Group 2 activity5
•
0 likes•73 views
The document describes the integumentary system and its structures. It provides a learning outcome for identifying and describing key skin structures like the dermis, epidermis, hypodermis, hair root, hair shaft, hair follicle, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands. The document compares and contrasts thick and thin skin. It also labels and describes structures of the nail including the free edge, lunula, nail body, nail groove, eponychium, nail root, nail bed, hyponychium, and nail fold.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Group 2 activity6

The document describes an anatomy exercise on the skeletal system where students identify bones, structures, and divisions of the skeletal system. It discusses the skull, long bones, vertebral column, thoracic cage, and organization of the axial and appendicular skeleton. Students label diagrams, describe parts of bones, and discuss functions of the skeletal system.
3. Integumentary system (Skin).pptx

The skin is the largest organ of the body and has three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and provides a protective barrier. It has five layers including the stratum corneum. The dermis contains collagen, elastic fibers, blood vessels, nerves and skin appendages. The hypodermis is a subcutaneous layer containing fat and lobules. Skin has several functions like protection, sensation, temperature regulation and immunity. It also contains appendages like hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands.
Lesson-2-Integumentary-System.pptx

The document describes the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands. It discusses the layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis), associated glands like sweat and sebaceous glands, the structure and layers of hair, and the parts and function of nails. The integumentary system acts as a protective barrier for the body, regulates temperature, and has sensory, excretory and synthetic functions.
Integumentary system

The document discusses the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, and nails. It describes the layers of the skin - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis - and their functions in protecting the body from abrasion, bacteria, dehydration, and UV radiation. Hair grows out of the skin across most of the body in different types. Nails are also made of keratin and are alive at their roots under the skin, with a plate and cuticle.
Powerpoint of integumentary syytem

The document discusses the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands that cover the body. It defines the system and describes its functions of protection, temperature regulation, and vitamin D production. It then examines the structure and features of skin, hair, nails, hooves, horns and glands in different vertebrate groups like mammals, birds, reptiles and fish. Key parts of skin like the epidermis and dermis are also defined, along with sweat and sebaceous glands.
Powerpoint of integumentary system of vertebrates

The document discusses the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands that cover the body. It defines the system and describes its functions of protection, temperature regulation, and vitamin D production. It then examines the structure and features of skin, hair, nails, hooves, horns and glands in different vertebrate groups like mammals, birds, reptiles and fish. Key parts of skin like the epidermis and dermis are also defined, along with sweat and sebaceous glands.
"ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE SKIN".pdf

anatomy and physiology of the skin, layer of the skin, function of the skin, physiology of the skin, nursing assessment, physical assessment
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM BY EVA KIPTOO.pptx

This document provides an overview of the integumentary system, also known as the skin. It discusses the main layers of the skin - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis - and describes the cells and tissues found in each layer. The epidermis is the outermost layer and contains keratinocytes, melanocytes and other cells. Its five sublayers provide protection and regulate hydration. The dermis below contains collagen, blood vessels and glands. The deepest layer, the hypodermis, comprises fat tissue that insulates the body. Important appendages like hair and nails are also introduced.
Recommended
Group 2 activity6

The document describes an anatomy exercise on the skeletal system where students identify bones, structures, and divisions of the skeletal system. It discusses the skull, long bones, vertebral column, thoracic cage, and organization of the axial and appendicular skeleton. Students label diagrams, describe parts of bones, and discuss functions of the skeletal system.
3. Integumentary system (Skin).pptx

The skin is the largest organ of the body and has three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and provides a protective barrier. It has five layers including the stratum corneum. The dermis contains collagen, elastic fibers, blood vessels, nerves and skin appendages. The hypodermis is a subcutaneous layer containing fat and lobules. Skin has several functions like protection, sensation, temperature regulation and immunity. It also contains appendages like hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands.
Lesson-2-Integumentary-System.pptx

The document describes the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands. It discusses the layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis), associated glands like sweat and sebaceous glands, the structure and layers of hair, and the parts and function of nails. The integumentary system acts as a protective barrier for the body, regulates temperature, and has sensory, excretory and synthetic functions.
Integumentary system

