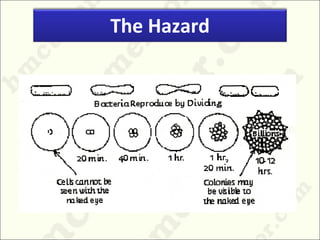
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a systematic approach to identify, evaluate, and control food safety hazards. It has 7 principles including conducting a hazard analysis, determining critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, and establishing corrective actions. HACCP aims to ensure food is safe for consumption by increasing awareness of food handling techniques and understanding how to take corrective action. It was originally developed by NASA to prevent astronauts from getting food poisoning and produce 100% safe food. Proper training and commitment to food safety standards among all food handlers is required for effective HACCP implementation.