The document discusses the concept and dynamics of effective small groups and teams, emphasizing the importance of group interaction, communication, and member roles in achieving shared goals. It outlines the stages of small group work, from forming to adjourning, and identifies techniques for improving group performance and cooperation. Additionally, it highlights challenges faced in group settings and provides guidelines for promoting effective collaboration among members.














![ Large group method :
Number is more than 30
A] Lecture
B] Panel discussion
C] Symposium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupddynamicsteambuildinginteaching-171226091124/85/Groupd-dynamics-amp-team-building-in-teaching-15-320.jpg)
![Small Group Method:
Number will be up to 30
A] Work shop
B] Group discussion
C] Field visit
D] Seminar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupddynamicsteambuildinginteaching-171226091124/85/Groupd-dynamics-amp-team-building-in-teaching-16-320.jpg)
![Individual
A] Project work
B] Self study
C] Assignments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupddynamicsteambuildinginteaching-171226091124/85/Groupd-dynamics-amp-team-building-in-teaching-17-320.jpg)
![ 1. Group Discussions
2. Seminar
3. Tutorial
4. Demonstration
5. Work shop
6. Role play
7. Practical [ Lab, bedside, field work ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupddynamicsteambuildinginteaching-171226091124/85/Groupd-dynamics-amp-team-building-in-teaching-18-320.jpg)


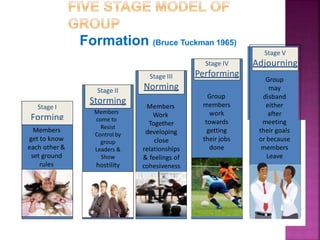
![ For effective functioning of a group certain
guidelines are framed.
Functioning of a group undergoes Five stages
1. Forming [ stage I]
2. Storming [ stage II ]
3. Norming [ Stage III ]
4. Performing [ Stage IV ]
5. Adjourning or Transforming [stage V]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupddynamicsteambuildinginteaching-171226091124/85/Groupd-dynamics-amp-team-building-in-teaching-21-320.jpg)





















![3. Learning outcome from a badly conducted
group discussion would be still better than
that from a good lecture
4. All Teams are Groups but all Groups are not
Teams.[teams are difficult to form and it
takes long time]
TEAM – Together Everyone Achieves More](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/groupddynamicsteambuildinginteaching-171226091124/85/Groupd-dynamics-amp-team-building-in-teaching-44-320.jpg)
