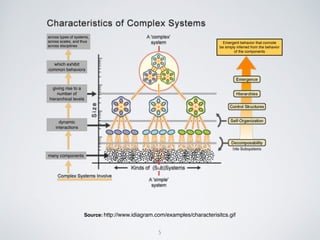
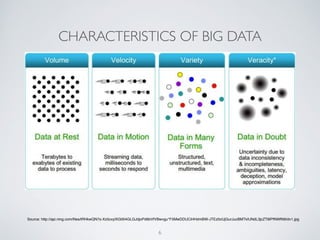
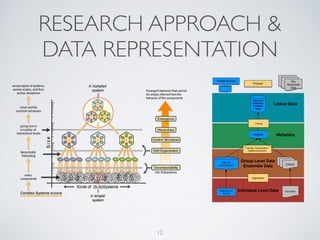
(1) The document discusses challenges of managing large and complex datasets for interdisciplinary research projects. It presents Hadoop and the Etosha data catalog as solutions.
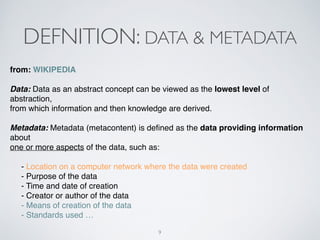
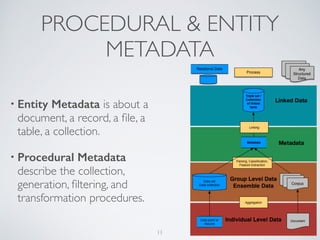
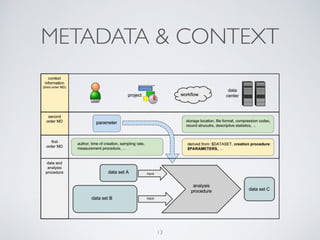
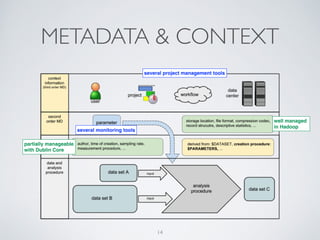
(2) Etosha aims to publish and link metadata about datasets to enable discovery and sharing across distributed research clusters. It focuses on descriptive, structural and administrative metadata rather than just technical metadata.
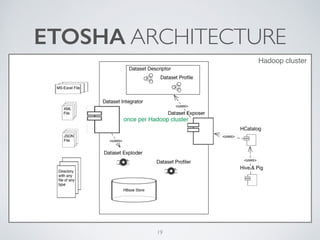
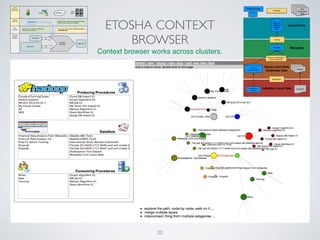
(3) Etosha's architecture includes a distributed metadata service and context browser that can query metadata from different Hadoop clusters to support federated querying and subquery delegation.