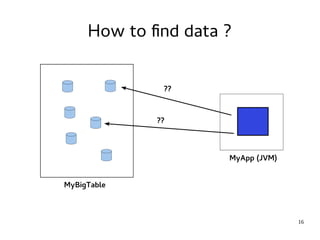
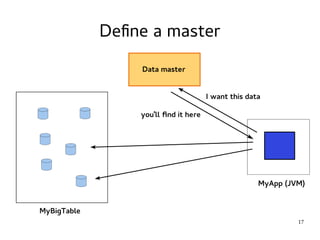
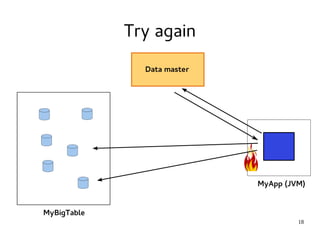
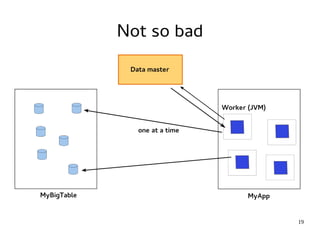
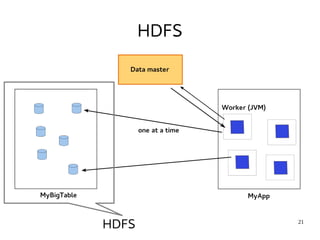
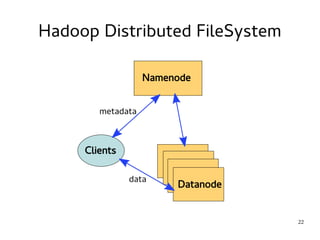
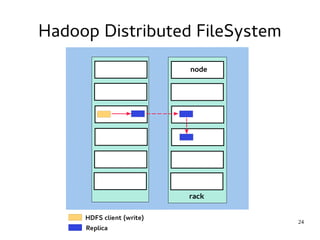
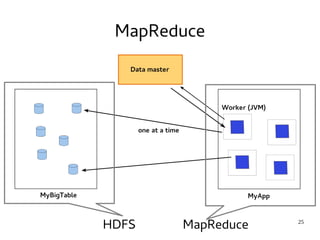
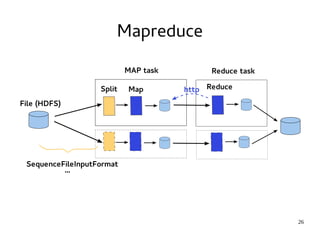
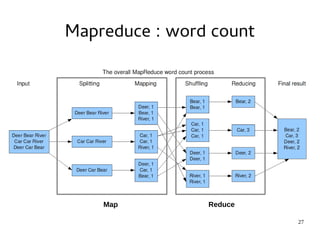
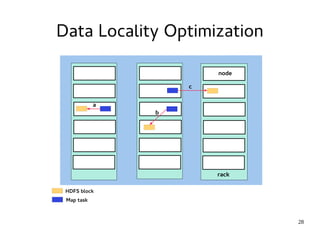
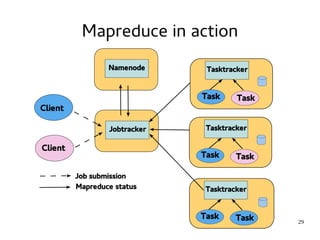
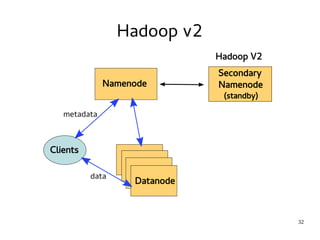
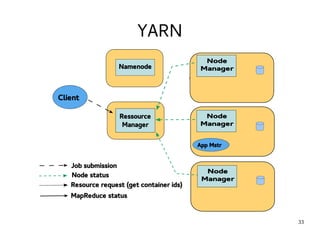
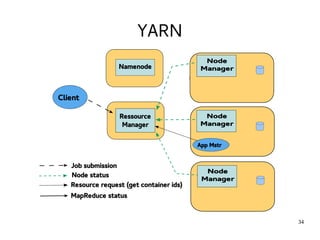
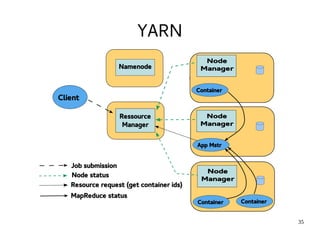
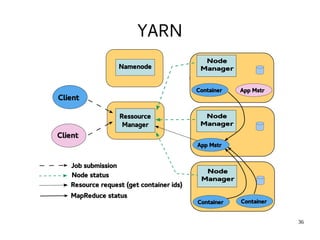
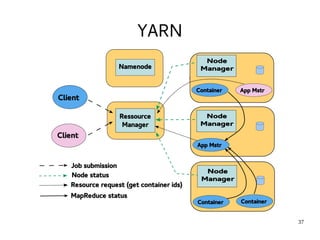
This document provides an introduction to Hadoop. It discusses how Hadoop was created to deal with high volumes of data by splitting data across commodity servers. It describes the key Hadoop components like HDFS for distributed storage and MapReduce for distributed processing. The document also outlines newer Hadoop technologies like YARN and how they improve upon earlier versions of Hadoop. Finally it provides two examples of projects using Hadoop at Credit Mutuel Arkea for anti-money laundering and operational reporting.