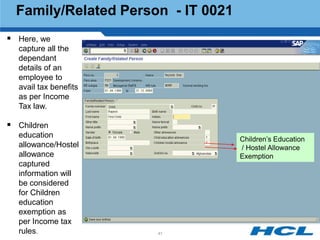
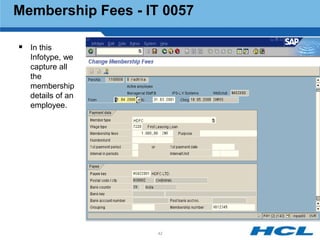
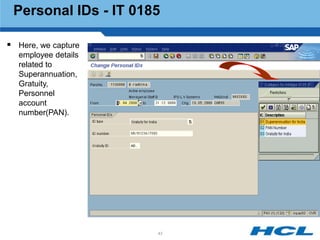
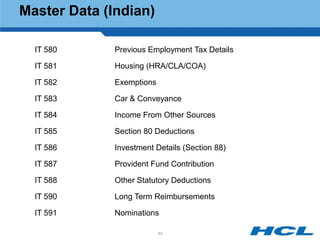
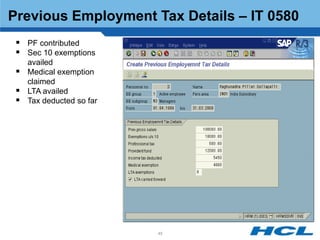
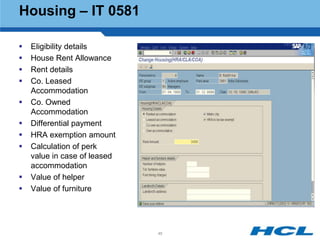
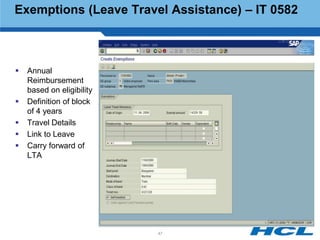
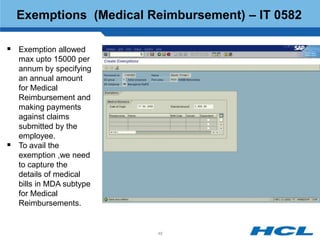
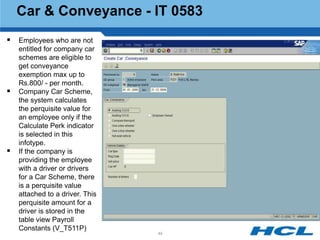
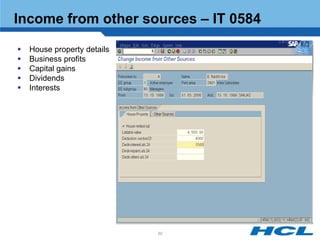
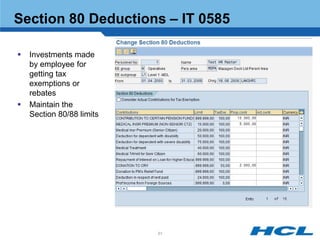
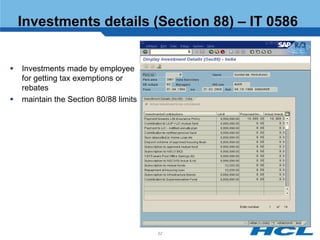
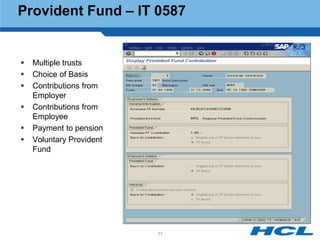
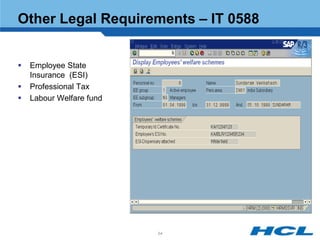
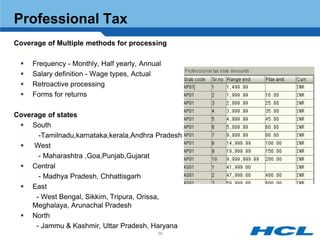
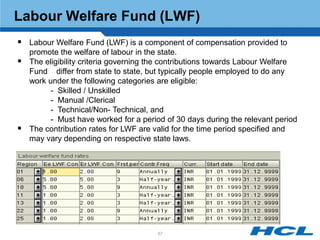
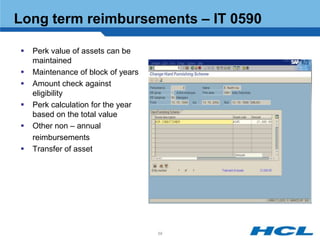
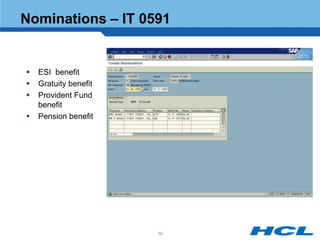
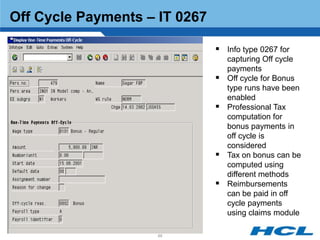
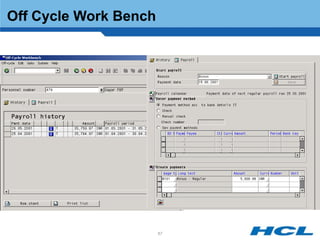
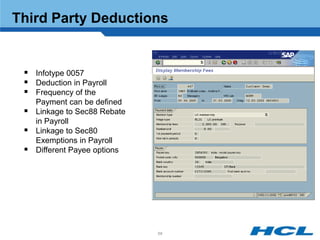
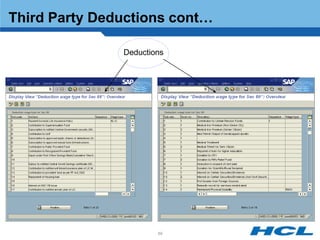
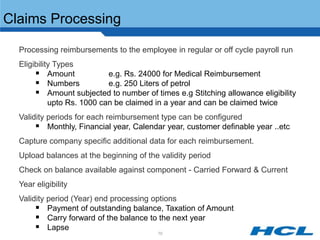
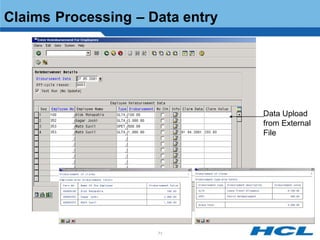
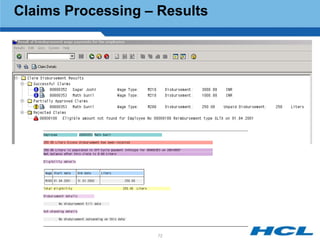
