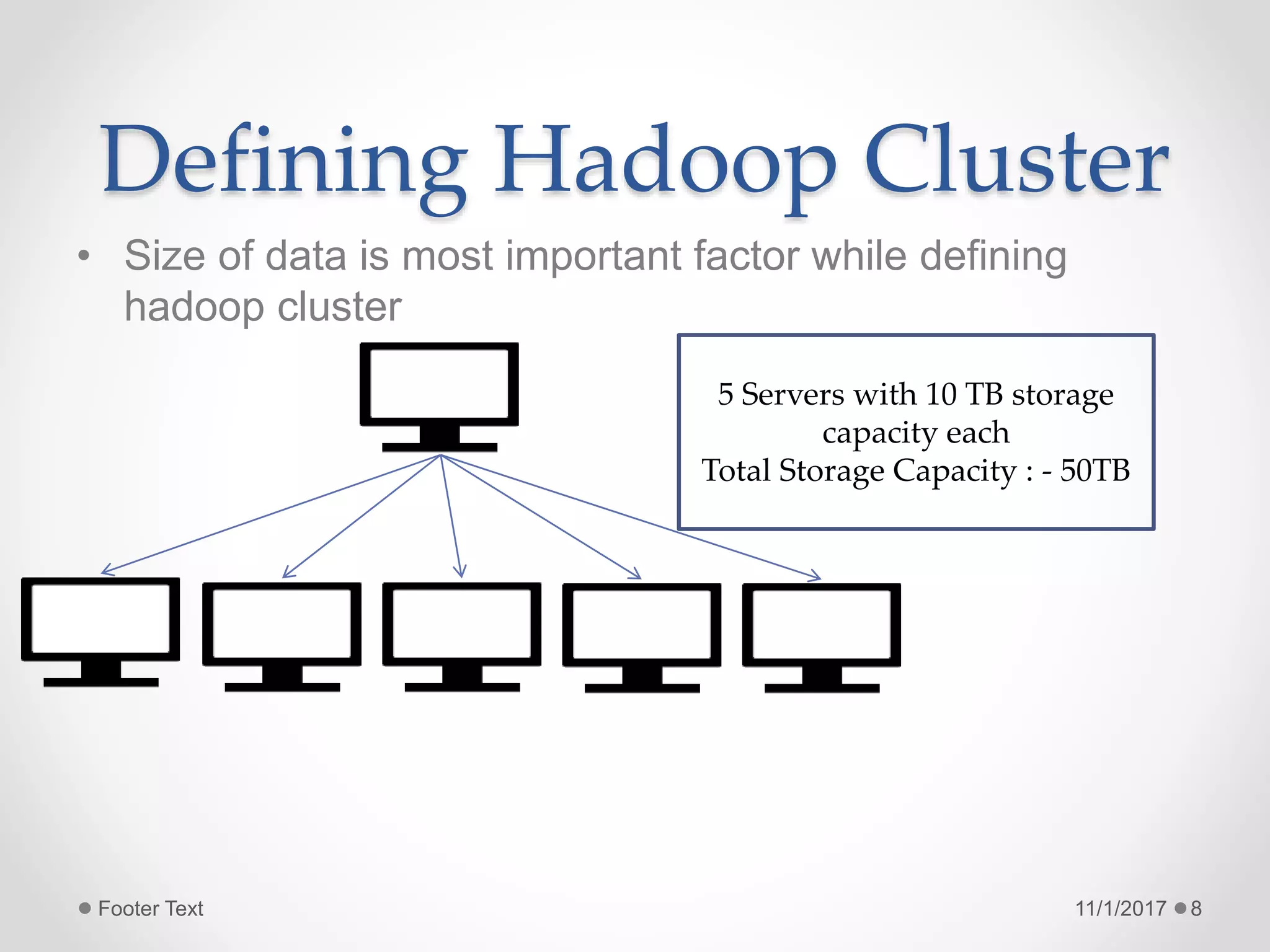
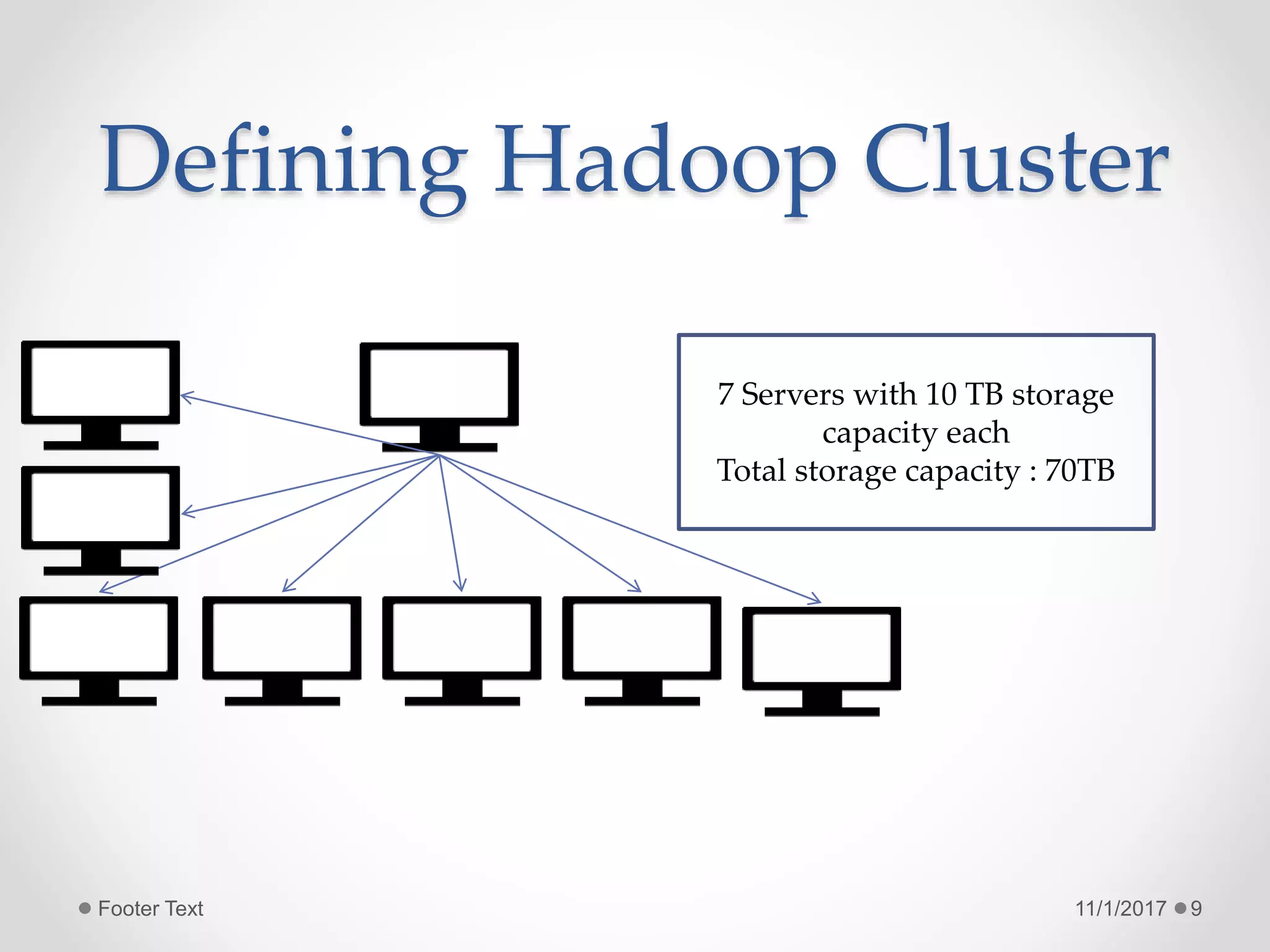
