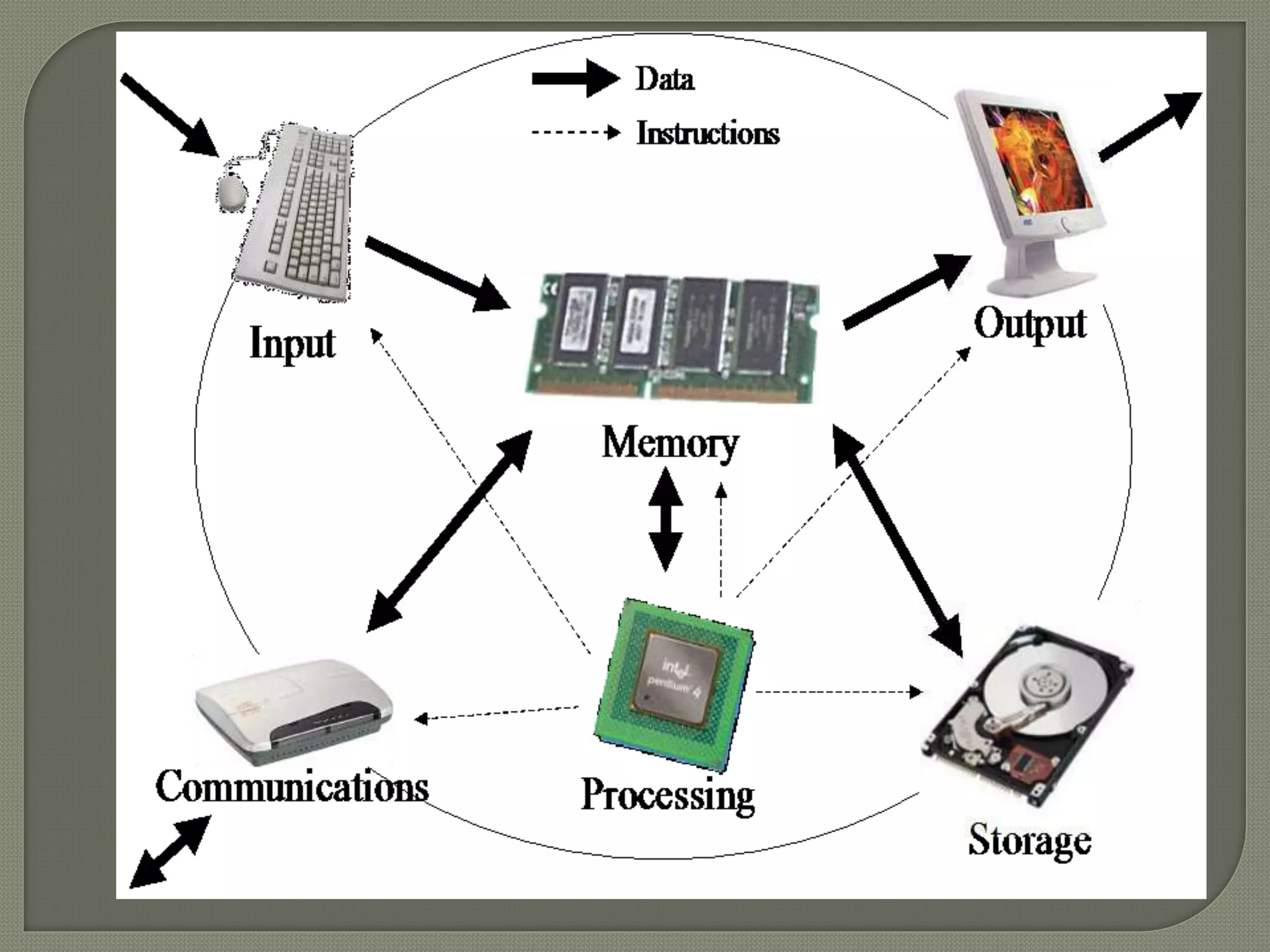
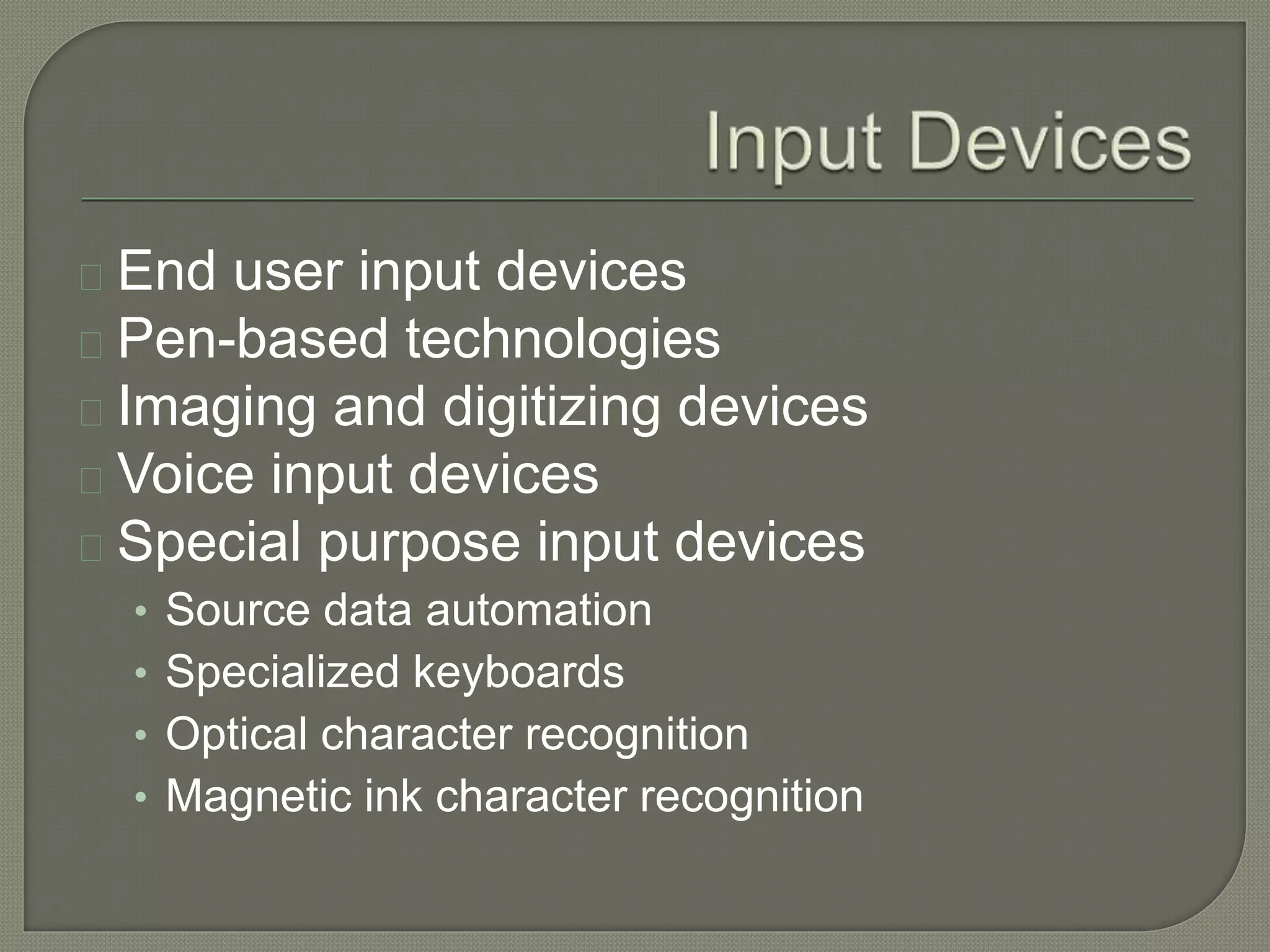
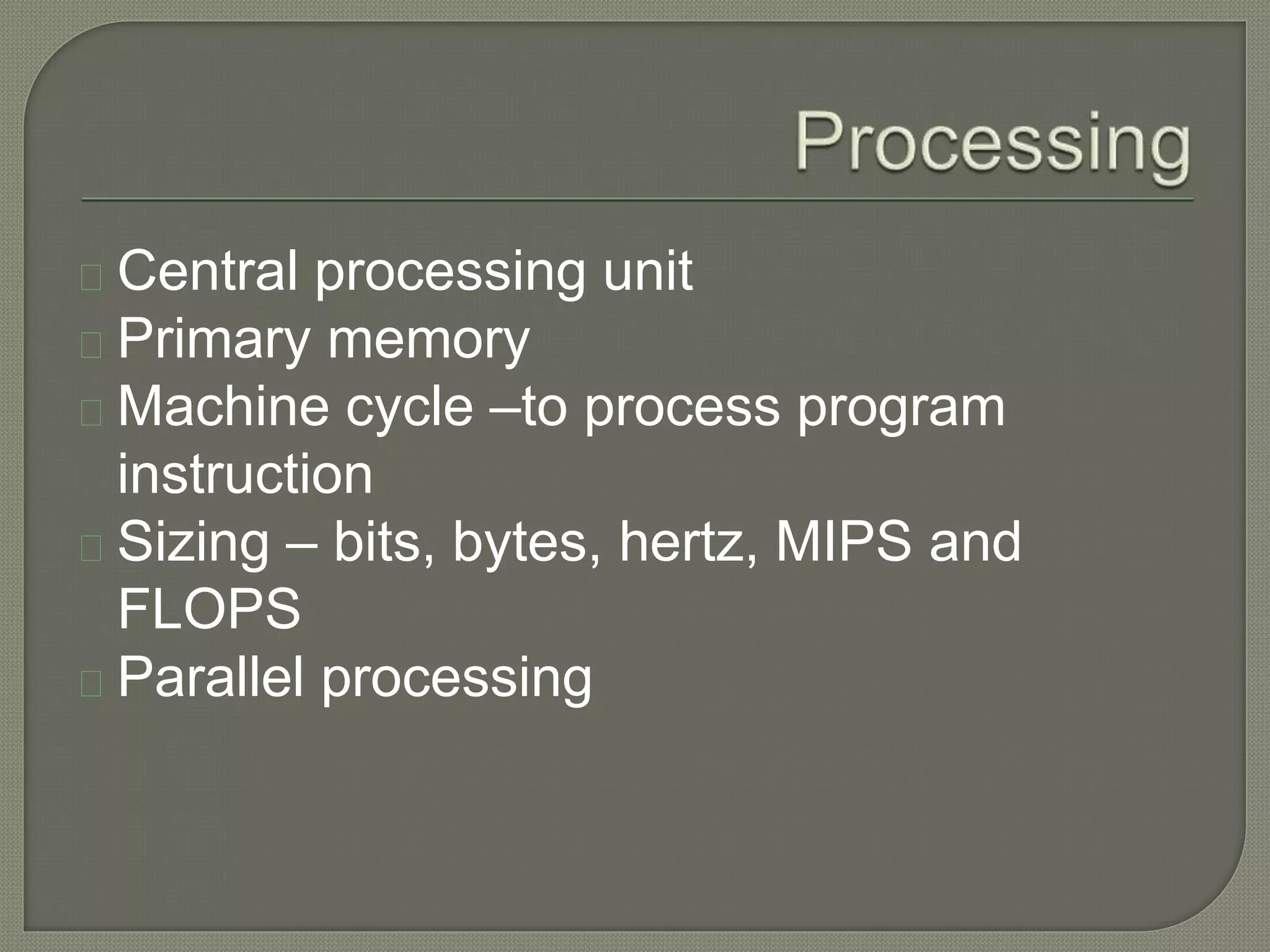
