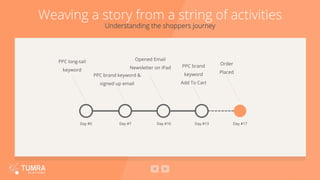
This document provides a summary of using Apache Spark for continuous analytics and optimization. It discusses using Spark for collecting data from various sources, processing the data using Spark's capabilities for streaming, machine learning and SQL queries, and reporting insights. An example use case is presented for social media analysis using Spark Streaming to process a real-time data stream from Kafka and analyze the data using both the Spark SQL and core Spark APIs in Scala.