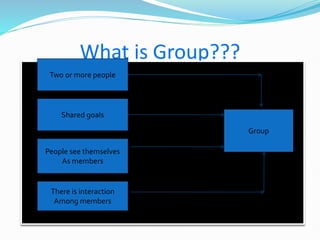
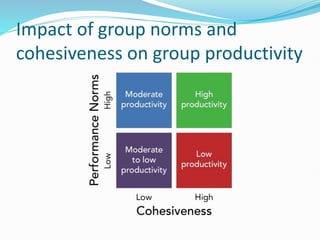
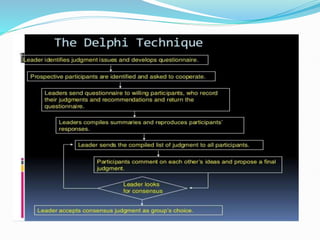
The document discusses groups and group dynamics. It defines groups as consisting of two or more people who see themselves as members working toward shared goals and interacting with one another. Group dynamics refers to the forces that emerge within a group as a result of member interaction and how this impacts the group's productivity and decision-making. High group cohesiveness and norms can increase productivity, while an absence of norms despite cohesiveness may decrease it. The stages of group development are also outlined.