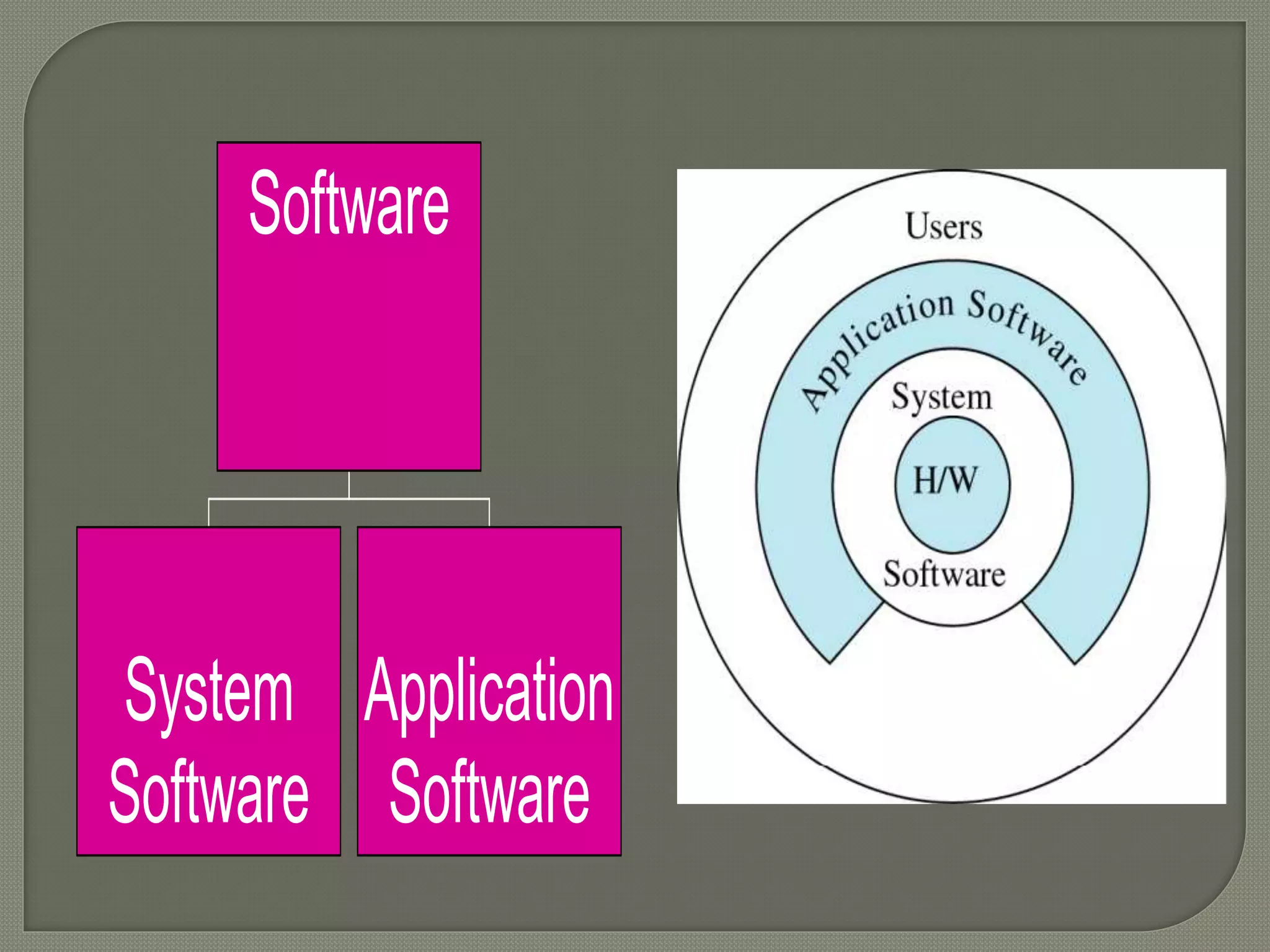
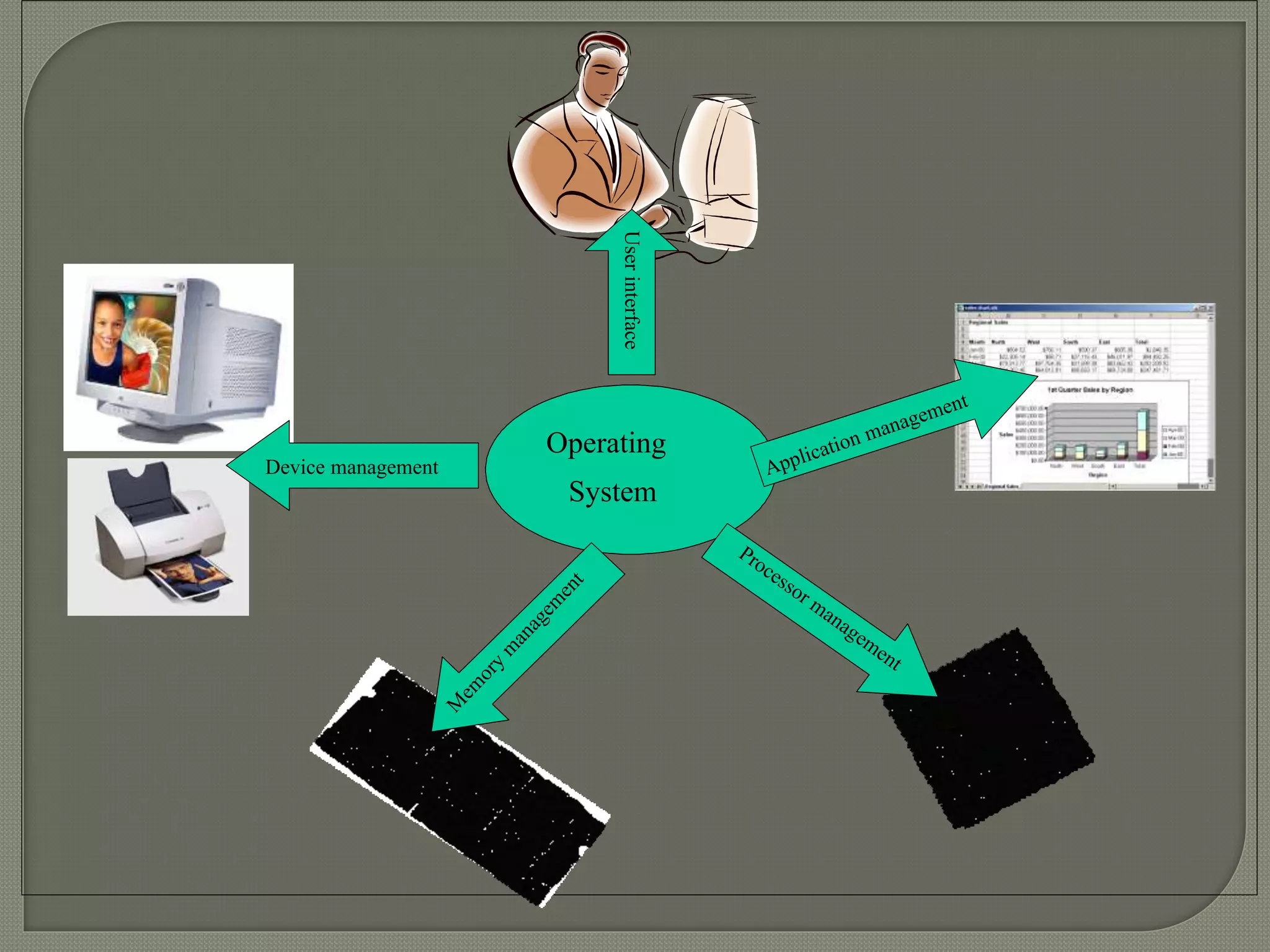
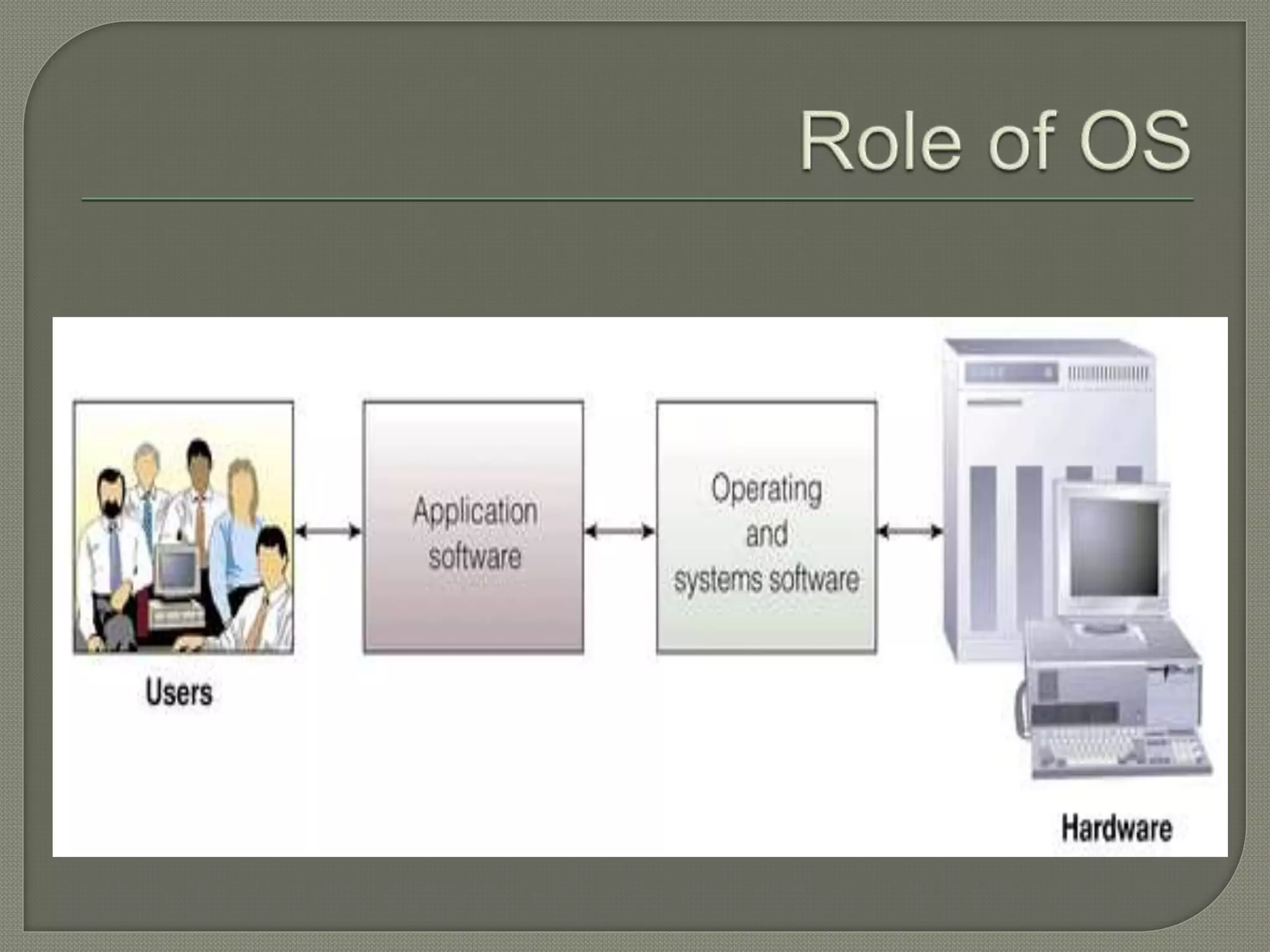
