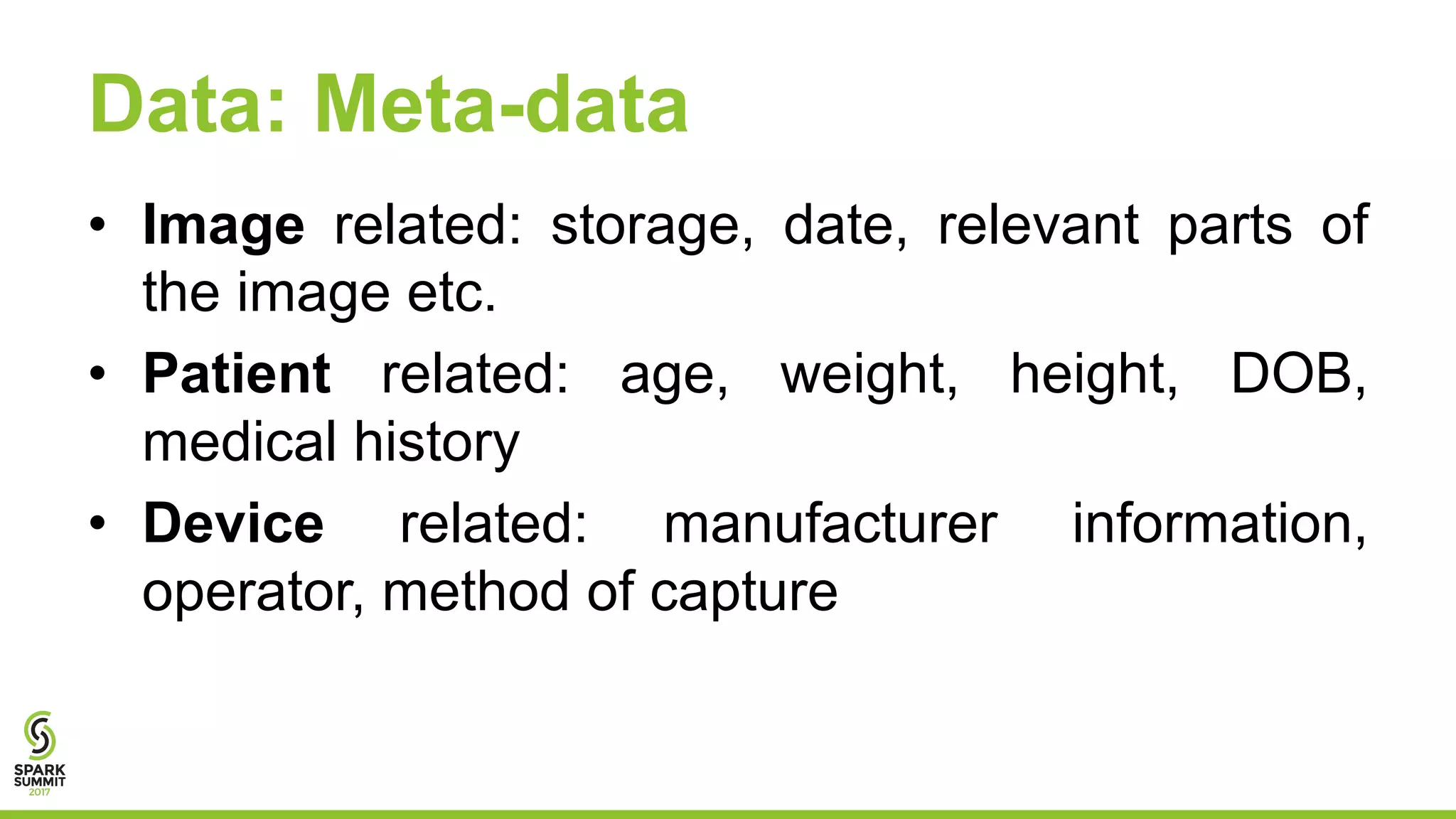
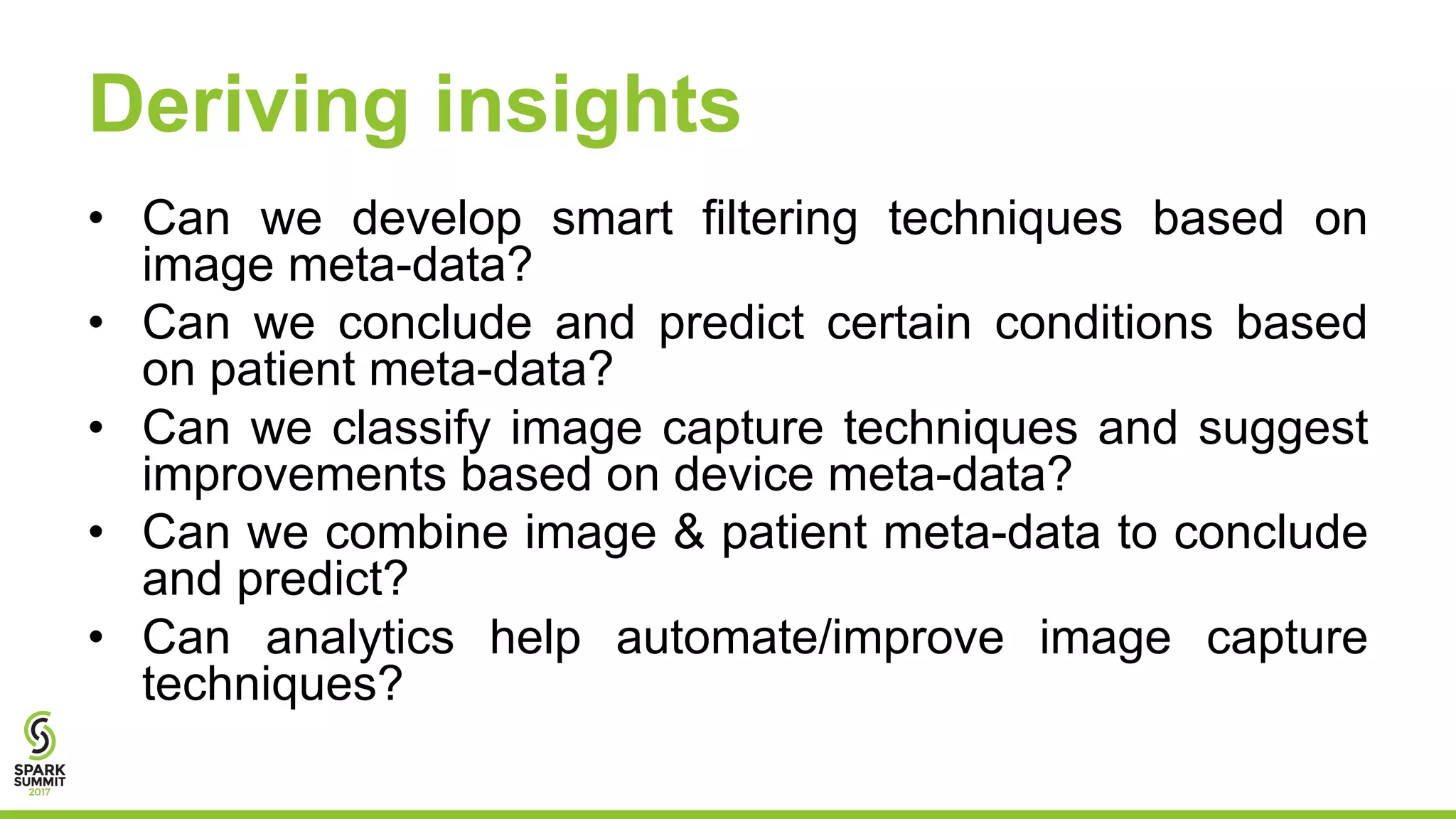
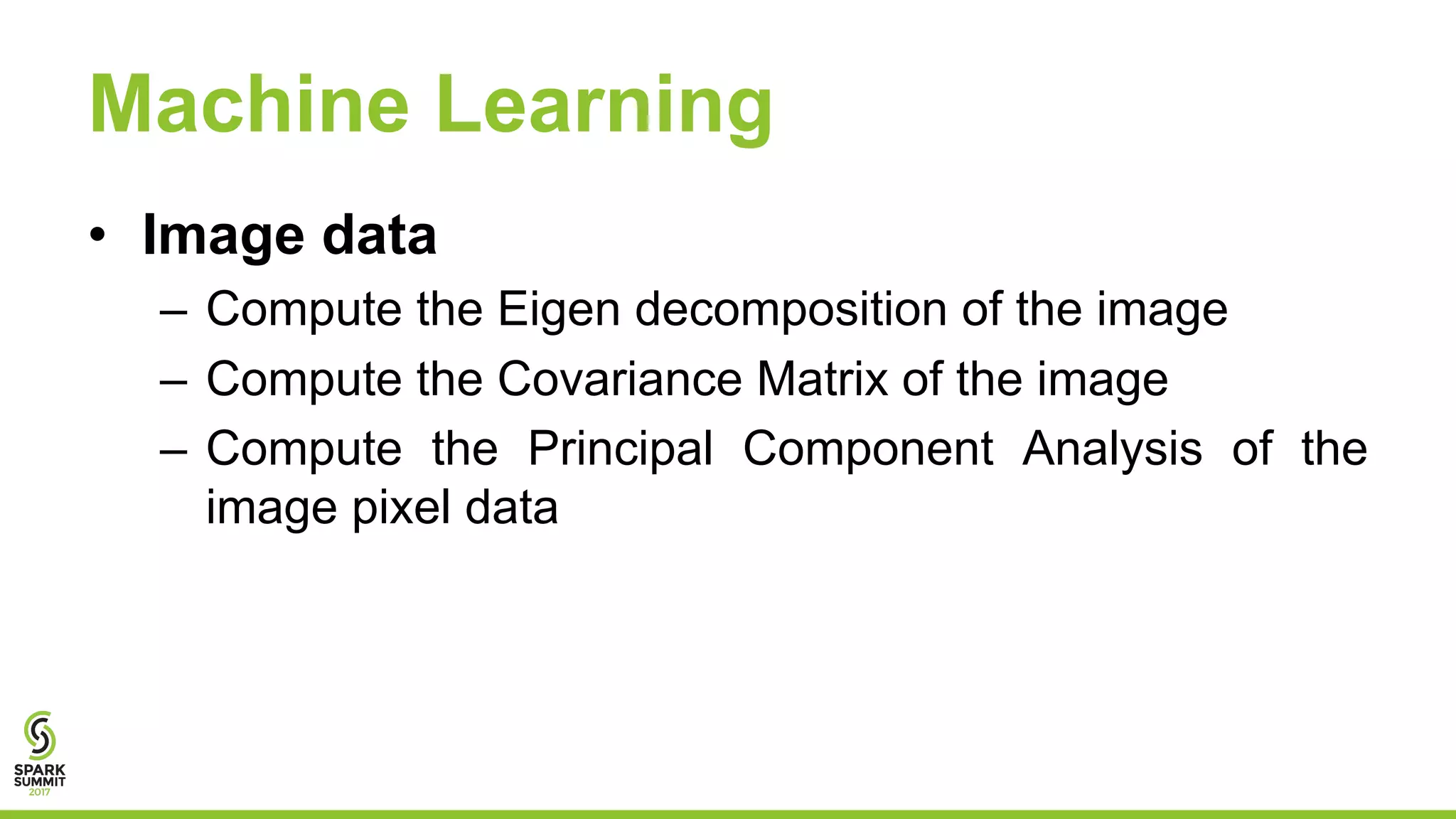
