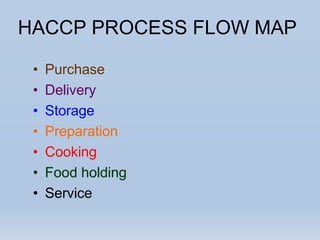
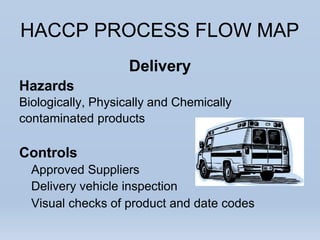
The document provides an overview of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), a food safety management system. It defines HACCP and explains that it identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards that are significant for food safety. The seven principles of HACCP are described, including conducting a hazard analysis, determining critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring systems, corrective actions, verification procedures, and documentation. Key food hazards like physical, chemical and biological hazards are also outlined. The presentation concludes with an example HACCP process flow map from purchase to service.