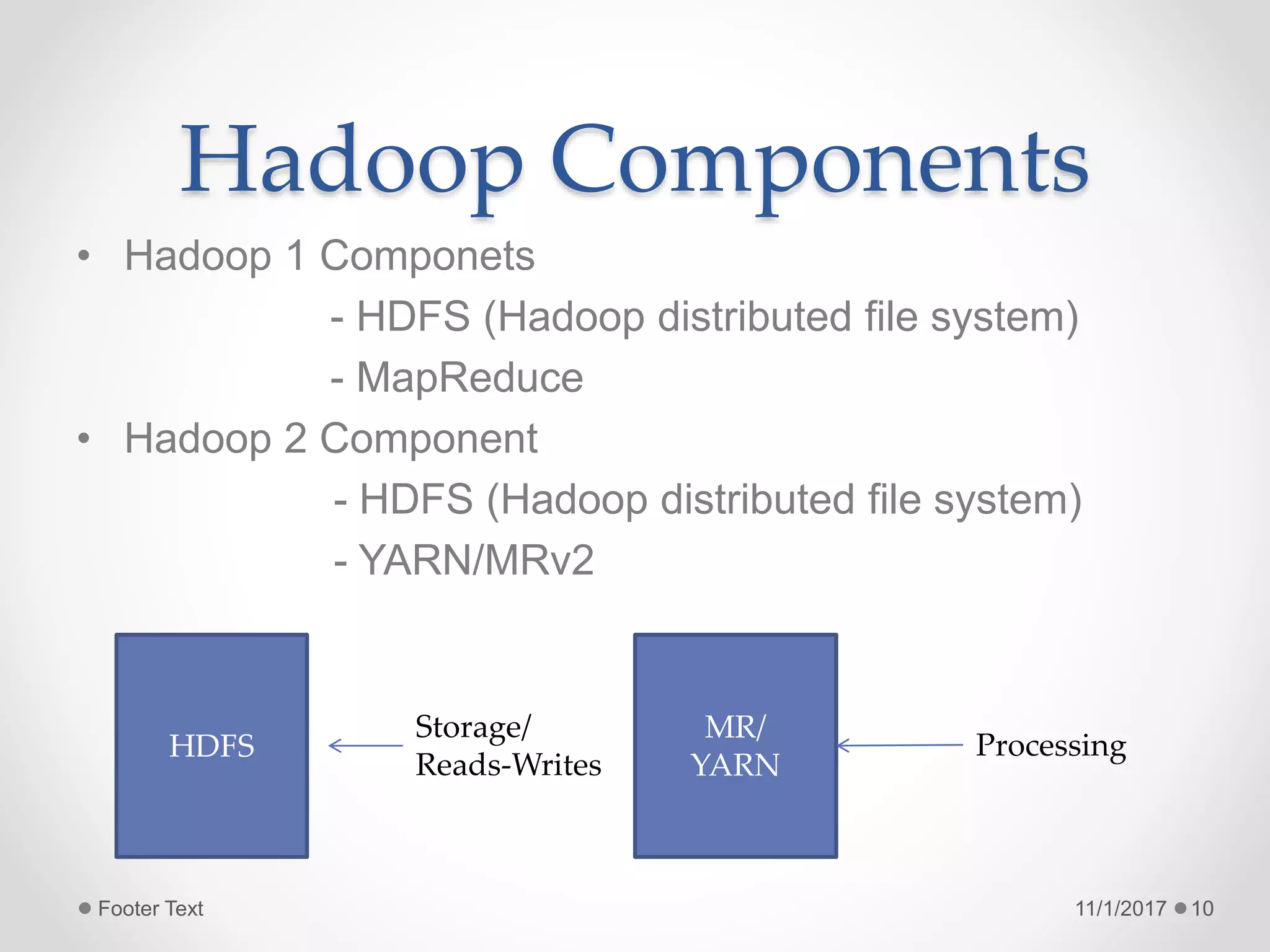
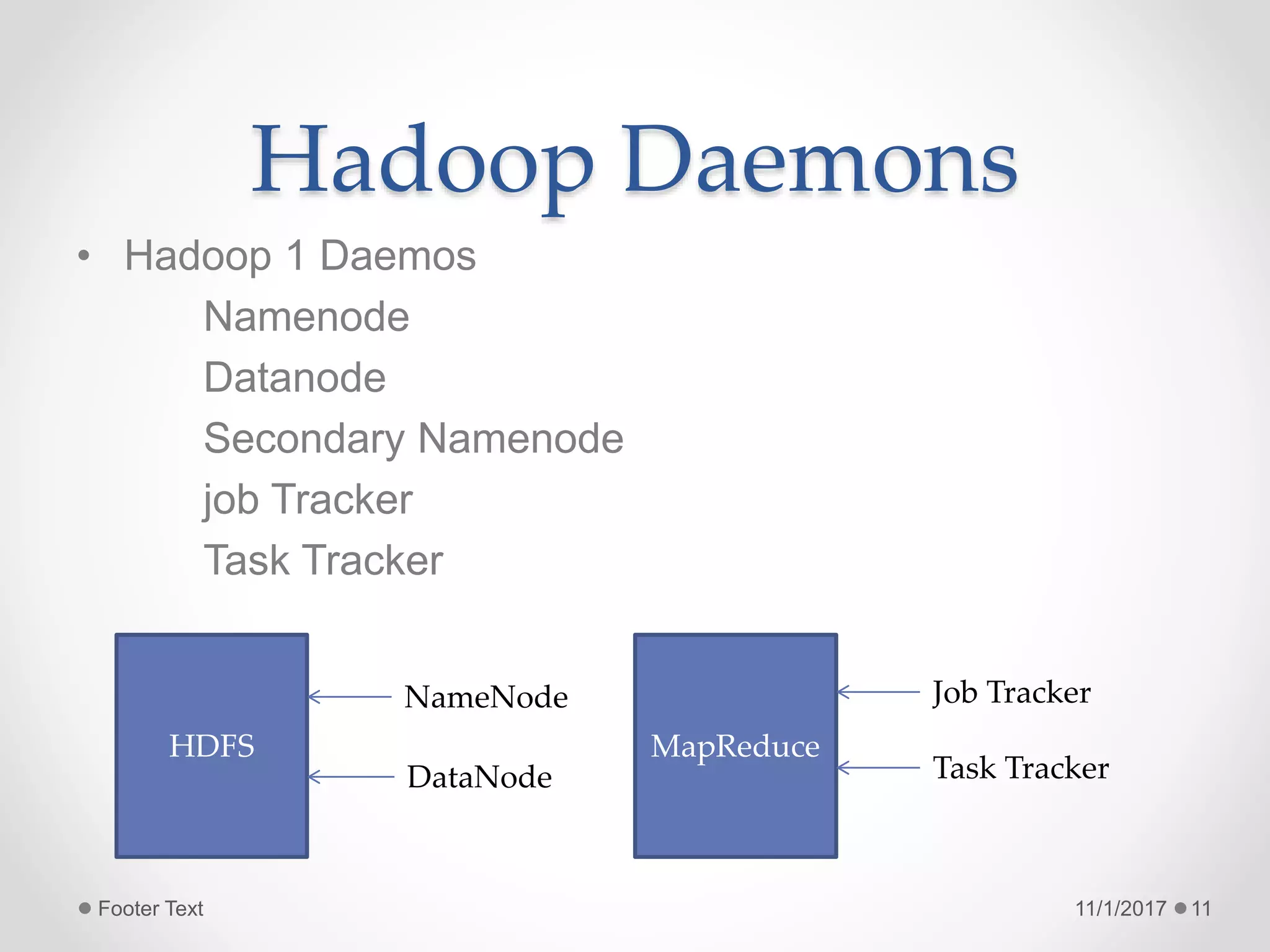
