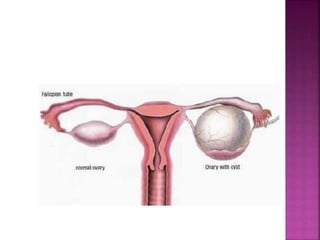
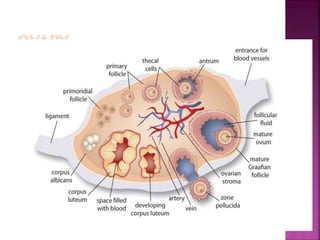
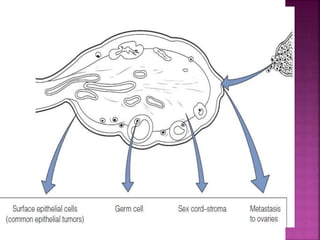
This document discusses ovarian cysts, dividing them into non-neoplastic and neoplastic categories. Non-neoplastic cysts are further divided into functional, pathological, and other types. Functional cysts include follicular cysts, corpus luteal cysts, and theca lutein cysts, which are asymptomatic and typically resolve on their own within weeks. Pathological cysts include those seen in polycystic ovary syndrome and endometriotic cysts. Other non-neoplastic cysts include para-ovarian and para-fimbrial cysts. Neoplastic cysts include benign tumors, borderline tumors, and malignant tumors. The document provides details on characteristics, diagnosis,




![ I. Non-Neoplastic :
A] Functional:
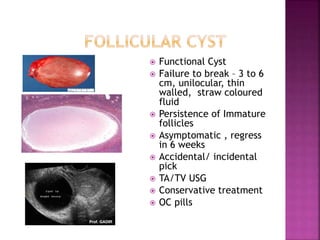
1. Follicular cyst,
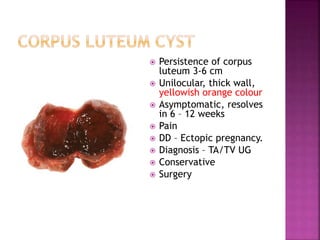
2. Corpus Luteal Cyst
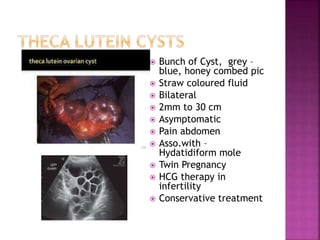
3. Theca Lutein Cyst
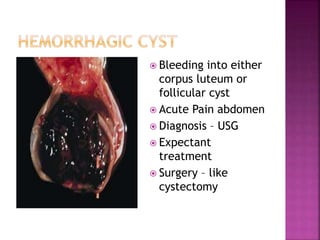
4. Haemorrhagic Cyst
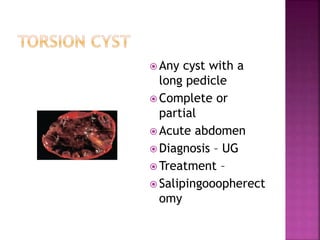
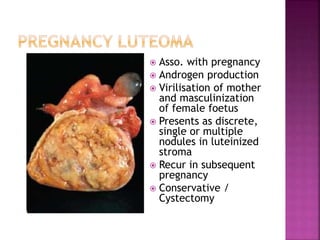
5. Luteoma of Ovary in Pregnancy
B] Pathological:
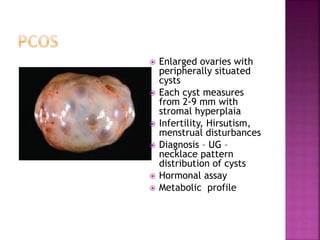
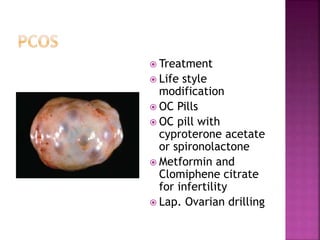
1. PCOS
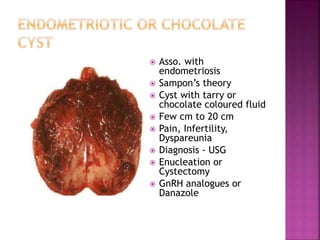
2. Chocolate cyst or Endometriotic cyst
3. Tubo-ovarian mass](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-200324092310/85/7-ovarian-cysts-9-320.jpg)
![C] Others: [Embryological defect]
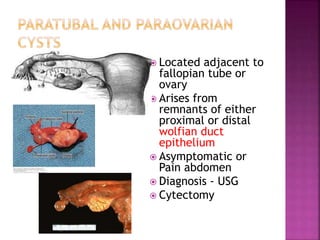
1. Para-ovarian Cyst
2. Para-fimbrial Cyst
II. Neoplatic:
A] Benign tumours
B] Borderline or
Tumours of Lo Malignant PotentialPM
C] Malignant tumours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-200324092310/85/7-ovarian-cysts-10-320.jpg)
![ Collection or retention of excess fluid in
preformed cavities resulting in enlargement
of ovary
Not capable of proliferation [mostly]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-200324092310/85/7-ovarian-cysts-11-320.jpg)