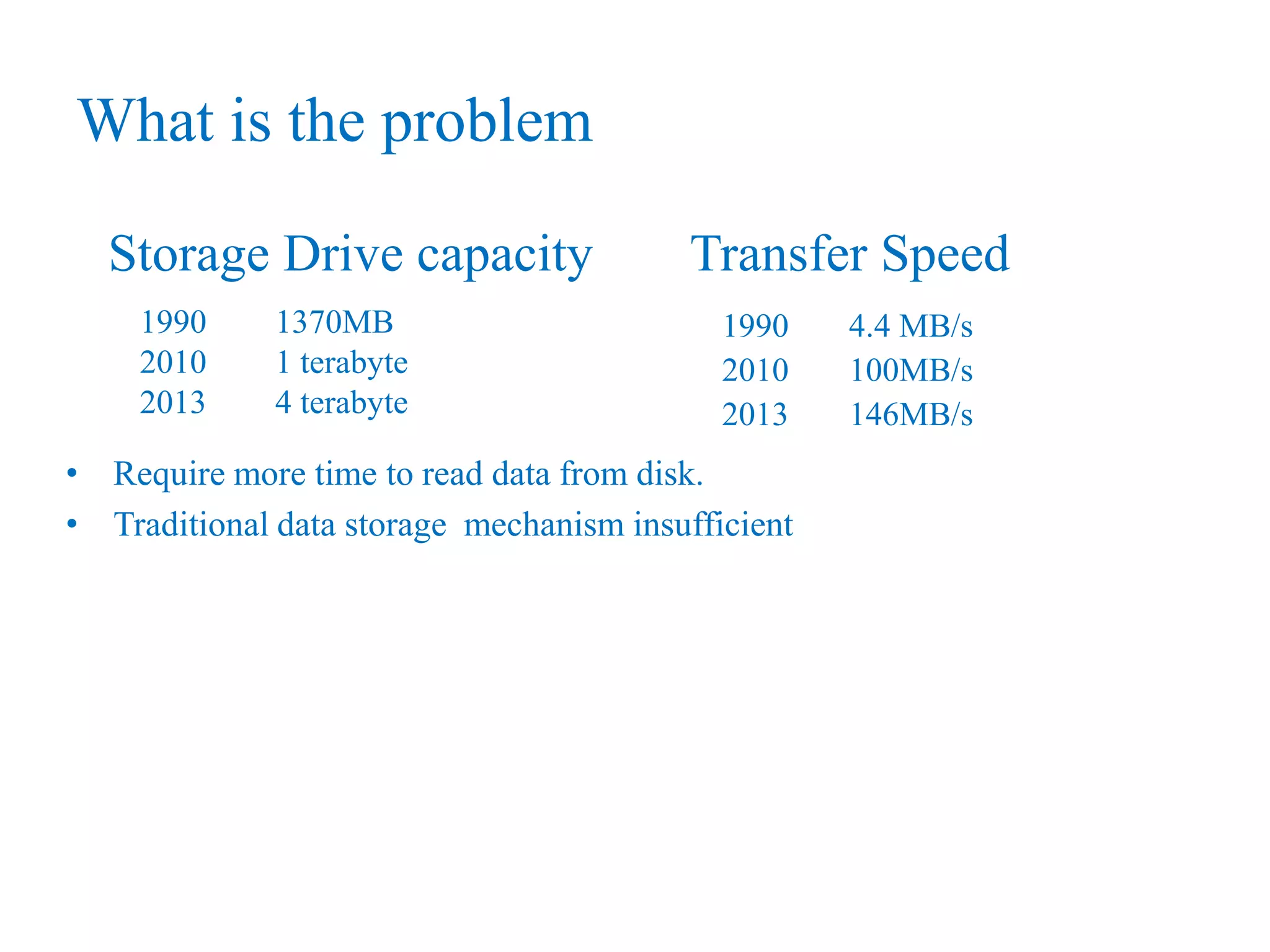
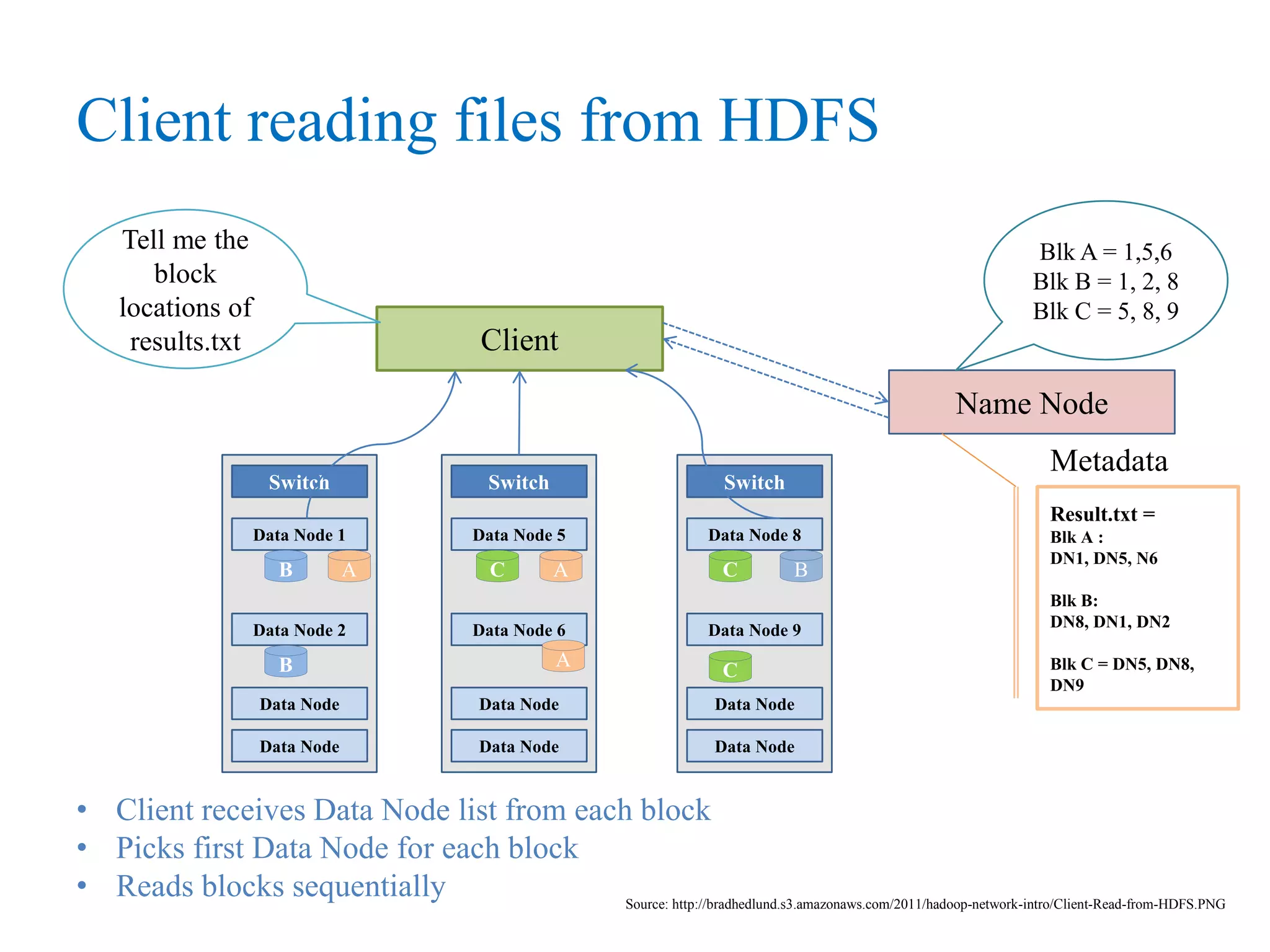
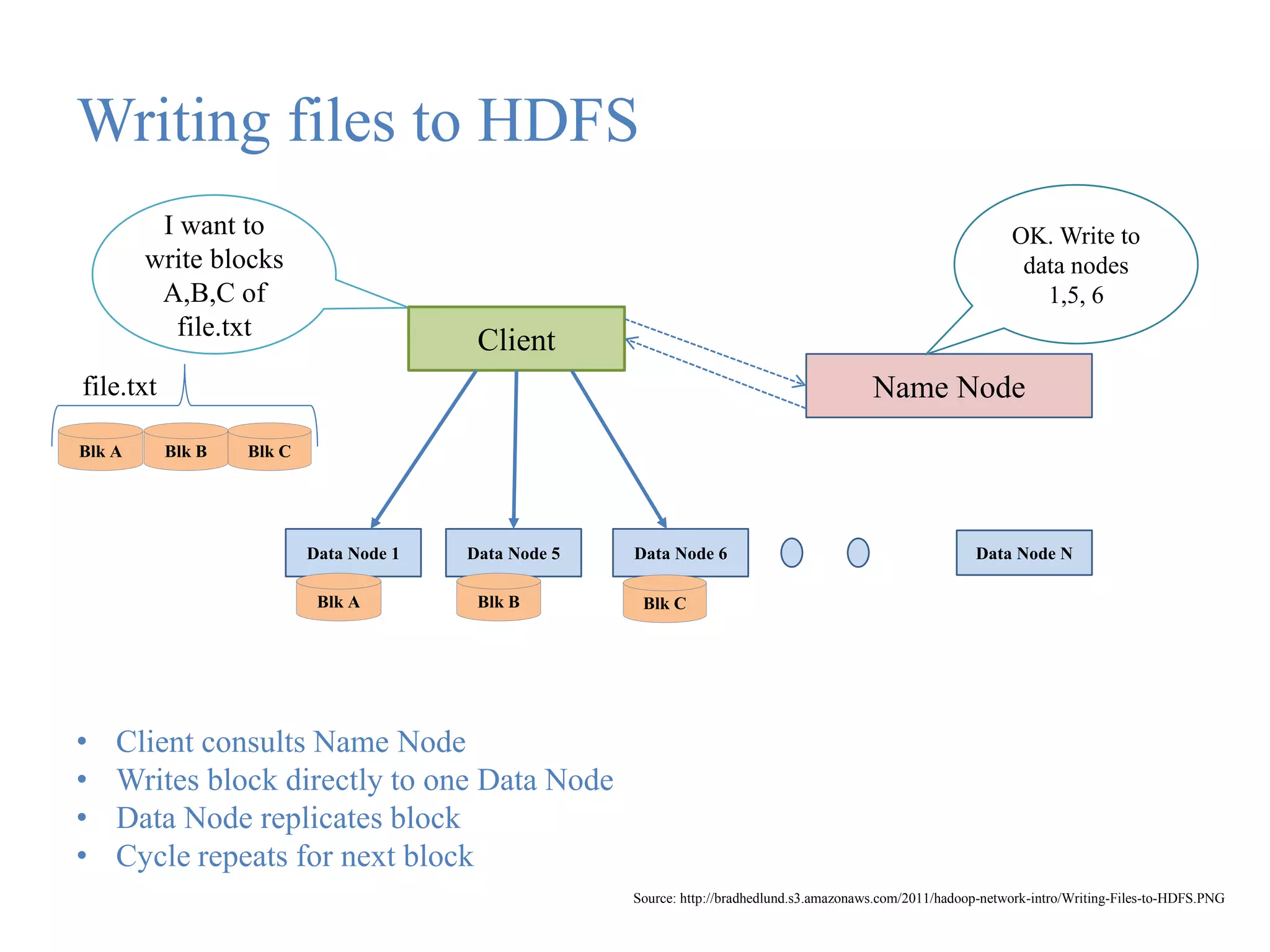