The document discusses the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, and nails. It describes the layers of the skin - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis - and their functions in protecting the body from abrasion, bacteria, dehydration, and UV radiation. Hair grows out of the skin across most of the body in different types. Nails are also made of keratin and are alive at their roots under the skin, with a plate and cuticle.
Powerpoint of integumentary syytem

The document discusses the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands that cover the body. It defines the system and describes its functions of protection, temperature regulation, and vitamin D production. It then examines the structure and features of skin, hair, nails, hooves, horns and glands in different vertebrate groups like mammals, birds, reptiles and fish. Key parts of skin like the epidermis and dermis are also defined, along with sweat and sebaceous glands.
Powerpoint of integumentary system of vertebrates

The document discusses the integumentary system, which includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands that cover the body. It defines the system and describes its functions of protection, temperature regulation, and vitamin D production. It then examines the structure and features of skin, hair, nails, hooves, horns and glands in different vertebrate groups like mammals, birds, reptiles and fish. Key parts of skin like the epidermis and dermis are also defined, along with sweat and sebaceous glands.
"ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE SKIN".pdf

anatomy and physiology of the skin, layer of the skin, function of the skin, physiology of the skin, nursing assessment, physical assessment
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM BY EVA KIPTOO.pptx

This document provides an overview of the integumentary system, also known as the skin. It discusses the main layers of the skin - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis - and describes the cells and tissues found in each layer. The epidermis is the outermost layer and contains keratinocytes, melanocytes and other cells. Its five sublayers provide protection and regulate hydration. The dermis below contains collagen, blood vessels and glands. The deepest layer, the hypodermis, comprises fat tissue that insulates the body. Important appendages like hair and nails are also introduced.
EVA KIPTOO DENTAL PRESENTATION - Copy.pptx

The document provides information about the integumentary system (skin). It discusses the key components of the skin including the three layers (epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis), the main cell types found in each layer (keratinocytes, melanocytes, etc.), and the functions of the skin layers and cells. It also describes the appendages of the skin like hair, nails, and glands. In summary, the document outlines the structure and functions of the integumentary system with a focus on its layers, cells, and appendages.
anatomy -skin

The skin is the largest organ of the body and acts as a protective barrier. It has several layers, including the epidermis and dermis, and contains structures like hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands. The skin regulates body temperature, protects against pathogens, and plays a role in sensation and nonverbal communication. Its appendages include hair, nails, and glands that lubricate and protect the skin surface.
Anatomy of skin

The skin has three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and contains keratinocytes that produce keratin, and melanocytes that produce melanin pigment. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains collagen, elastic fibers, and sensory receptors. The deepest layer, the subcutaneous tissue, contains fat and connective tissue. Skin has appendages like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails. The skin acts as a barrier and regulates body temperature, and contains sensory receptors for touch, pressure, and temperature.
[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf![[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
The integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures. The skin has two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and provides protection, while the dermis contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and glands. The skin regulates body temperature, protects the body, and produces vitamin D. Accessory structures include hair, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands that also have protective and regulatory functions. Injuries like burns damage the skin layers and heal in stages from the surface to deeper tissues.
Integumentary system

The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, and nails and acts as a protective barrier for the body. It has several important functions, including protecting against pathogens and injury, regulating body temperature, removing waste, and producing vitamin D. The skin is the body's largest organ and is composed of two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is a thin outer layer made up of dead skin cells that sheds regularly, while the dermis contains blood vessels, glands, and hair follicles. Together, these layers provide protection, temperature regulation, sensation, and other critical functions for the body.
Dermatology 5th year, 1st lecture (Dr. Kazhan)

The document provides information about human skin anatomy, organization, histology, function and diagnosis. It discusses the key components and layers of the skin including the epidermis, dermis and skin appendages. The epidermis is composed of the basal, spinous, granular and stratum corneum layers. The dermis contains collagen, elastic and ground substance fibers. The skin has important protective, sensory and temperature regulating functions. Common skin lesions and their characteristics are also defined.
Integumentary system

The document summarizes the key components and functions of the integumentary system. It describes that the integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures, including hair, nails, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. It provides details on the structure and layers of the skin, functions such as temperature regulation and protection, and the roles of hair, nails, and glands.
Structure of skin.ppt

