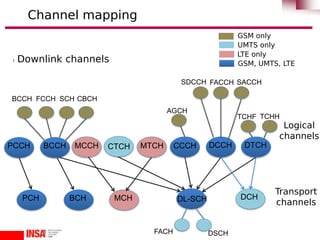
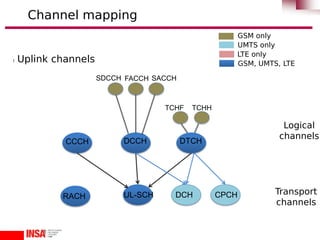
The document details mobile network architectures focusing on logical channels, user and control planes, and data transmission paths (downlink and uplink). It outlines physical, transport, and logical channels used in networks like GSM, UMTS, and LTE for efficient data transmission and resource allocation. It also provides a call establishment scenario illustrating the process of setting up a call in a mobile network.