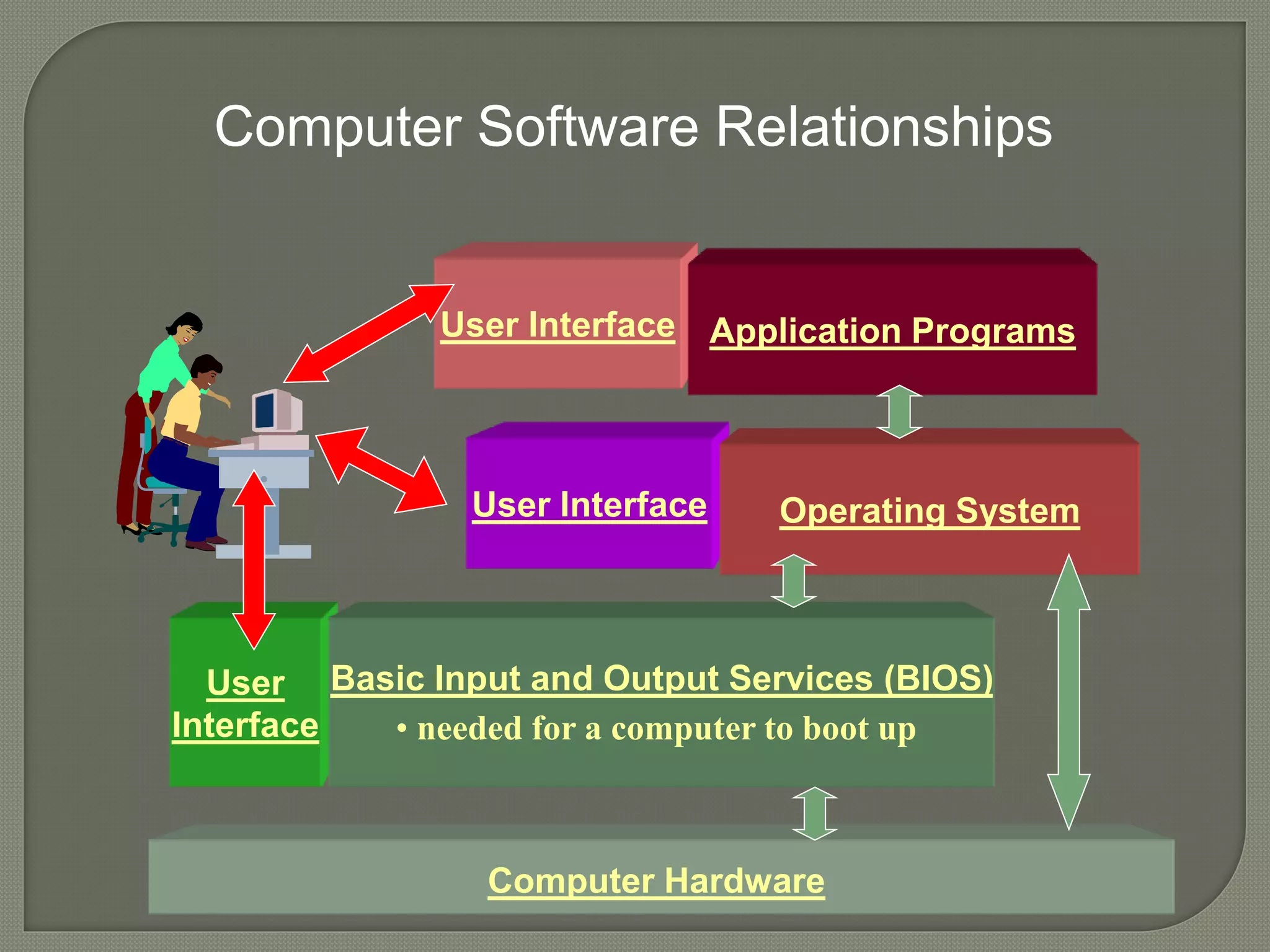
The document outlines the components of organizational computing, detailing hardware and software aspects, including types of computing such as large-system, standalone, and network computing. It covers various input and output devices, the functionality of the central processing unit, and the structure of application and system software, including operating systems and language translators. Additional focus is on the relationships between user interfaces and programs, as well as addressing software engineering and managerial issues in application development.