The skin has two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and has several sublayers including the stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum and stratum germinativum. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains connective tissue, blood vessels, hair follicles and glands. Skin appendages include hair, sebaceous glands which secrete sebum, sweat glands which help regulate temperature, and nails. The skin provides protection, sensation, regulation of temperature and water, and synthesis of vitamin D.
Integumentary System.pptx

This presentation aims to discuss the parts of the integumentary system i.e. the skin, hair, and nails and describe the functions of each part. T
Basic Skin Structure

Basic Skin Structure
Prepared By
RASHIDUL HASAN ROBEL
B. PHARM (RU), M. PHARM (RU)
REG. NO. A4968
PGD-HRM (BIM)
EMBA (ULAB)
Skin anatomy and physiology

basics of skin, review of skin, Integumentary system, the structure of the skin, Functions of skin, skin appendages, Hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, Nails, dermis, epidermis,
subcutaneous tissue. anatomy and physiology
Integumentary System SMP B. Pharm Sem I.ppt

The integumentary system is the physical system that forms the barrier between the external environment and the internal systems of the body. In humans, this system consists of skin, hair, nails, and related glands.
Altogether, the integumentary system forms the largest organ in the body. The main function of this system is to protect bones, organs, and other internal structures from harm. In addition, the integumentary system performs important immune functions, cell fluid maintenance, synthesis of Vitamin D, body temperature regulation, and detection of stimuli.
F. Y. B. Pharm Sem I: Unit II: 1. Integumentary System

The document provides an overview of the integumentary system including the skin, hair, and nails. It discusses the three layers of the skin - epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis - and describes their structures and functions. Hair and nails are also summarized, outlining their roles in protection, sensation, and other integumentary functions. The integumentary system works together with other body systems to regulate temperature, protect the body, and detect sensations.
Epithelium 

The document discusses the structure and functions of the skin and integumentary system. It describes the skin as the largest organ of the body, which is made up of two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is the superficial layer made of stratified squamous epithelium, while the dermis is the deep layer made of dense connective tissue. The skin plays important roles in protecting the body, regulating temperature, and producing vitamins and pigments. It also contains appendages like hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands that further aid its functions.
Skin 

The document discusses skin anatomy and skin grafts. It describes the three layers of skin - epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. Skin grafts are either full thickness or split thickness and involve completely detaching skin from a donor site and placing it on a host bed. Proper wound preparation is essential for graft survival, ensuring good blood supply and removal of debris. Full thickness grafts resemble natural skin more but have poorer survival rates than split thickness grafts.
integumentrysystem-190205115329 (1).pdf

The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and glands. The skin is the largest organ and has three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis contains keratinocytes and has multiple layers. Hair grows from hair follicles and provides protection. Nails cover the ends of fingers and toes. Glands in the skin secrete sweat, oil, and other substances. This system acts as a protective barrier for the body.
Integumentry system

This presentation will give you a clear idea about the Integumentary system that what is it and what is it for and how it is very much essential for the body. Skin is the most important thing to be understood in this Integumentary system.
skin and appendages Histology

The skin has two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer and provides a protective barrier. It has five layers including the stratum corneum. The dermis lies beneath and contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. It consists of two layers - the papillary and reticular layers. Skin appendages like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands develop at the epidermal-dermal junction. Hair has a root that goes deep in the dermis and a shaft that projects out. Sweat glands secrete sweat which helps cool the body and remove waste.
Integumentary system prep.pptx

The integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures. The skin is made up of three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer and provides protection from pathogens and environmental damage. Below the epidermis is the dermis, which contains blood vessels, hair follicles and glands. The deepest layer is the hypodermis, comprising connective tissue and fat. In addition to protection, the skin regulates temperature and synthesizes vitamin D. Accessory structures include hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands. Skin disorders include wounds, burns and skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and melanoma.
176-Anatomy-Integumentary-System.ppt

The document summarizes the key components and functions of the integumentary system. It describes that the integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures like hair, nails, and glands. It then provides details on the layers of the skin, including the epidermis and dermis. It explains the functions of skin in regulating temperature, providing sensation and protection. It also summarizes the structures and roles of hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands in the integumentary system.
MICROBIAL INTERACTION PPT/ MICROBIAL INTERACTION AND THEIR TYPES // PLANT MIC...

