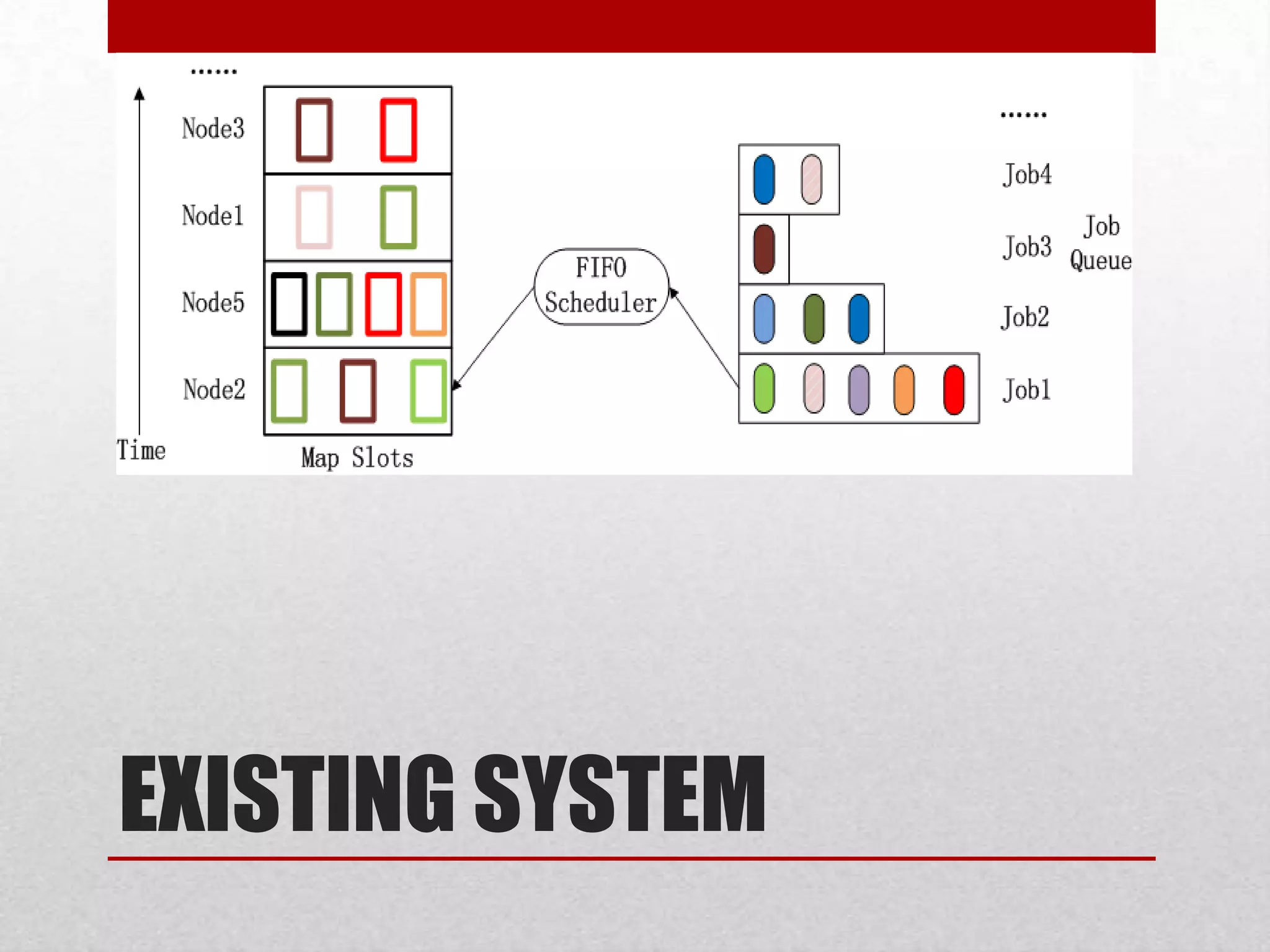
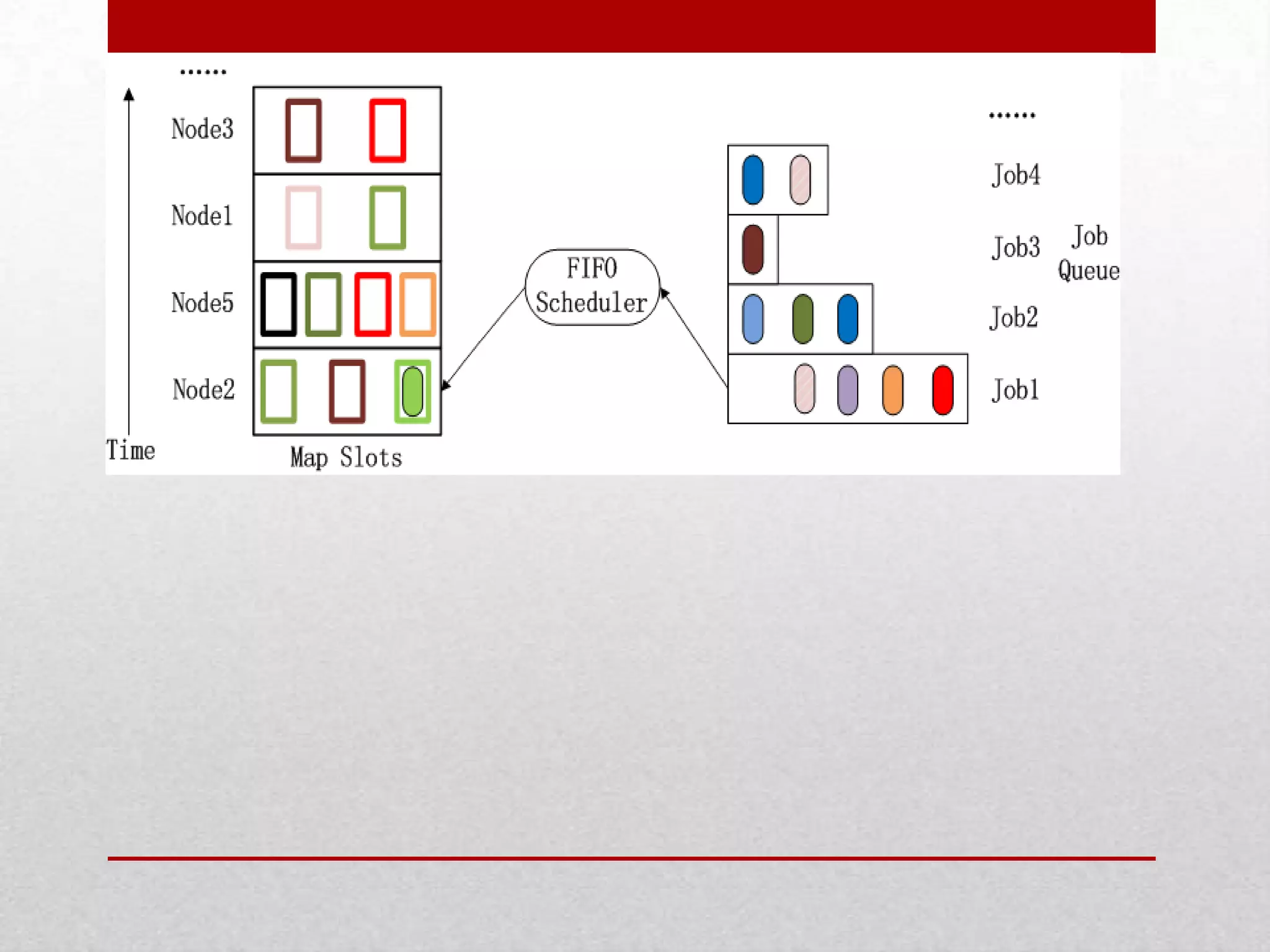
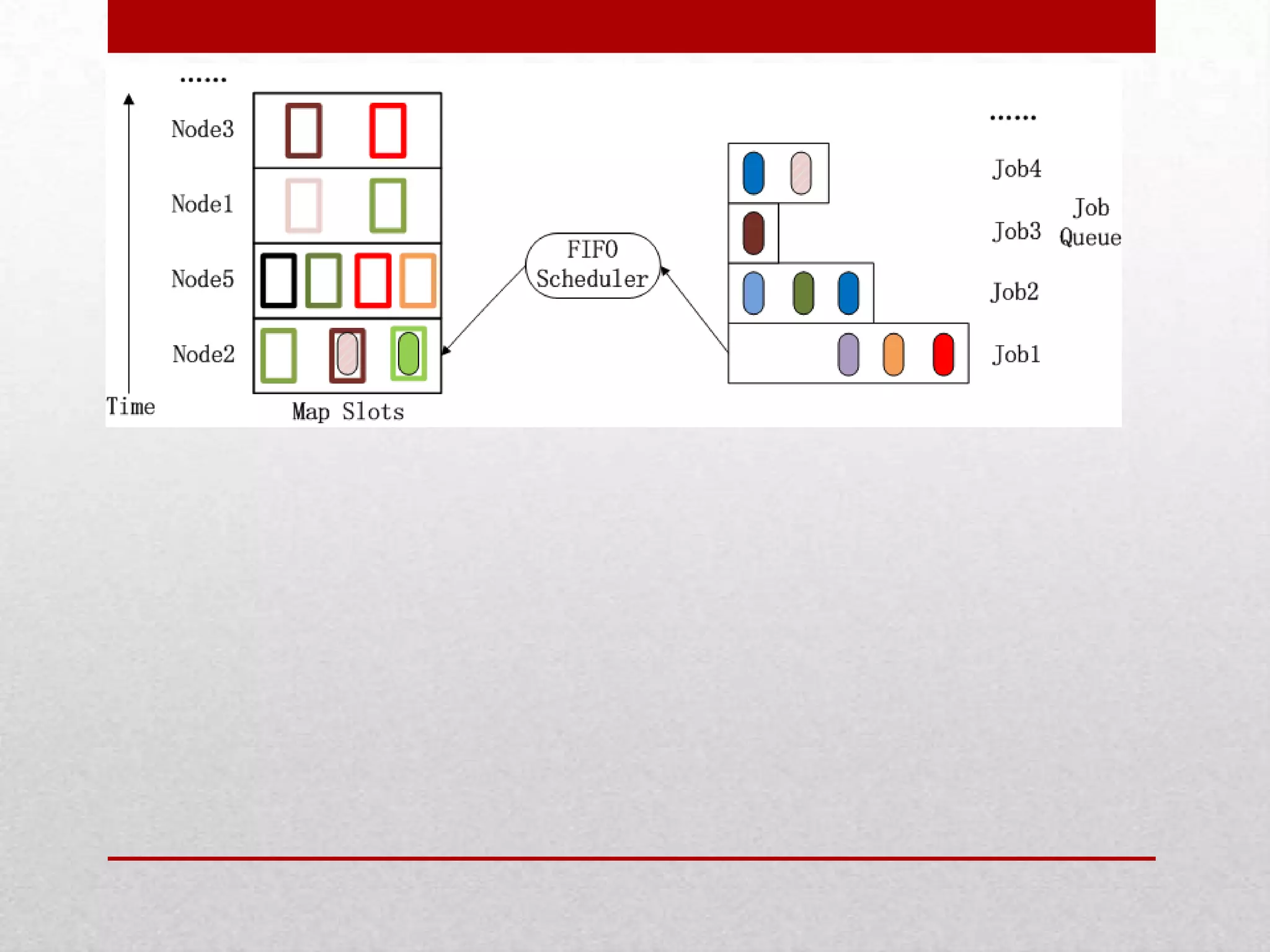
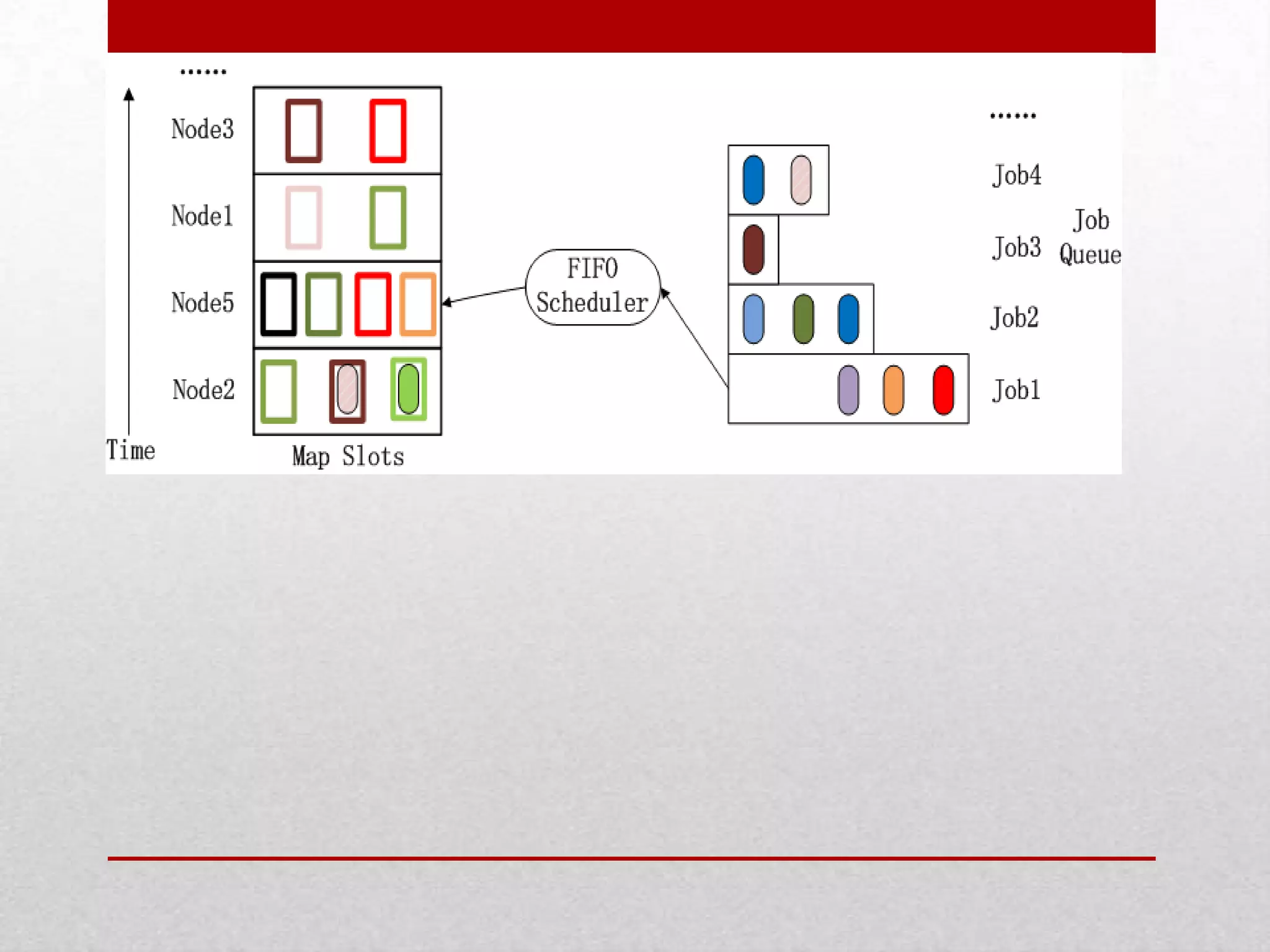
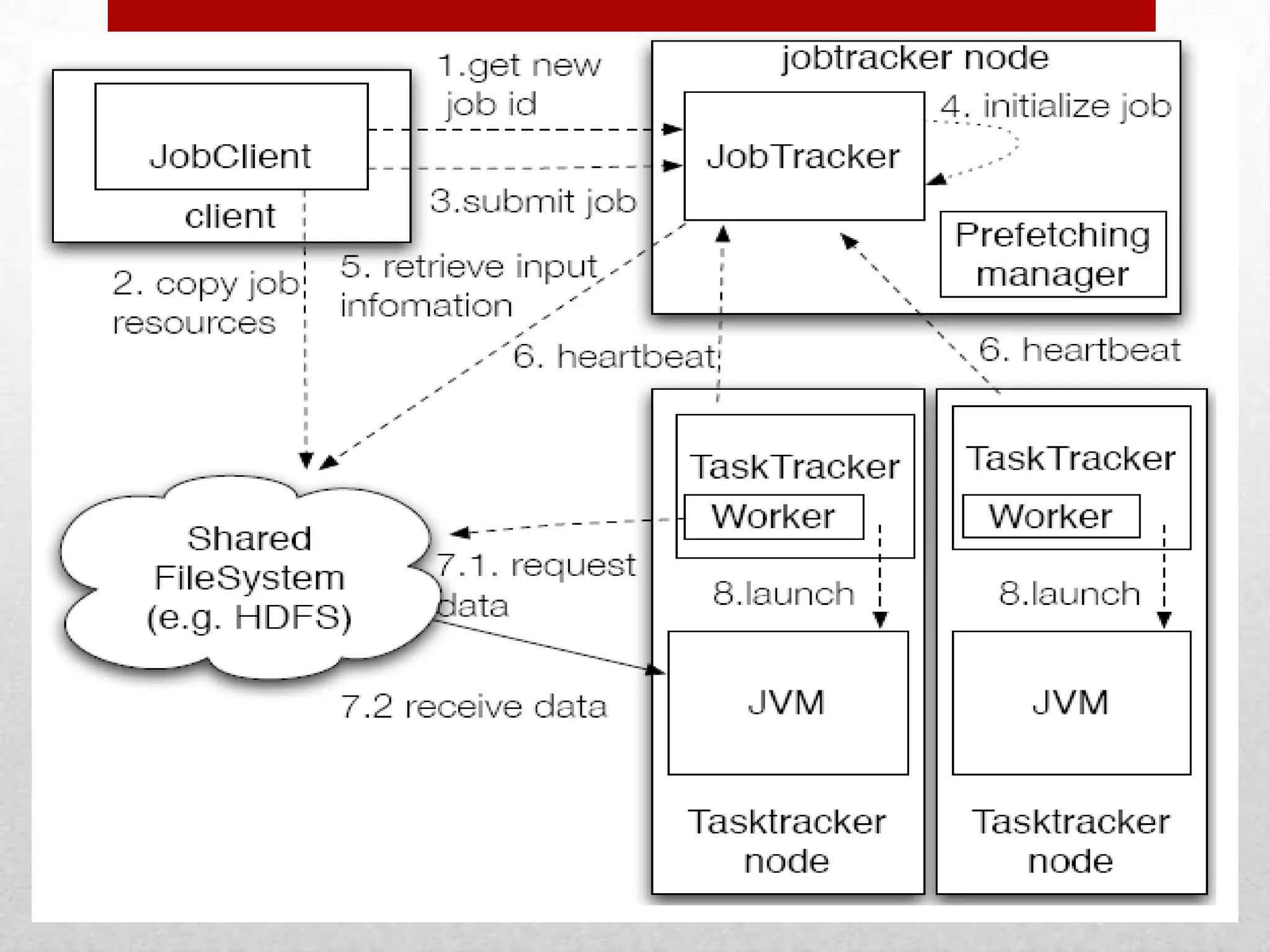
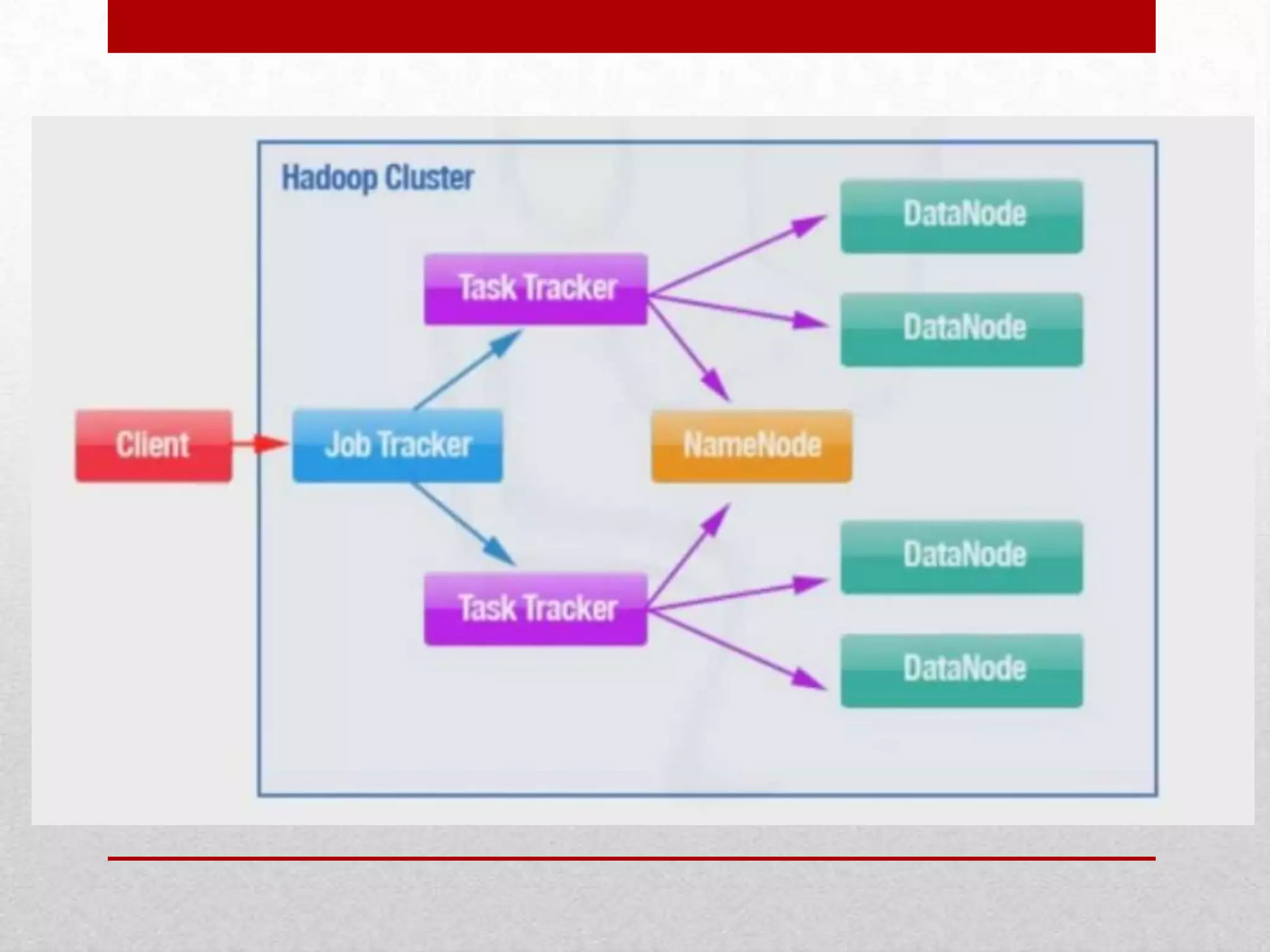
This document discusses a research project on scheduling schemes for Hadoop clusters. It begins with an introduction to Hadoop and its two main components, MapReduce and HDFS. It then reviews existing scheduling systems like FIFO, Facebook's Fair Scheduler, and Yahoo's Capacity Scheduler. The proposed system aims to address issues like CPU and I/O underutilization in the existing systems by using a predictive scheduler and prefetching mechanism. This predictive scheduler would assign tasks to appropriate task trackers and allow prefetching of data blocks. The prefetching module would help avoid I/O stalls and maximize CPU utilization. In comparison to existing systems, the proposed system is expected to provide higher I/O performance,


![SYSTEM
FEATURES
DISADVANTAG
ES
Hadoop FIFO
scheduing
Implements by
FIFO principle
Can not assign
priority for jobs
Facebook’s Fair
scheduler
Even allocation of No preemption
resources
support for large
tasks
REF [4]
Yahoo’s Capacity
scheduler
FIFO scheduler
based on priority
REF[6]
Problem in
assigning
priorities
LITERATURE SURVEY
REFERENCE
REF [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scheduling-140305102512-phpapp02/75/Scheduling-scheme-for-hadoop-clusters-9-2048.jpg)