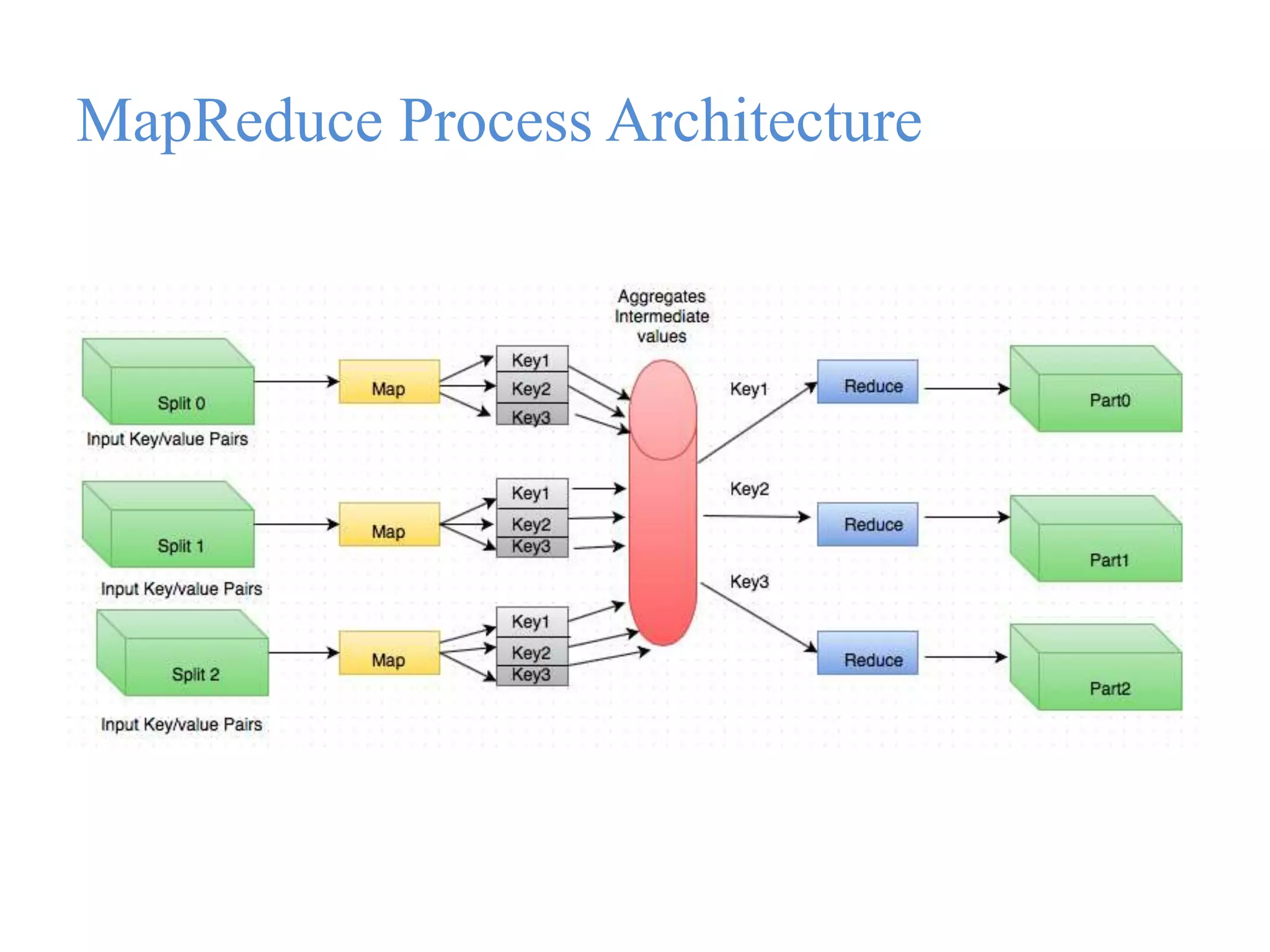
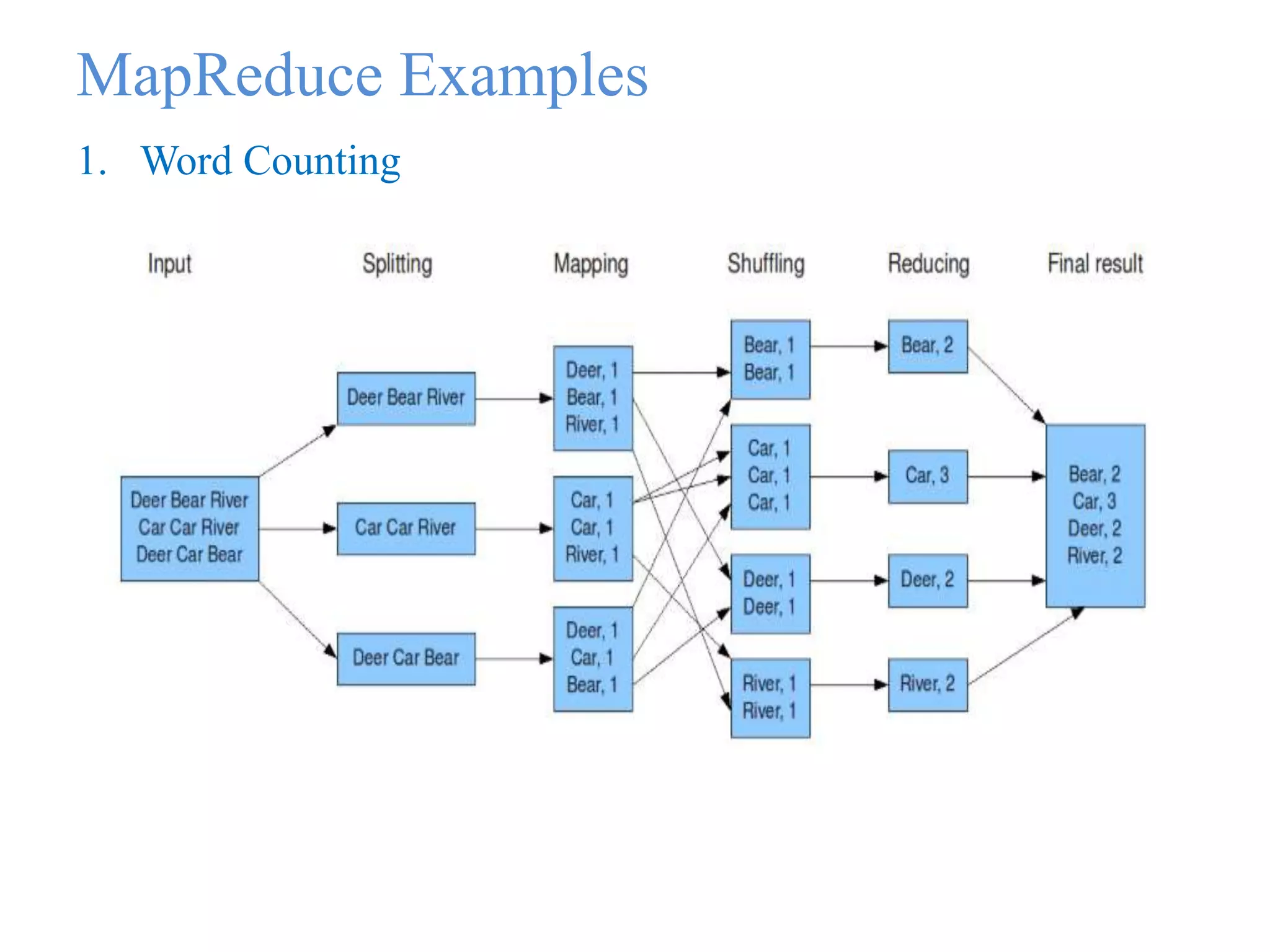
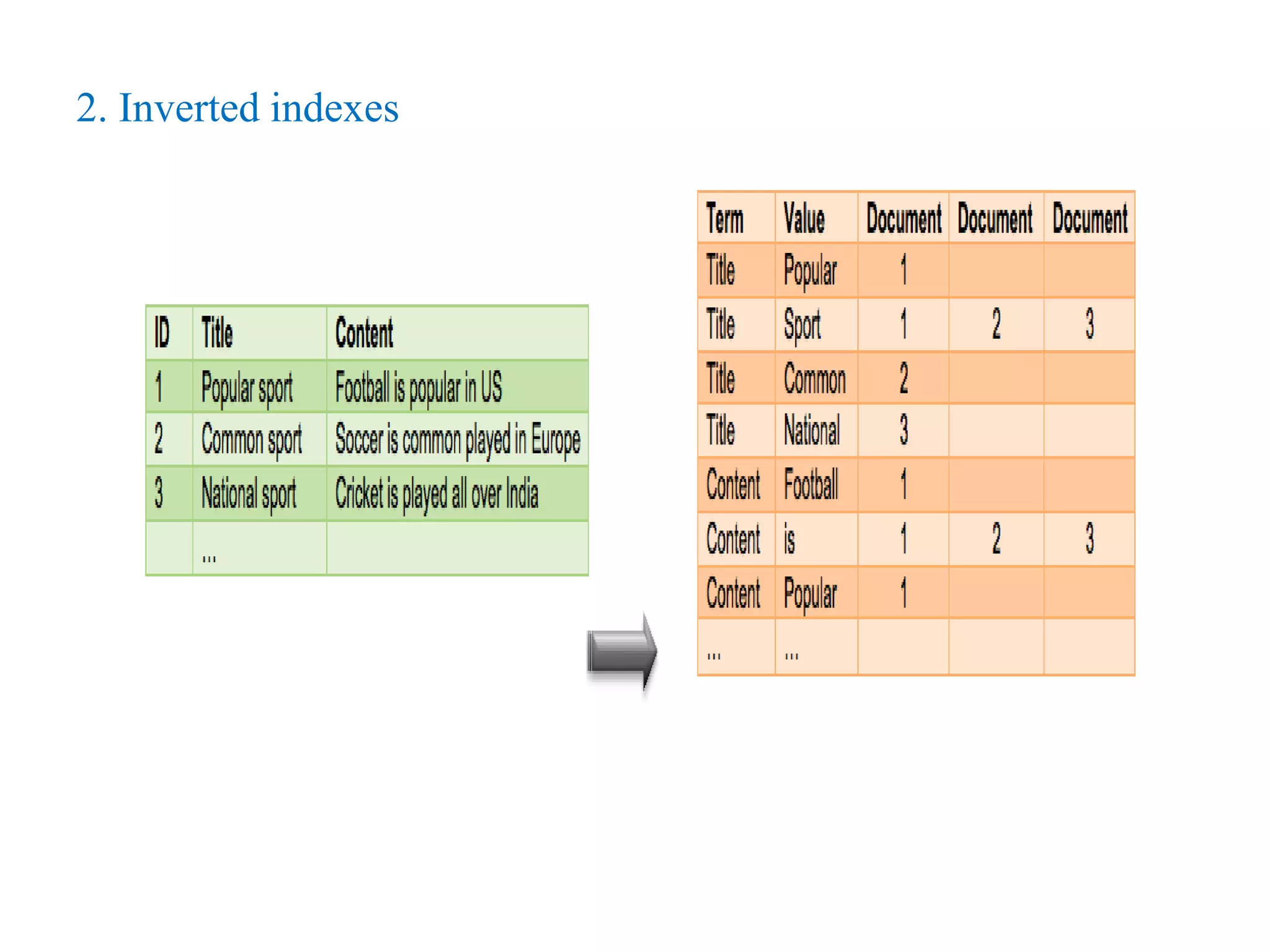
This document provides an overview of Hadoop, MapReduce, and HDFS. It discusses how Hadoop uses a cluster of commodity hardware and HDFS to reliably store and process large amounts of data in a distributed manner. MapReduce is the programming model used by Hadoop to process data in parallel across nodes. The document describes the core Hadoop modules and architecture, how HDFS stores and retrieves data blocks, and how MapReduce distributes work and aggregates results. Examples of using MapReduce for word counting and inverted indexes are also presented.