MICROBIAL INTERACTION PPT/ MICROBIAL INTERACTION AND THEIR TYPES // PLANT MIC...ABHISHEK SONI NIMT INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL AND PARAMEDCIAL SCIENCES , GOVT PG COLLEGE NOIDA
Microbial interaction
Microorganisms interacts with each other and can be physically associated with another organisms in a variety of ways.
One organism can be located on the surface of another organism as an ectobiont or located within another organism as endobiont.
Microbial interaction may be positive such as mutualism, proto-cooperation, commensalism or may be negative such as parasitism, predation or competition
Types of microbial interaction
Positive interaction: mutualism, proto-cooperation, commensalism
Negative interaction: Ammensalism (antagonism), parasitism, predation, competition
I. Mutualism:
It is defined as the relationship in which each organism in interaction gets benefits from association. It is an obligatory relationship in which mutualist and host are metabolically dependent on each other.
Mutualistic relationship is very specific where one member of association cannot be replaced by another species.
Mutualism require close physical contact between interacting organisms.
Relationship of mutualism allows organisms to exist in habitat that could not occupied by either species alone.
Mutualistic relationship between organisms allows them to act as a single organism.
Examples of mutualism:
i. Lichens:
Lichens are excellent example of mutualism.
They are the association of specific fungi and certain genus of algae. In lichen, fungal partner is called mycobiont and algal partner is called
II. Syntrophism:
It is an association in which the growth of one organism either depends on or improved by the substrate provided by another organism.
In syntrophism both organism in association gets benefits.
Compound A
Utilized by population 1
Compound B
Utilized by population 2
Compound C
utilized by both Population 1+2
Products
In this theoretical example of syntrophism, population 1 is able to utilize and metabolize compound A, forming compound B but cannot metabolize beyond compound B without co-operation of population 2. Population 2is unable to utilize compound A but it can metabolize compound B forming compound C. Then both population 1 and 2 are able to carry out metabolic reaction which leads to formation of end product that neither population could produce alone.
Examples of syntrophism:
i. Methanogenic ecosystem in sludge digester
Methane produced by methanogenic bacteria depends upon interspecies hydrogen transfer by other fermentative bacteria.
Anaerobic fermentative bacteria generate CO2 and H2 utilizing carbohydrates which is then utilized by methanogenic bacteria (Methanobacter) to produce methane.
ii. Lactobacillus arobinosus and Enterococcus faecalis:
In the minimal media, Lactobacillus arobinosus and Enterococcus faecalis are able to grow together but not alone.
The synergistic relationship between E. faecalis and L. arobinosus occurs in which E. faecalis require folic acid
Direct Seeded Rice - Climate Smart Agriculture

Direct Seeded Rice - Climate Smart AgricultureInternational Food Policy Research Institute- South Asia Office
PPT on Direct Seeded Rice presented at the three-day 'Training and Validation Workshop on Modules of Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) Technologies in South Asia' workshop on April 22, 2024.
More Related Content
Similar to Group 2 activity5
EVA KIPTOO DENTAL PRESENTATION - Copy.pptx

The document provides information about the integumentary system (skin). It discusses the key components of the skin including the three layers (epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis), the main cell types found in each layer (keratinocytes, melanocytes, etc.), and the functions of the skin layers and cells. It also describes the appendages of the skin like hair, nails, and glands. In summary, the document outlines the structure and functions of the integumentary system with a focus on its layers, cells, and appendages.
anatomy -skin

The skin is the largest organ of the body and acts as a protective barrier. It has several layers, including the epidermis and dermis, and contains structures like hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands. The skin regulates body temperature, protects against pathogens, and plays a role in sensation and nonverbal communication. Its appendages include hair, nails, and glands that lubricate and protect the skin surface.
Anatomy of skin

The skin has three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and contains keratinocytes that produce keratin, and melanocytes that produce melanin pigment. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains collagen, elastic fibers, and sensory receptors. The deepest layer, the subcutaneous tissue, contains fat and connective tissue. Skin has appendages like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and nails. The skin acts as a barrier and regulates body temperature, and contains sensory receptors for touch, pressure, and temperature.
[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf![[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
The integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures. The skin has two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and provides protection, while the dermis contains connective tissue, hair follicles, and glands. The skin regulates body temperature, protects the body, and produces vitamin D. Accessory structures include hair, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands that also have protective and regulatory functions. Injuries like burns damage the skin layers and heal in stages from the surface to deeper tissues.
Integumentary system

