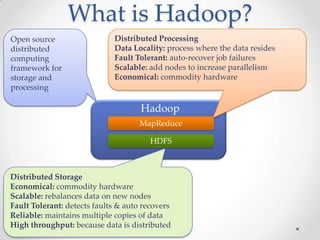
Hadoop is an open-source software framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of commodity hardware. It addresses challenges in big data by providing reliability, scalability, and fault tolerance. Hadoop allows distributed processing of large datasets across clusters using MapReduce and can scale from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. It is widely used for applications such as log analysis, data warehousing, and web indexing.
















![Hadoop for R
Sys.setenv(HADOOP_HOME="/home/istvan/hadoop")
Sys.setenv(HADOOP_CMD="/home/istvan/hadoop/bin/hadoop")
library(rmr2)
library(rhdfs)
setwd("/home/istvan/rhadoop/blogs/")
gdp <- read.csv("GDP_converted.csv")
head(gdp)
hdfs.init()
gdp.values <- to.dfs(gdp)
# AAPL revenue in 2012 in millions USD
aaplRevenue = 156508
gdp.map.fn <- function(k,v) {
key <- ifelse(v[4] < aaplRevenue, "less", "greater")
keyval(key, 1)
}
count.reduce.fn <- function(k,v) {
keyval(k, length(v))
}
count <- mapreduce(input=gdp.values,
map = gdp.map.fn,
reduce = count.reduce.fn)
from.dfs(count)
• RHadoop package
o rmr
o rhdfs
o Rhbase
• Uses Hadoop
Streaming
• Example on the right
determines how
many countries
have greater GDP
than Apple
Source: http://bighadoop.wordpress.com/2013/02/25/r-and-hadoop-data-analysis-rhadoop/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadoopoverview-130820023344-phpapp01/85/Hadoop-overview-20-320.jpg)



