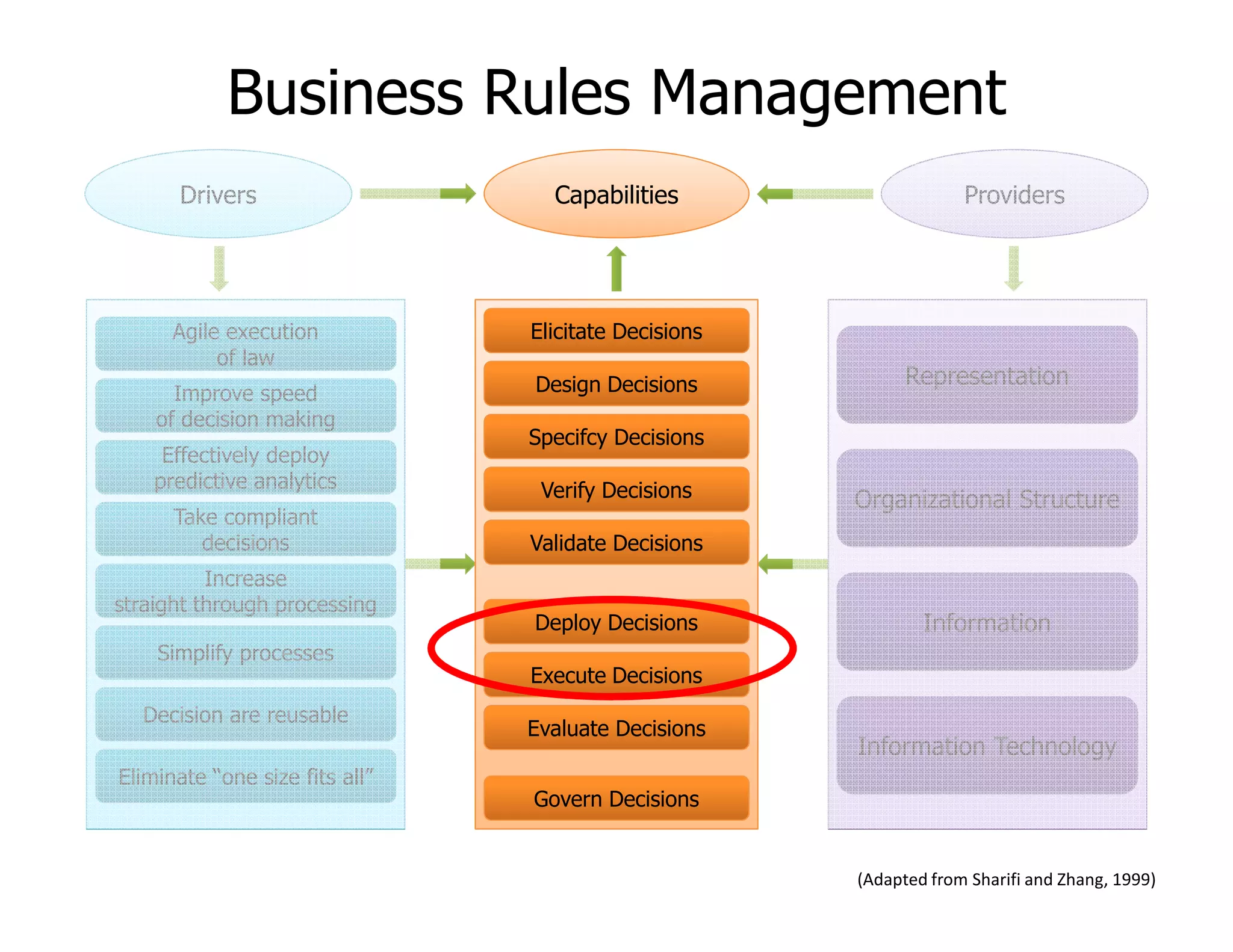
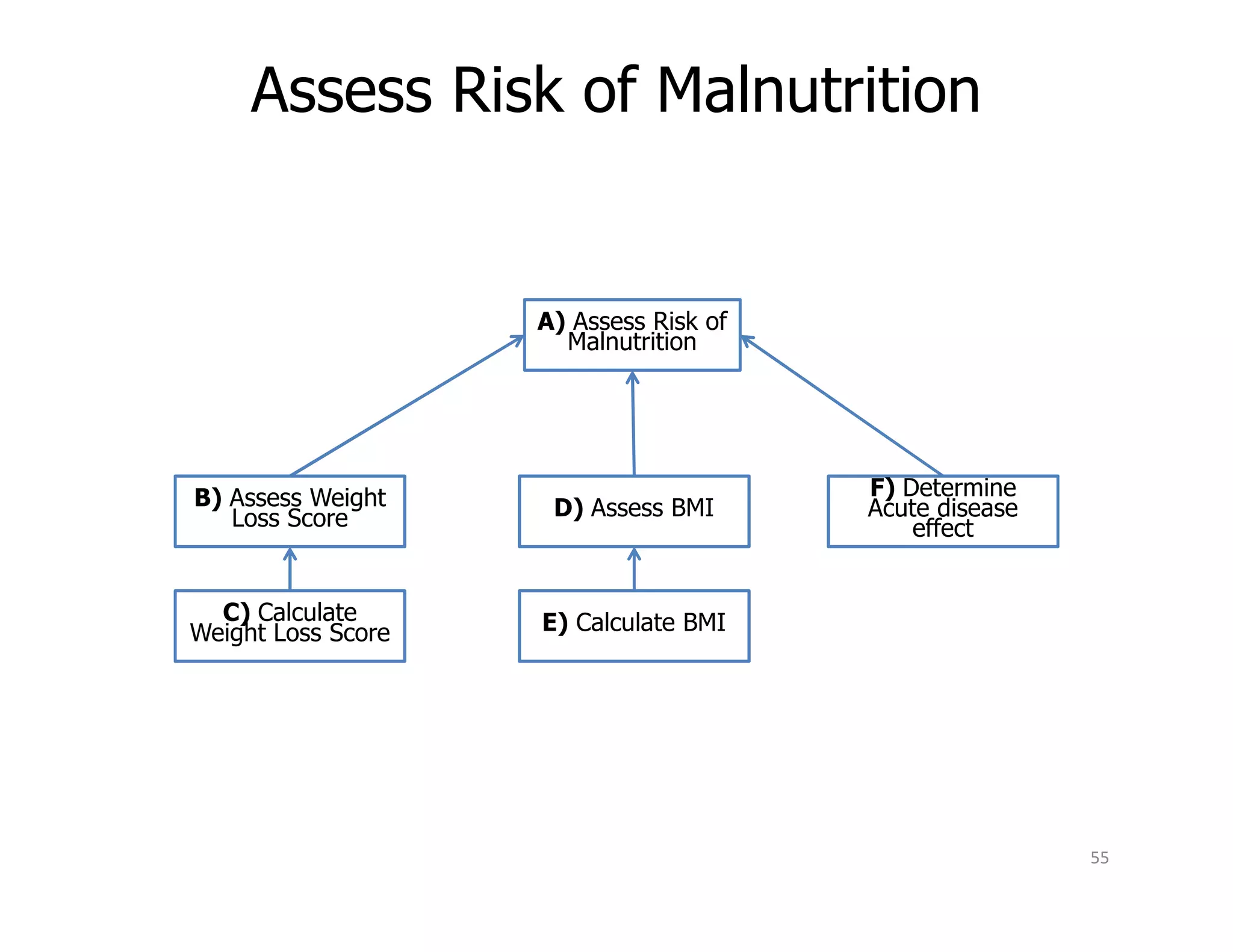
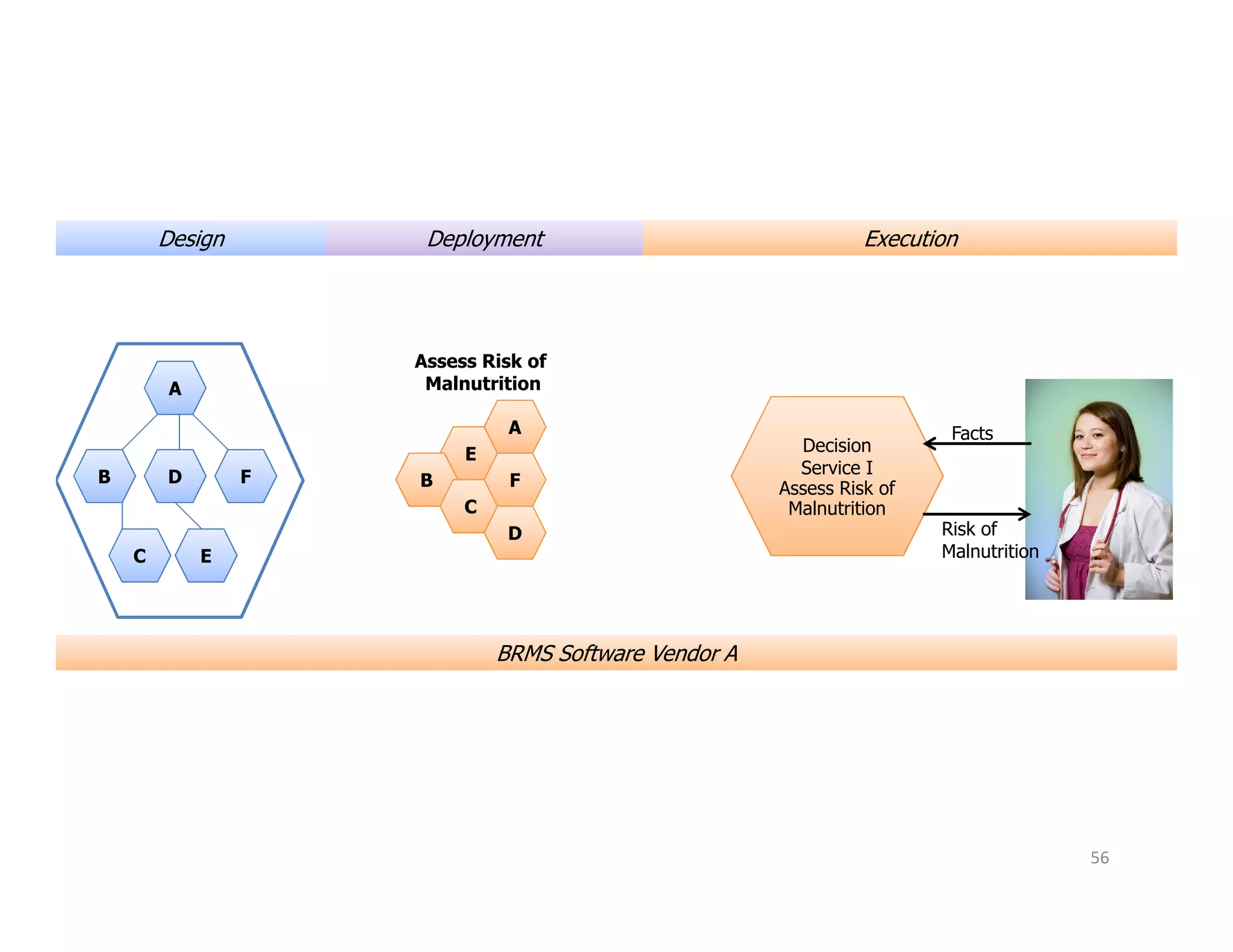
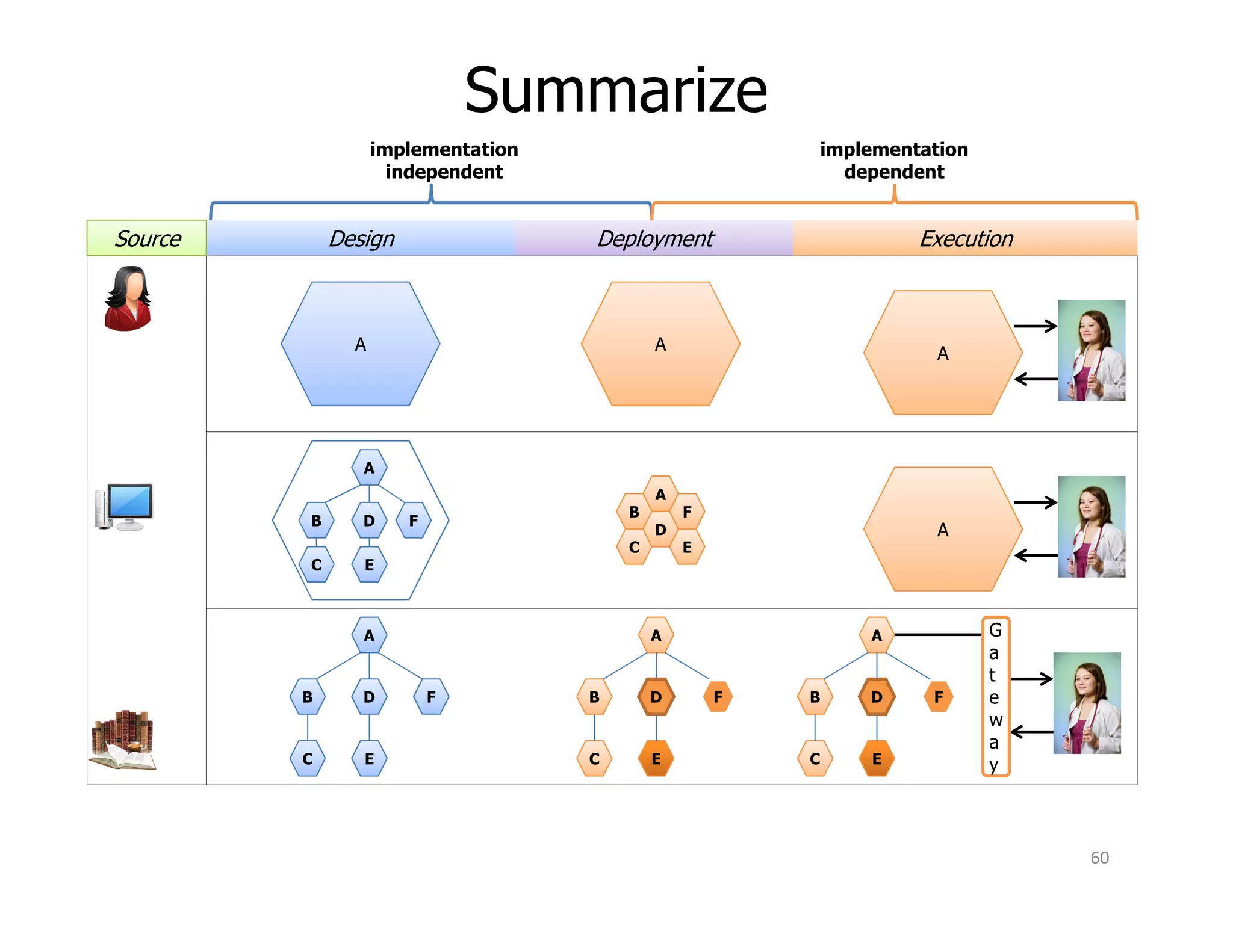
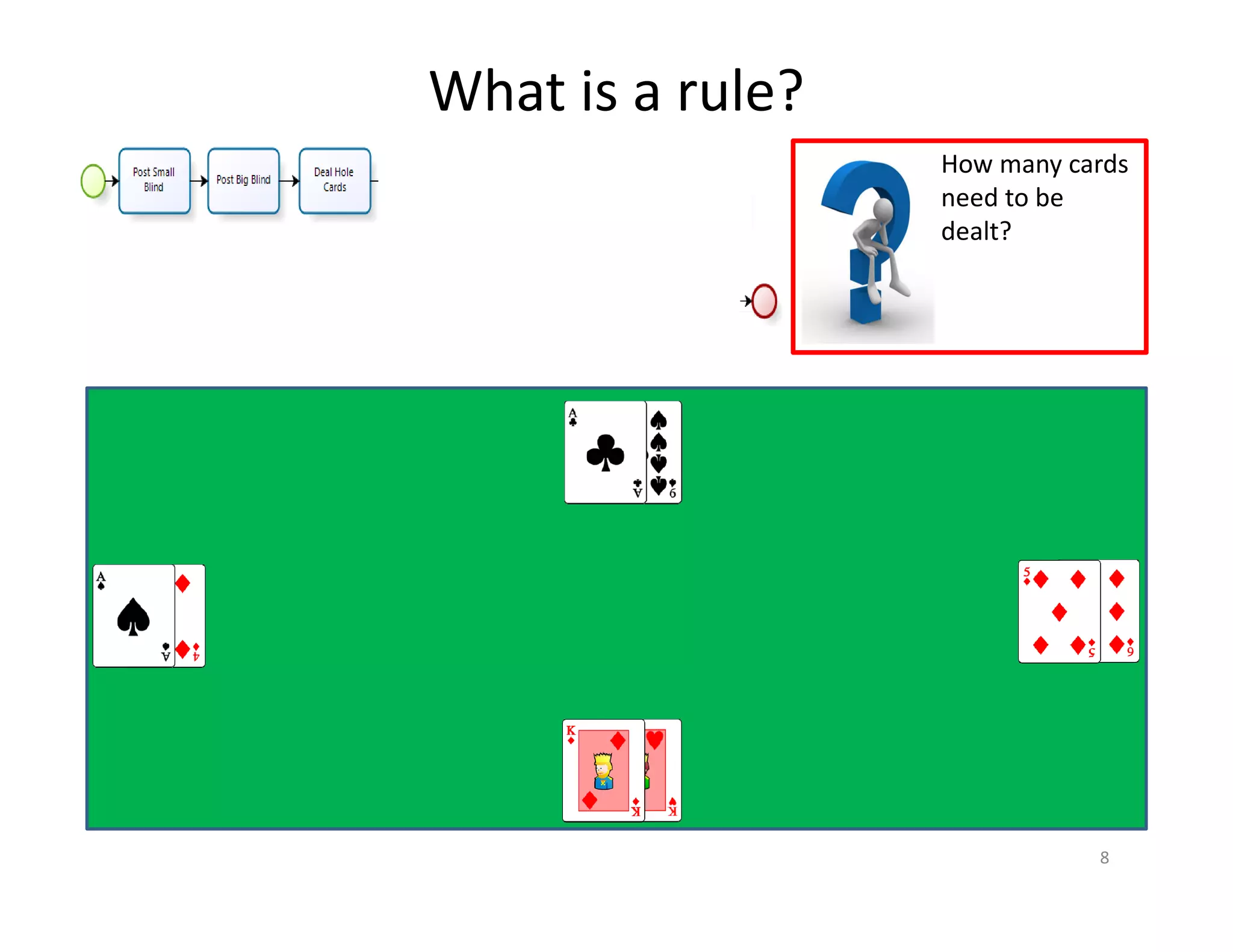
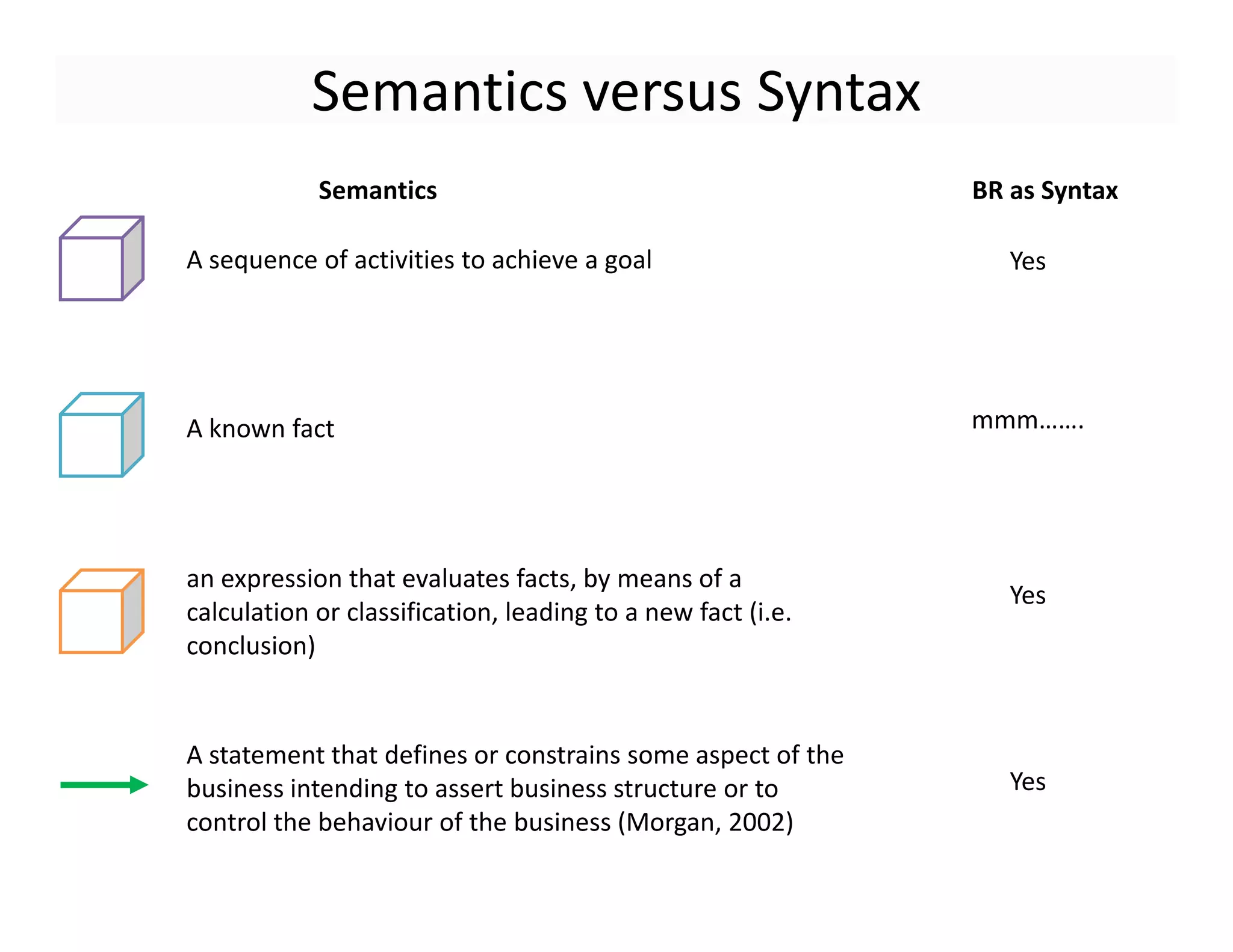
The document discusses various aspects of business rules management (BRM) and decision management, highlighting the importance of effective management techniques and tools in implementing business