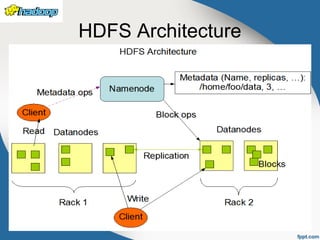
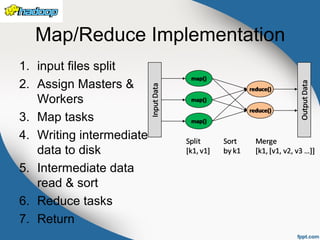
The document provides an overview of Hadoop, an open-source framework for storing and processing large datasets using distributed systems. It covers key components such as Hadoop Common, HDFS, and MapReduce, detailing their functionalities and architecture. The text emphasizes the efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of Hadoop in handling large-scale data processing tasks.