The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, and nails and acts as a protective barrier for the body. It has several important functions, including protecting against pathogens and injury, regulating body temperature, removing waste, and producing vitamin D. The skin is the body's largest organ and is composed of two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is a thin outer layer made up of dead skin cells that sheds regularly, while the dermis contains blood vessels, glands, and hair follicles. Together, these layers provide protection, temperature regulation, sensation, and other critical functions for the body.
Dermatology 5th year, 1st lecture (Dr. Kazhan)

The document provides information about human skin anatomy, organization, histology, function and diagnosis. It discusses the key components and layers of the skin including the epidermis, dermis and skin appendages. The epidermis is composed of the basal, spinous, granular and stratum corneum layers. The dermis contains collagen, elastic and ground substance fibers. The skin has important protective, sensory and temperature regulating functions. Common skin lesions and their characteristics are also defined.
Integumentary system

The document summarizes the key components and functions of the integumentary system. It describes that the integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures, including hair, nails, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. It provides details on the structure and layers of the skin, functions such as temperature regulation and protection, and the roles of hair, nails, and glands.
Structure of skin.ppt

The skin has two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous epithelium and has several sublayers including the stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum and stratum germinativum. The dermis lies below the epidermis and contains connective tissue, blood vessels, hair follicles and glands. Skin appendages include hair, sebaceous glands which secrete sebum, sweat glands which help regulate temperature, and nails. The skin provides protection, sensation, regulation of temperature and water, and synthesis of vitamin D.
Integumentary System.pptx

This presentation aims to discuss the parts of the integumentary system i.e. the skin, hair, and nails and describe the functions of each part. T
Basic Skin Structure

Basic Skin Structure
Prepared By
RASHIDUL HASAN ROBEL
B. PHARM (RU), M. PHARM (RU)
REG. NO. A4968
PGD-HRM (BIM)
EMBA (ULAB)
Skin anatomy and physiology

basics of skin, review of skin, Integumentary system, the structure of the skin, Functions of skin, skin appendages, Hair, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, Nails, dermis, epidermis,
subcutaneous tissue. anatomy and physiology
Integumentary System SMP B. Pharm Sem I.ppt

The integumentary system is the physical system that forms the barrier between the external environment and the internal systems of the body. In humans, this system consists of skin, hair, nails, and related glands.
Altogether, the integumentary system forms the largest organ in the body. The main function of this system is to protect bones, organs, and other internal structures from harm. In addition, the integumentary system performs important immune functions, cell fluid maintenance, synthesis of Vitamin D, body temperature regulation, and detection of stimuli.
F. Y. B. Pharm Sem I: Unit II: 1. Integumentary System

The document provides an overview of the integumentary system including the skin, hair, and nails. It discusses the three layers of the skin - epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis - and describes their structures and functions. Hair and nails are also summarized, outlining their roles in protection, sensation, and other integumentary functions. The integumentary system works together with other body systems to regulate temperature, protect the body, and detect sensations.
Epithelium 

The document discusses the structure and functions of the skin and integumentary system. It describes the skin as the largest organ of the body, which is made up of two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is the superficial layer made of stratified squamous epithelium, while the dermis is the deep layer made of dense connective tissue. The skin plays important roles in protecting the body, regulating temperature, and producing vitamins and pigments. It also contains appendages like hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands that further aid its functions.
Skin 

The document discusses skin anatomy and skin grafts. It describes the three layers of skin - epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. Skin grafts are either full thickness or split thickness and involve completely detaching skin from a donor site and placing it on a host bed. Proper wound preparation is essential for graft survival, ensuring good blood supply and removal of debris. Full thickness grafts resemble natural skin more but have poorer survival rates than split thickness grafts.
integumentrysystem-190205115329 (1).pdf

The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, nails, and glands. The skin is the largest organ and has three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis contains keratinocytes and has multiple layers. Hair grows from hair follicles and provides protection. Nails cover the ends of fingers and toes. Glands in the skin secrete sweat, oil, and other substances. This system acts as a protective barrier for the body.
Integumentry system