rules. It also mentions common mistakes in decision-making processes and emphasizes the relevance of properly managing technologies to enhance organizational decision-making capabilities. A significant focus is placed on the role of predictive analytics and agile decision execution in improving business outcomes.


























![“The Romance
of the Gut”
These results have interesting implications for the use of
decision support systems in procurement management. At
this point, it seems appropriate to quote Meehl’s (1986):
“Computer Phobia”
Review and reflection indicate that no more than 5% of what was written in the 1954 book entitled,
Clinical Versus Statistical Prediction (Meehl, 1954), needs to be retracted 30 years later. If anything,
these retractions would result in the book’s being more actuarial than it was. Seven factors appear
to account for the failure of mental health professionals to apply in practice the strong and clearly
supported empirical generalizations demonstrating the superiority of actuarial over clinical
prediction.
“A gut is a personal nontransferable
attribute, which increases the value of a
good one.”
32
1. Simple Business Rules;
2. Predictive Analytics;
3. Students;
4. Young Professional;
5. Experienced Professional.
this point, it seems appropriate to quote Meehl’s (1986):
‘‘There is no controversy in social science that shows
such a large body of qualitatively diverse studies
coming out so uniformly in the same direction as
this one [the relative validity of statistical versus clinical
prediction]. When you are pushing 90 investigations
[now over 130], predicting everything from the outcome
of football games to the diagnosis of liver disease and
when you can hardly come up with a half
dozen studies showing even a weak tendency in
favour of the clinician, it is time to draw a practical
conclusion.’’ (Meehl, 1986, pp. 372–373)
Meelh (1986) Grove and Meehl (1996) Wade and Travis (1998) Tazelaar and Batenburg (2003) Snijders and Tazelaar (2005)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20151010universiteitutrecht-151024091510-lva1-app6891/75/Guest-Lecture-Business-Rules-Management-Decision-Management-Utrecht-University-32-2048.jpg)