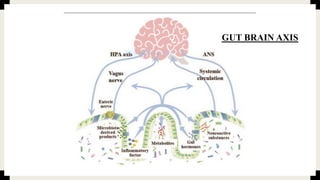
The document discusses the complex bidirectional communication between the gut and brain, known as the gut-brain axis. It outlines several key players in this communication: (1) the gut microbiome, which contains trillions of microbes that can influence brain development and mental health; (2) neuroactive substances like serotonin that are produced by microbes and can affect the brain; and (3) microbial metabolites like short-chain fatty acids and tryptophan derivatives that can modulate neuronal and immune function. The vagus nerve, gut hormones, and immune signals transmitted via the microbiome all help facilitate dialogue between the gut and brain. Disruptions to this gut-brain axis are implicated in several neurological and psychiatric disorders.

![INTRODUCTION
■ Bi-directional link
between CNS and
Enteric Nervous
System. [ENS]
■ Complex cross talk
between Endocrine
[HPA axis], Immune
[Cytokines,
Chemokines] and
Nervous System.
[ANS]
■ Microbiome plays a
pivotal role.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-2-320.jpg)
![THE GUT
MICROBIOME
■ MICROBIOTA:
Microbe population within a specific ecosystem
of Host [Skin, oral, nasal, Gut, Genito-urinary].
Gut contains 1013 – 1014 microbiota
approximately.
10 times more than other cells of the human
body.
FERMICUTES & BACTEROIDES: comprises
75% of gut microbiota.
Disruption of Gut Microbiota: associated with
Allergy, Autoimmune Disorders, Metabolic
Disorders, Neurodegenerative Disorders,
Psychiatric Disorders.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-3-320.jpg)

![DESCENDING
LIMBIC
PROJECTION
INTESTINE
BRAIN STEMTHALAMUS
HYPOTHALAMUS
[REGULATION OF
FOOD, HUNGER,
SATIETY.]
LIMBIC SYSTEM
[EMOTION,
MEMORY]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-8-320.jpg)


![■ SHORT CHAIN FATTY ACID
[SCFA]:
Through decomposition of fermentable
carbohydrate by gut microbiota.
Acetate, Propionate, Butyrate
Important role in Glucose Homeostasis,
reduction of Food intake, modulation of
lymphocytic function.
Through G-protein Coupled Receptor.
[GPCR]/ Epigenetic Modulator of Histone
Deacetylase.
Expressed in GUT, Muscle, Liver,
Pancreas, Adipocytes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-12-320.jpg)

![• TRYPTOPHAN
TRYPTOPHAN
MONO OXYGENASE
• INDOLE-3-
ACETAMIDE
INDOLE-3-
ACETAMIDE
HYDROLASE • INDOLE-3-
ACETIC ACID
INDOLE-3-ACETIC
ACID
DECARBOXYLASE
• 3-METHYL
INDOLE
ACTIVATE ARYL-
HYDROCARBON
RECEPTOR [AHR]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-14-320.jpg)
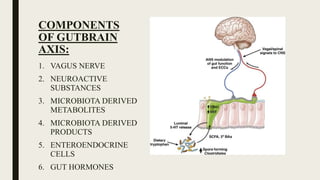
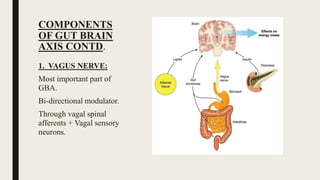
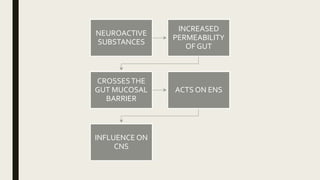
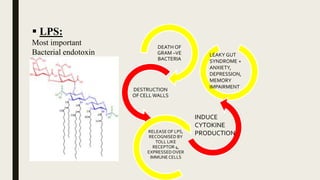
![COMPONENTS OF GUT BRAIN AXIS
CONTD.
4. MICROBIOTA DERIVED PRODUCTS:
4 products:
1. LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE [LPS]
2. LPS BINDING PROTEIN
3. PEPTIDOGLYCAN
4. FLAGELLIN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-15-320.jpg)
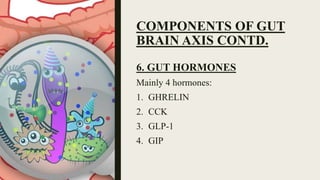
![COMPONENTS OF GUT BRAIN AXIS
CONTD.
5. ENTERO-ENDOCRINE CELLS
[EEC]
Represent only 1% of the epithelial
cells.
Scattered throughout the GI tract.
Release a variety of Gut Hormones in
response to diet related stimuli.
Prime importance in Gut motility,
Hormone release, appetite and
digestion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-17-320.jpg)
![■ GHRELIN
Released from proximal A cells of stomach.
During food restriction.
FOOD
RESTRICTION/FASTI
NG, INCREASED
GHRELIN
RECEPTORON
VAGALAFFERENT
AND NODOSE
GANGLION
SIGNALSTO BRAIN
DIRECTLY CROSS
BBB
HYPOTHALAMUS
[FOOD
REGULATORY
CENTRE]
INDUCES FOOD
INTAKE, PROMOTE
MEMORY
REGULATION
BINDTO GROWTH
HORMONE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-19-320.jpg)
![■ CCK
Also called
cholecystokinin.
Stimulates
digestion of Fat &
Protein.
Through G-PCR:
CCK-A and CCK-B
[Gut & Brain]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-20-320.jpg)
![■ GLP—1
[GLUCAGON LIKE
PEPTIDE]
Released from L cells
along with PYY [Peptide
YY]: mostly from Ileum
and Colon
Inhibitory effect on energy
intake, promotes satiety.
Widely distributed: Gut,
Kidney, Pancreas, Vagus
Nerve, Hypothalamus.
GLP-1 agonist: help to
treat DM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-21-320.jpg)
![■ GIP [GLUCOSE
DEPENDENT
INSULINOTROPI
C
POLYPEPTIDE]
Released from K cells
of Duodenum &
Jejunum
Promote Insulin
release
Maintain Glucose
Homeostasis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gutbraincrosstalk-200924140914/85/Gutbrain-cross-talk-22-320.jpg)