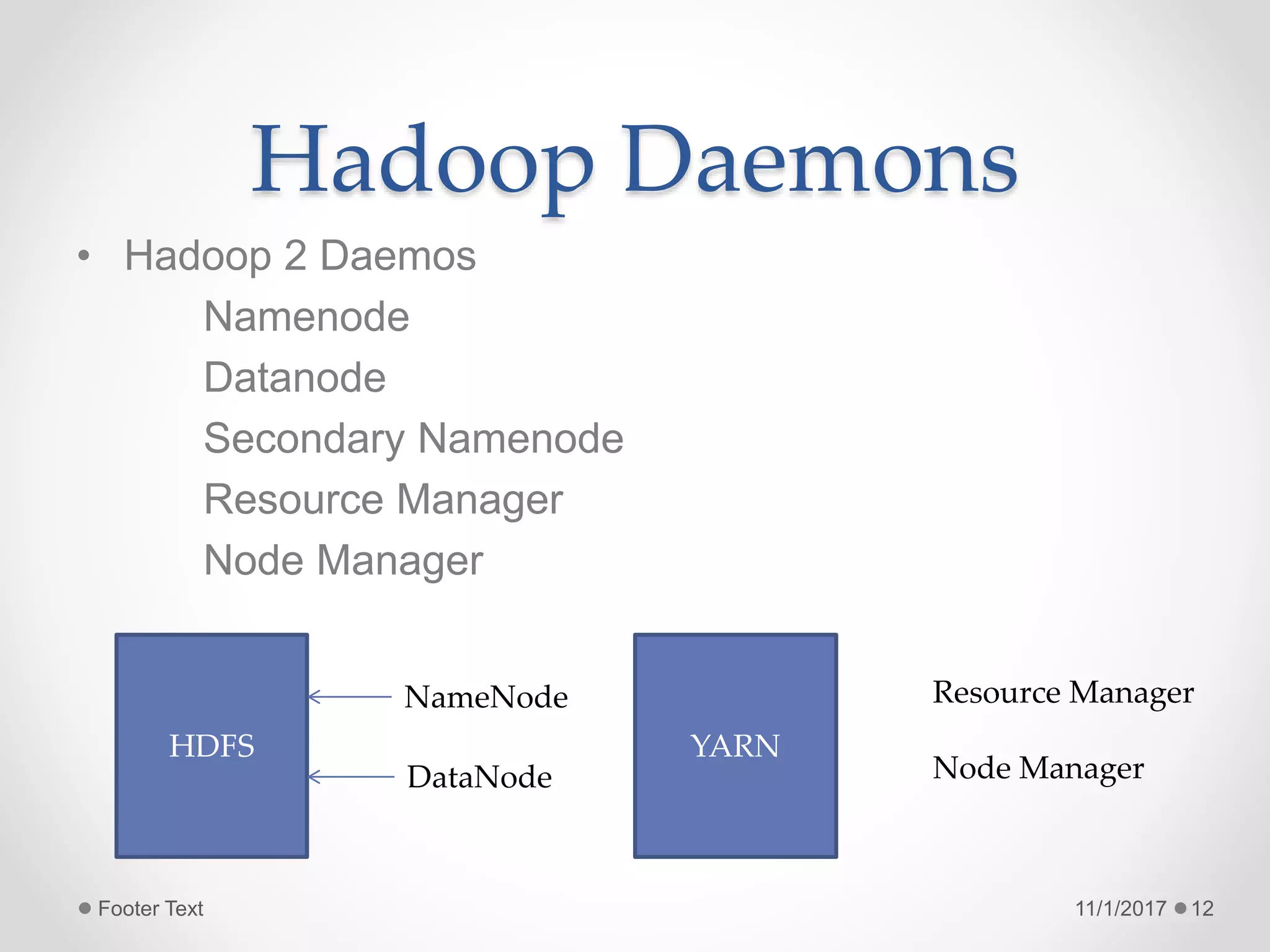
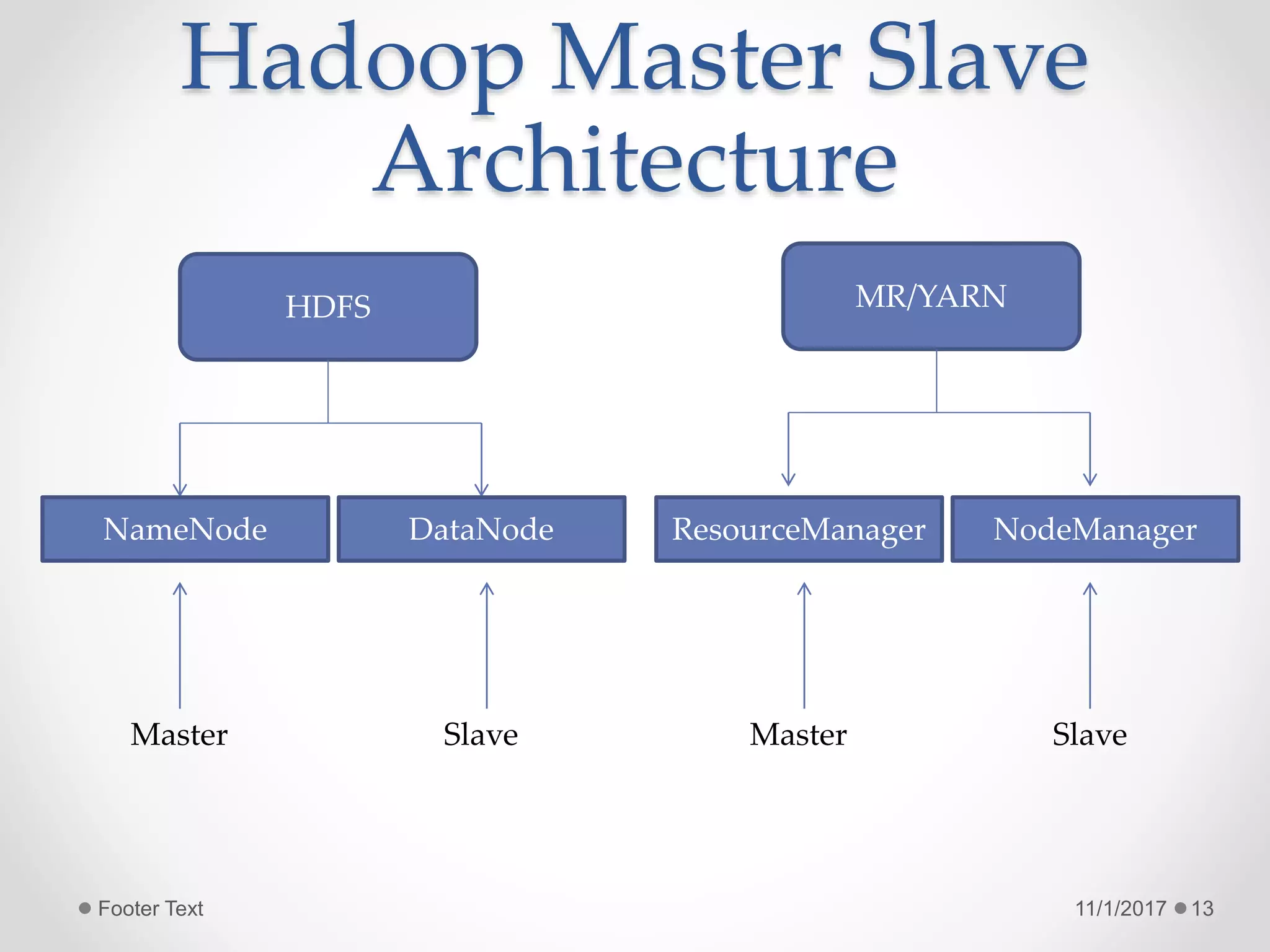
