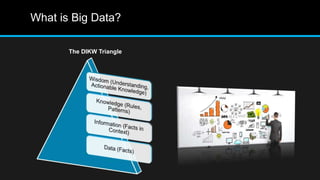
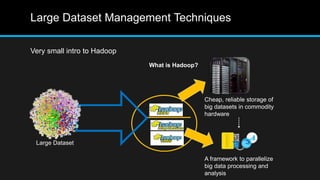
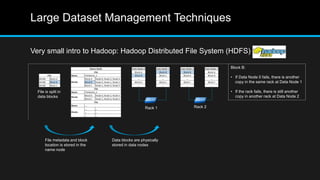
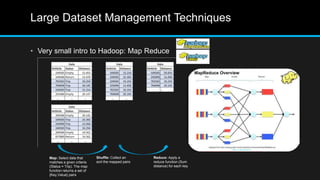
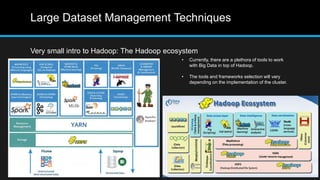
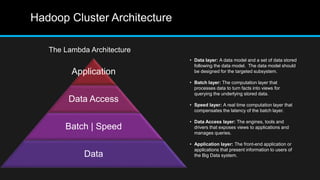
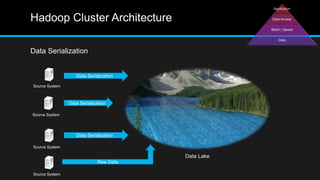
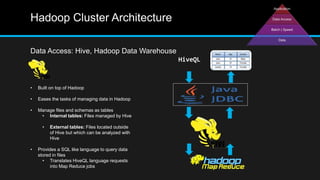
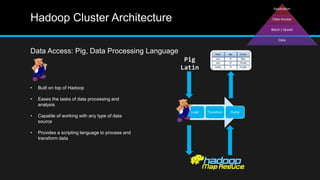
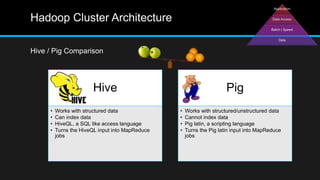
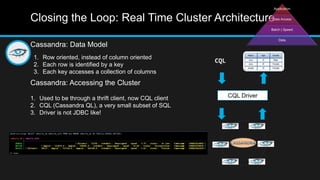
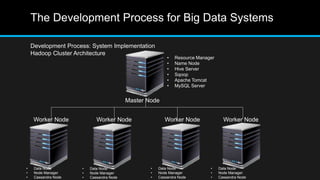
The document discusses the applications of big data, particularly in public traffic systems, and outlines key concepts such as large dataset management techniques and Hadoop architecture. It describes the various components of a Hadoop cluster, including batch and speed layers, and highlights the importance of real-time processing in big data environments. Additionally, it introduces tools like Hive and Pig for data analysis and management within the Hadoop ecosystem.