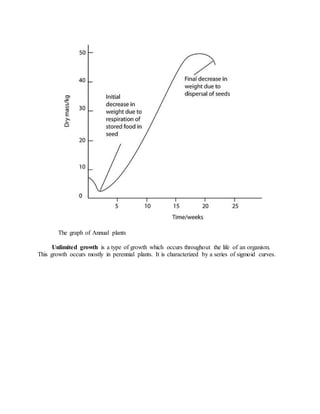
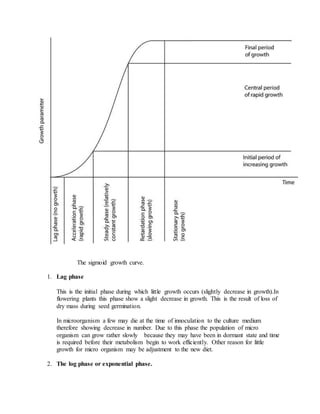
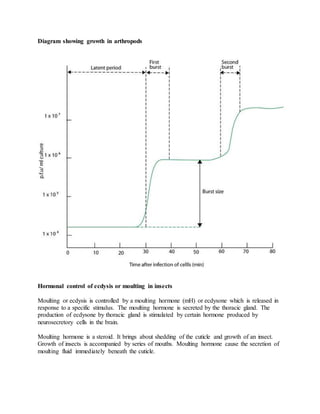
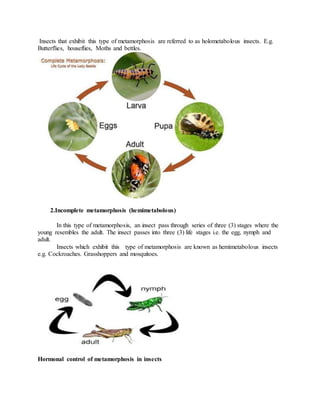
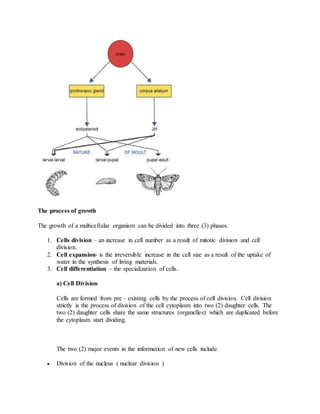
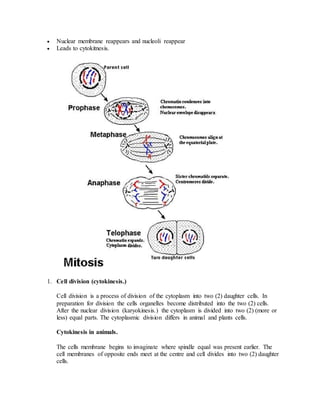
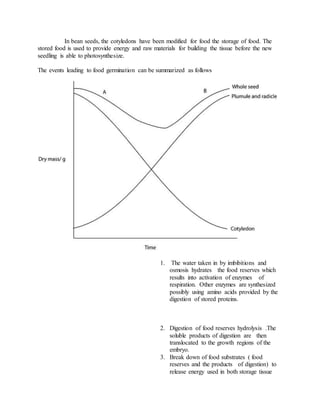
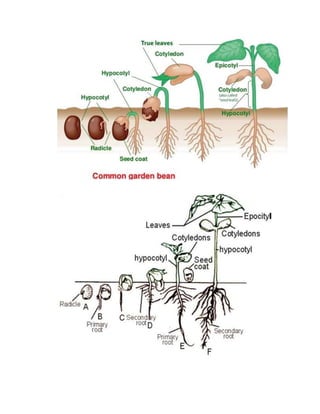
Growth is defined as an irreversible increase in an organism's dry mass due to protein synthesis. It is closely linked with development, which refers to increasing complexity through tissue and organ differentiation. Growth can be measured in various ways and typically follows a sigmoid curve with lag, log/exponential, stationary, and decelerating phases. Both external factors like nutrients and internal factors like genes influence growth. Arthropods grow intermittently through molting and shedding of their exoskeleton. Insects undergo complete or incomplete metamorphosis from egg to larva/nymph to adult stages controlled by moulting and juvenile hormones.