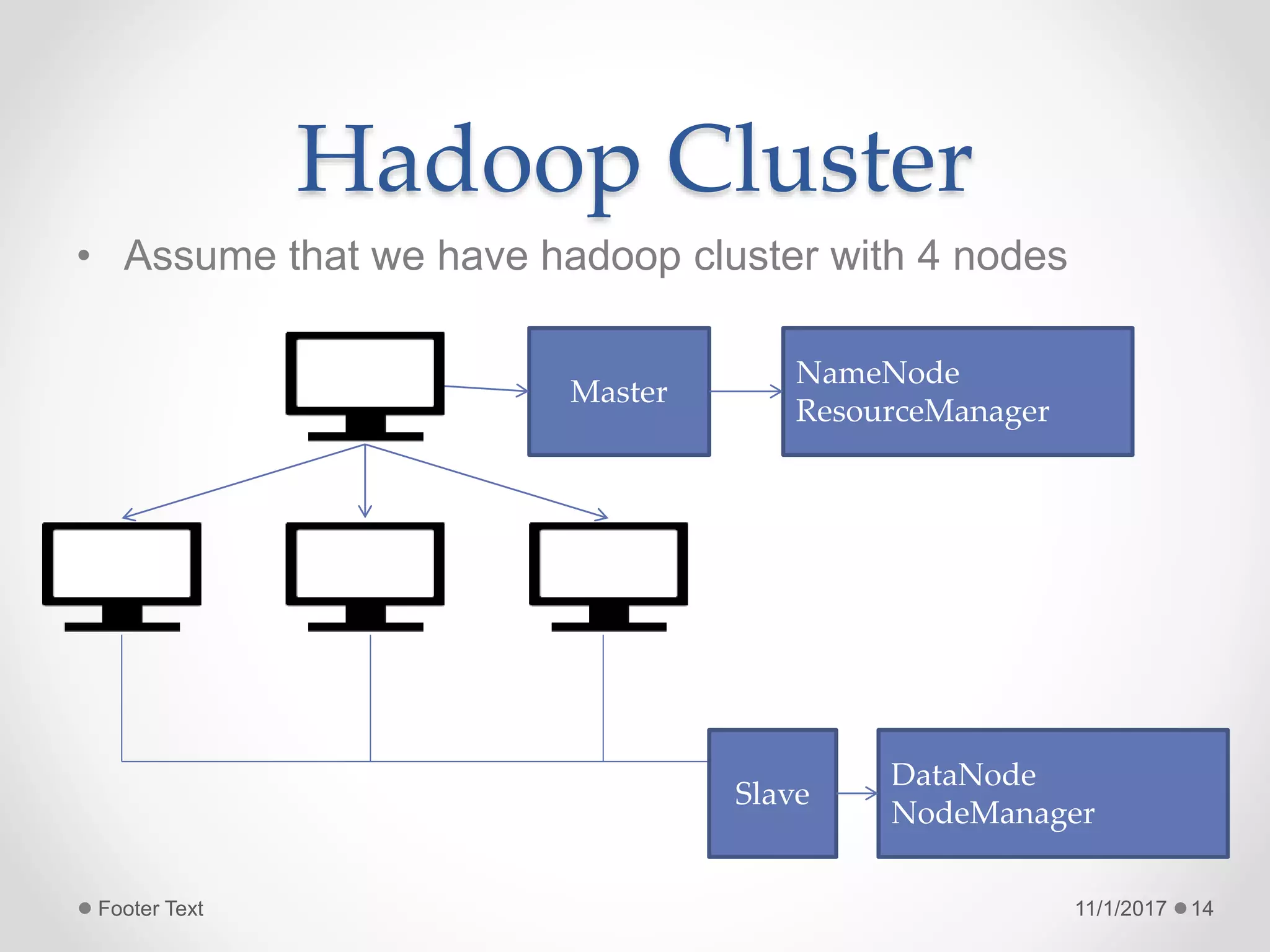
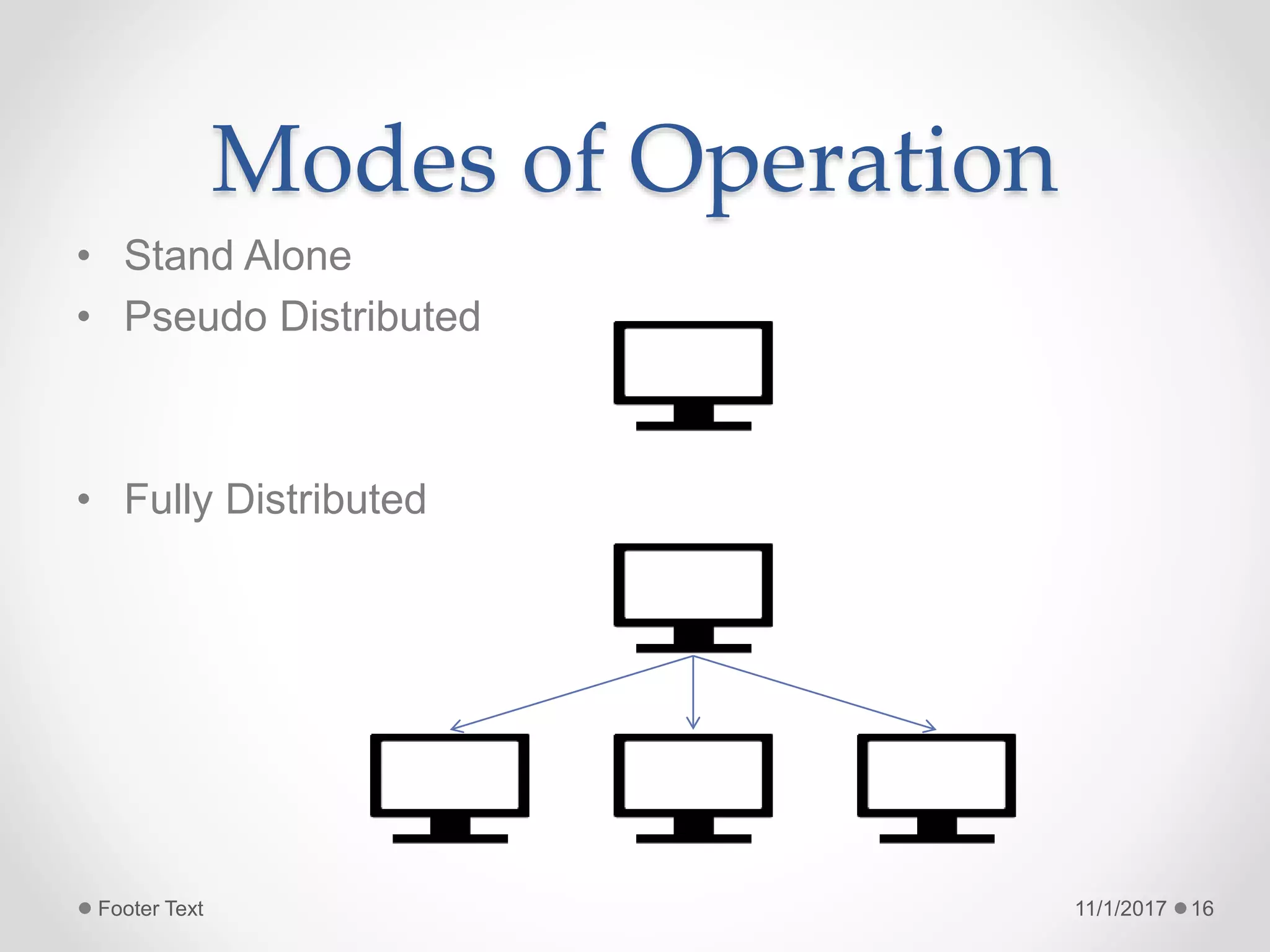
The document provides an introduction to big data and Hadoop, highlighting the challenges of storing and analyzing large datasets. It discusses the characteristics and sources of big data, along with use cases such as fraud detection and recommendation engines. Additionally, it outlines Hadoop's components, architecture, and operational modes.