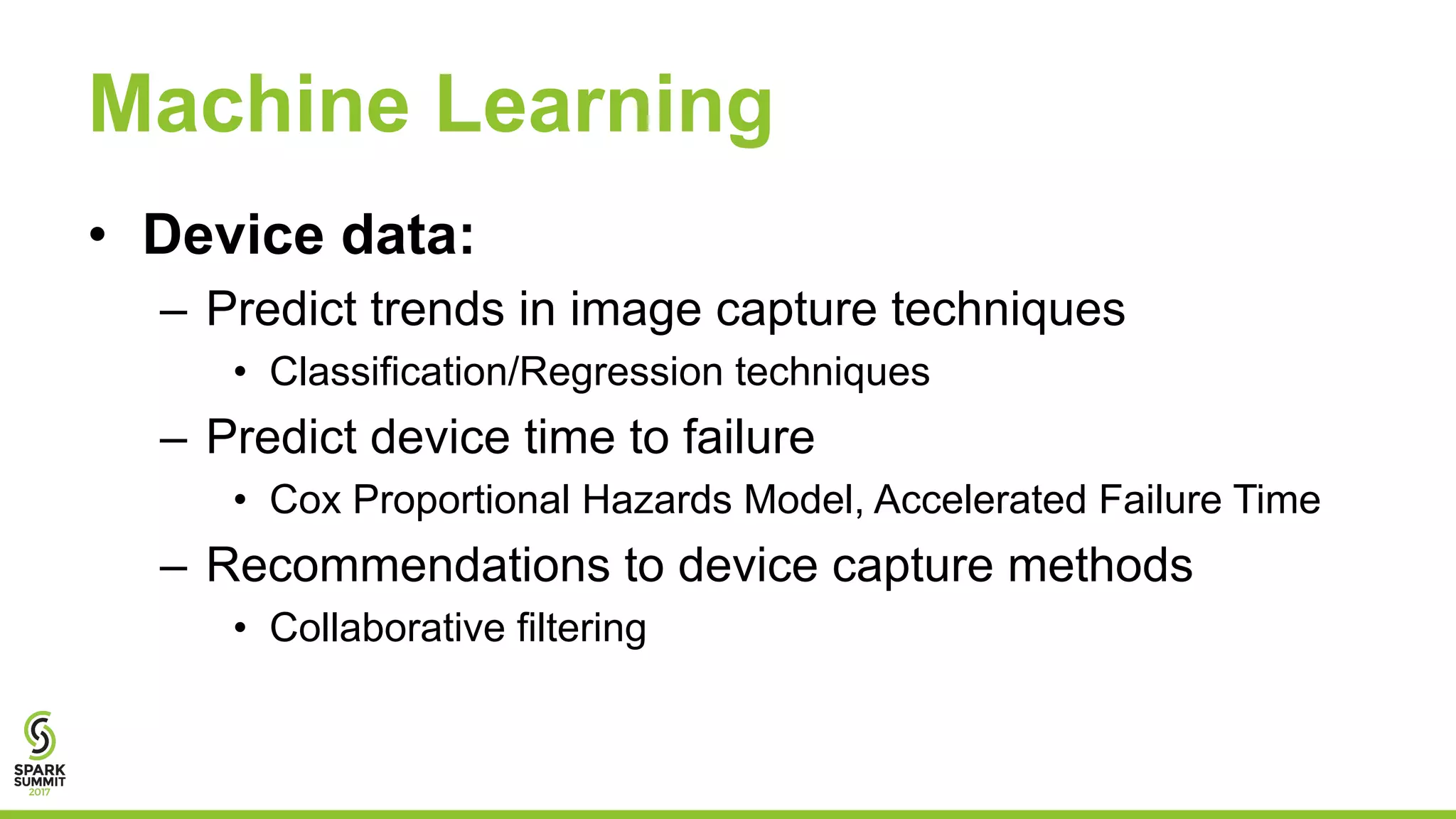
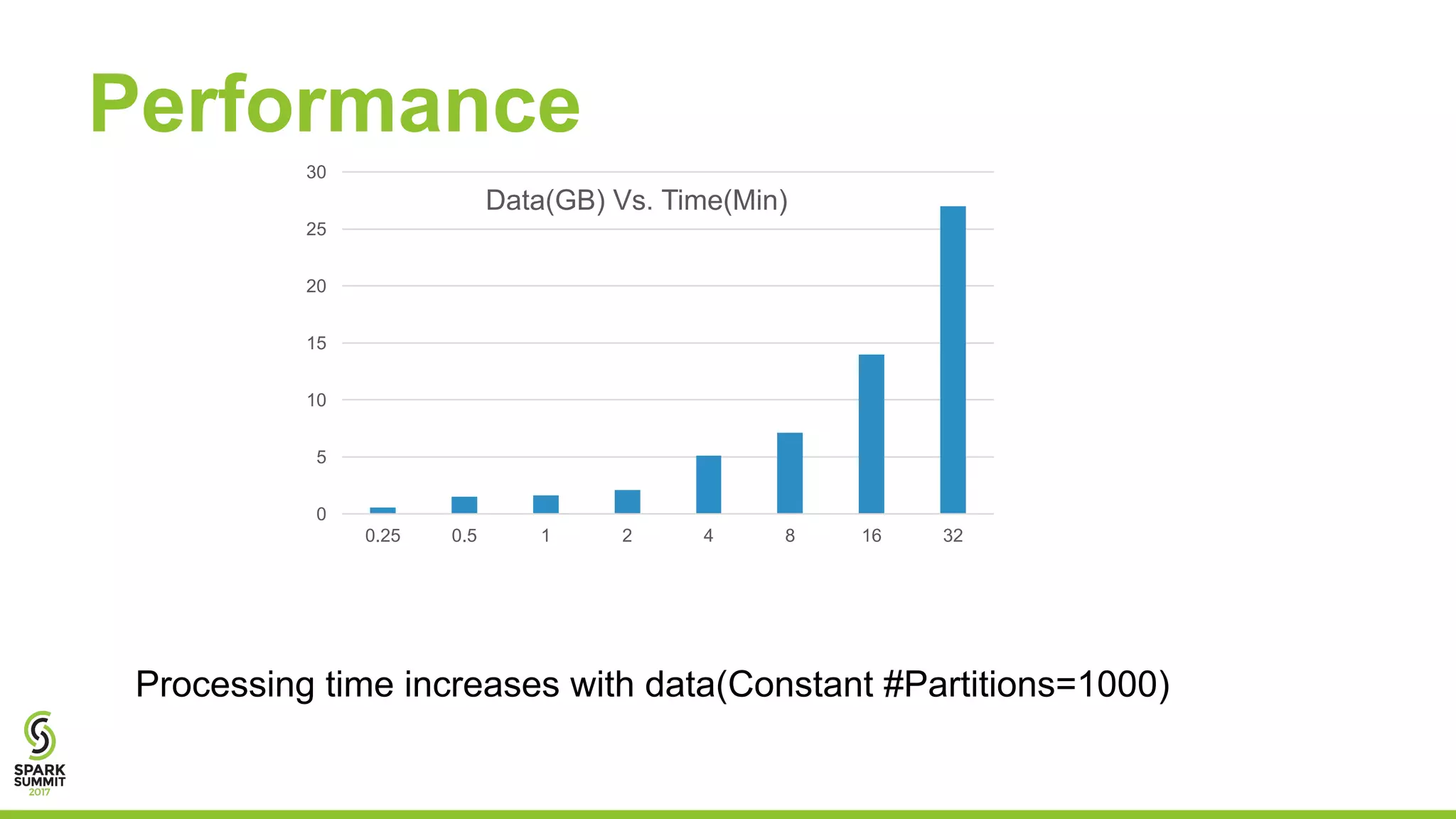