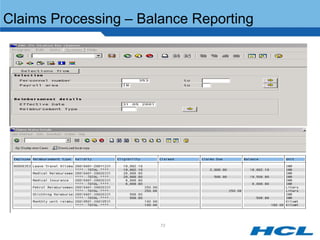
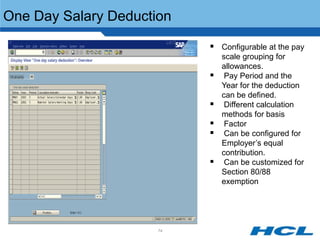
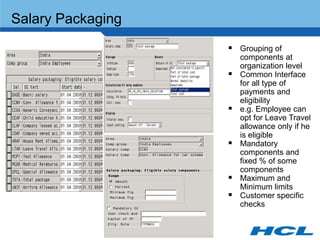
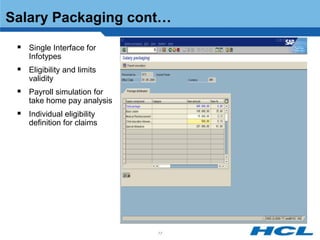
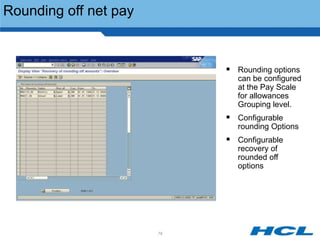
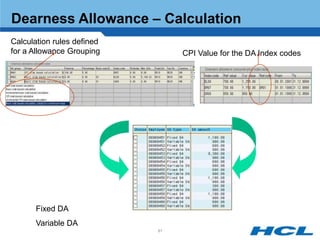
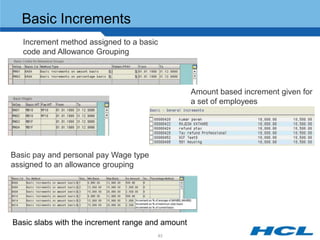
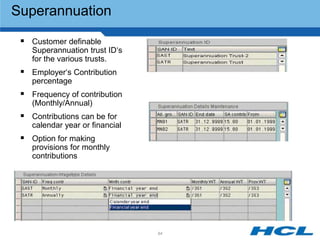
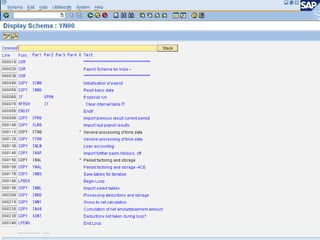
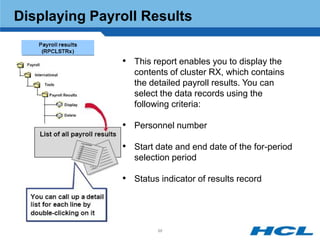
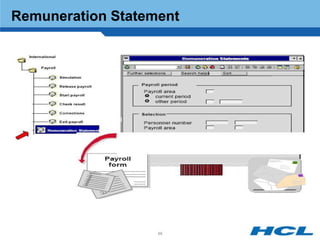
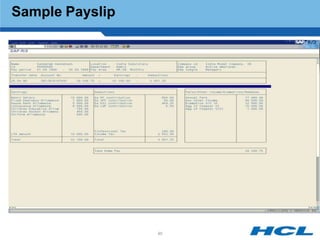
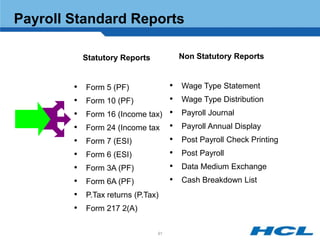
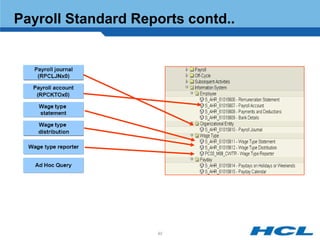
The document provides an overview of the key components and functionality of SAP's Indian Payroll module. It describes the objectives of the payroll component, introduces key terms and definitions, and outlines the statutory compliance features. The summary includes descriptions of the payroll structure, wage structure, infotypes, payroll processes, and coverage of components like taxes, allowances, and benefits.