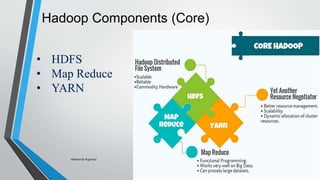
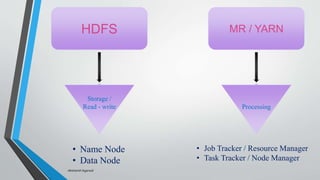
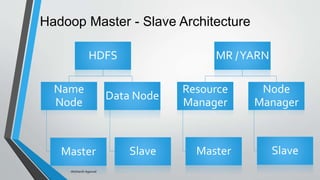
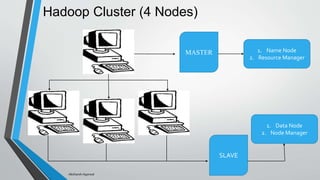
Big data refers to vast amounts of data generated from various sources, including digital activity and connected devices, and characterized by its volume, variety, and velocity. Hadoop is an open-source platform designed for storing and processing big data, known for its components such as HDFS and MapReduce, and it enables effective data management. The document emphasizes the importance of data collection, processing, and management for business growth and quality of life.