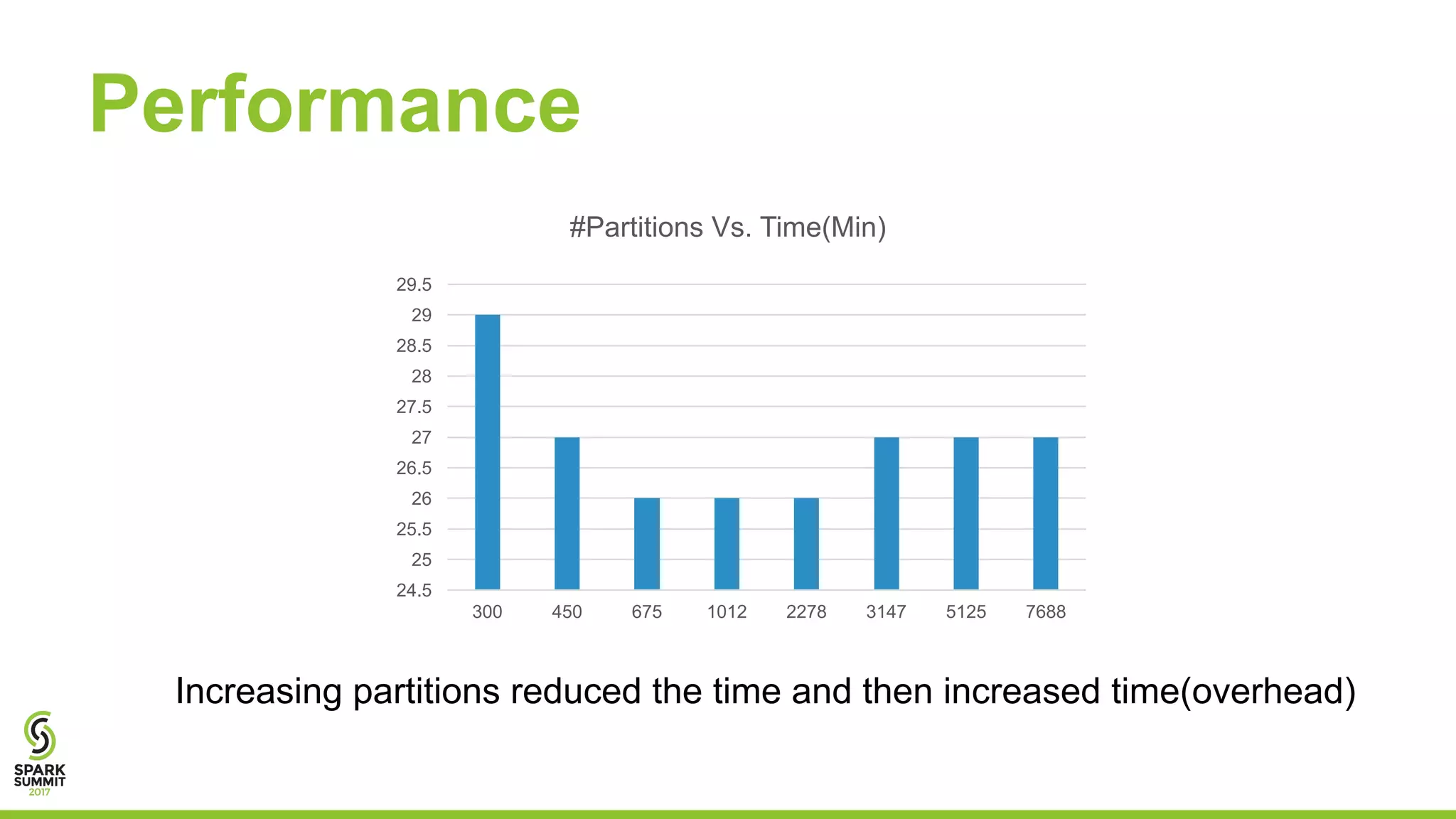
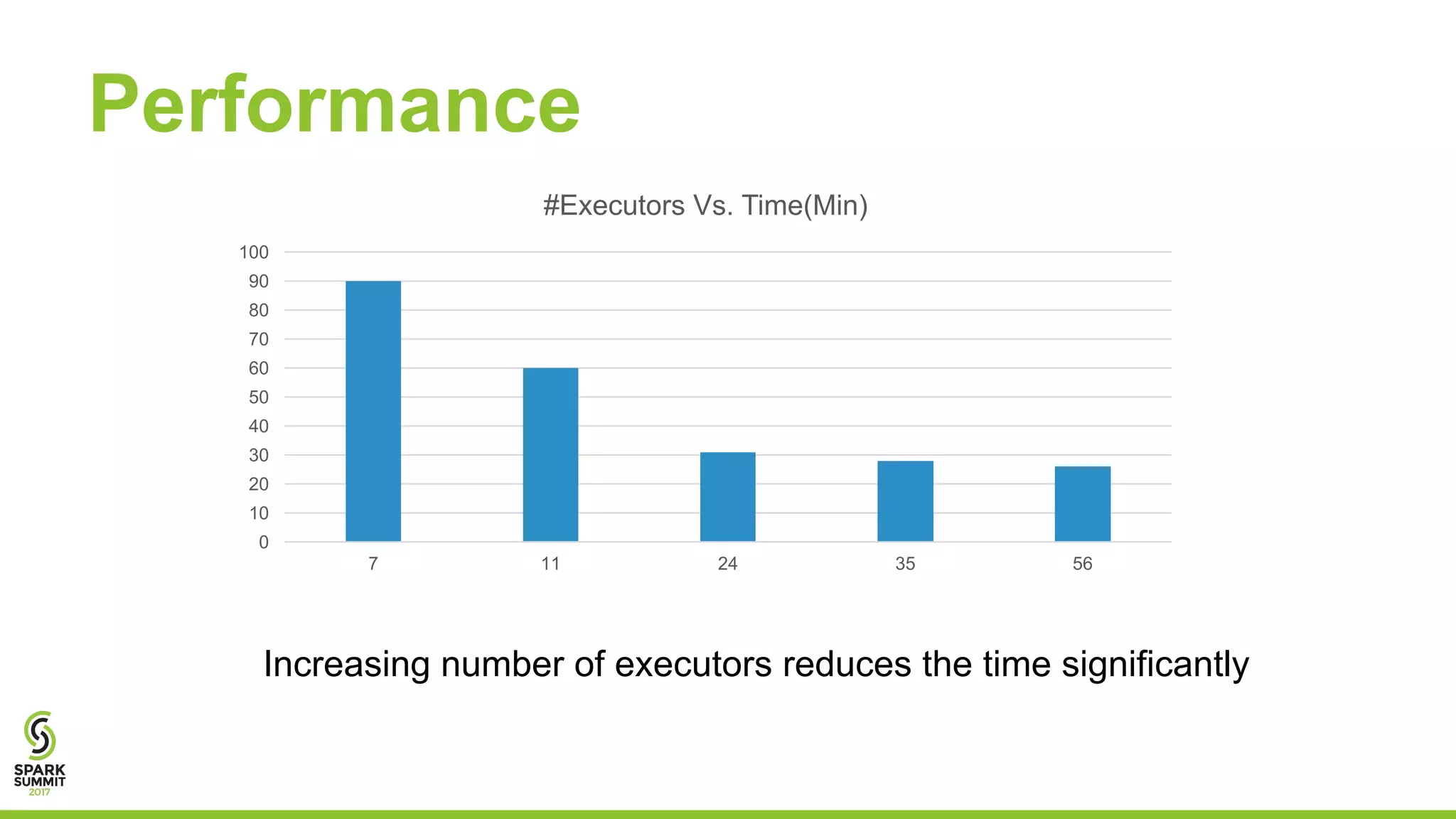
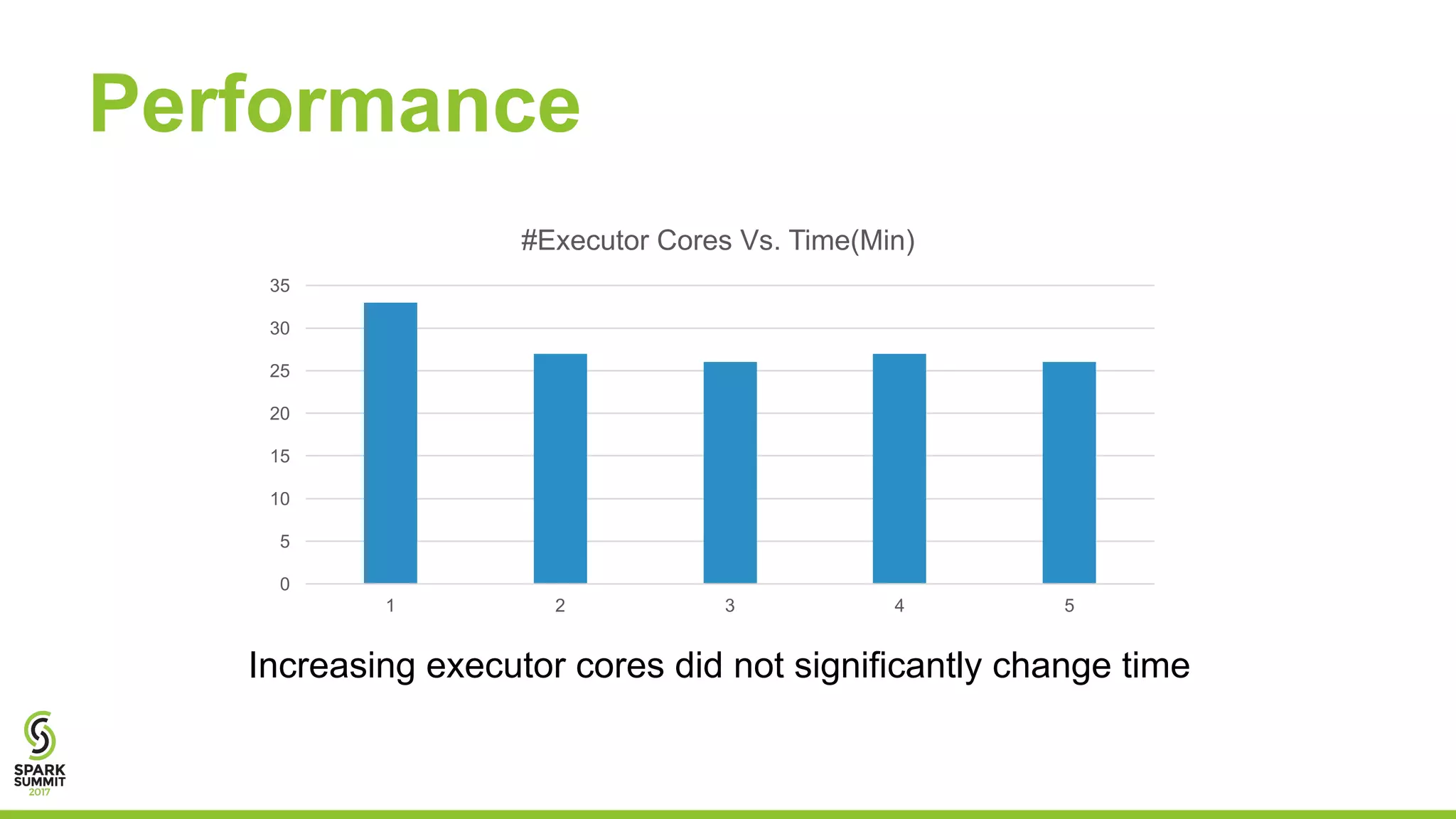
This document discusses using Apache Spark for predictive analytics on DICOM medical images. It describes challenges in working with medical image and metadata, and how tools like Spark, Spark-TK, and TensorFlow can help analyze this data at scale. A live demo then shows building machine learning models on DICOM data to derive insights and predict patient outcomes or device performance. Performance tests analyze the impact of data size, partitions, executors, and cores on processing time.