This presentation will give you a clear idea about the Integumentary system that what is it and what is it for and how it is very much essential for the body. Skin is the most important thing to be understood in this Integumentary system.
skin and appendages Histology

The skin has two main layers - the epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer and provides a protective barrier. It has five layers including the stratum corneum. The dermis lies beneath and contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. It consists of two layers - the papillary and reticular layers. Skin appendages like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands develop at the epidermal-dermal junction. Hair has a root that goes deep in the dermis and a shaft that projects out. Sweat glands secrete sweat which helps cool the body and remove waste.
Integumentary system prep.pptx

The integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures. The skin is made up of three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is the outermost layer and provides protection from pathogens and environmental damage. Below the epidermis is the dermis, which contains blood vessels, hair follicles and glands. The deepest layer is the hypodermis, comprising connective tissue and fat. In addition to protection, the skin regulates temperature and synthesizes vitamin D. Accessory structures include hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands. Skin disorders include wounds, burns and skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and melanoma.
176-Anatomy-Integumentary-System.ppt

The document summarizes the key components and functions of the integumentary system. It describes that the integumentary system consists of the skin and its accessory structures like hair, nails, and glands. It then provides details on the layers of the skin, including the epidermis and dermis. It explains the functions of skin in regulating temperature, providing sensation and protection. It also summarizes the structures and roles of hair, nails, sweat and sebaceous glands in the integumentary system.
Similar to Group 2 activity5 (20)
[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf![[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
[TRANS] HES 029 - Lecture 3 (The Integumentary System).pdf
F. Y. B. Pharm Sem I: Unit II: 1. Integumentary System

F. Y. B. Pharm Sem I: Unit II: 1. Integumentary System
Recently uploaded
MICROBIAL INTERACTION PPT/ MICROBIAL INTERACTION AND THEIR TYPES // PLANT MIC...

MICROBIAL INTERACTION PPT/ MICROBIAL INTERACTION AND THEIR TYPES // PLANT MIC...ABHISHEK SONI NIMT INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL AND PARAMEDCIAL SCIENCES , GOVT PG COLLEGE NOIDA
Microbial interaction
Microorganisms interacts with each other and can be physically associated with another organisms in a variety of ways.
One organism can be located on the surface of another organism as an ectobiont or located within another organism as endobiont.
Microbial interaction may be positive such as mutualism, proto-cooperation, commensalism or may be negative such as parasitism, predation or competition
Types of microbial interaction
Positive interaction: mutualism, proto-cooperation, commensalism
Negative interaction: Ammensalism (antagonism), parasitism, predation, competition
I. Mutualism:
It is defined as the relationship in which each organism in interaction gets benefits from association. It is an obligatory relationship in which mutualist and host are metabolically dependent on each other.
Mutualistic relationship is very specific where one member of association cannot be replaced by another species.
Mutualism require close physical contact between interacting organisms.
Relationship of mutualism allows organisms to exist in habitat that could not occupied by either species alone.
Mutualistic relationship between organisms allows them to act as a single organism.
Examples of mutualism:
i. Lichens:
Lichens are excellent example of mutualism.
They are the association of specific fungi and certain genus of algae. In lichen, fungal partner is called mycobiont and algal partner is called
II. Syntrophism:
It is an association in which the growth of one organism either depends on or improved by the substrate provided by another organism.
In syntrophism both organism in association gets benefits.
Compound A
Utilized by population 1
Compound B
Utilized by population 2
Compound C
utilized by both Population 1+2
Products
In this theoretical example of syntrophism, population 1 is able to utilize and metabolize compound A, forming compound B but cannot metabolize beyond compound B without co-operation of population 2. Population 2is unable to utilize compound A but it can metabolize compound B forming compound C. Then both population 1 and 2 are able to carry out metabolic reaction which leads to formation of end product that neither population could produce alone.
Examples of syntrophism:
i. Methanogenic ecosystem in sludge digester
Methane produced by methanogenic bacteria depends upon interspecies hydrogen transfer by other fermentative bacteria.
Anaerobic fermentative bacteria generate CO2 and H2 utilizing carbohydrates which is then utilized by methanogenic bacteria (Methanobacter) to produce methane.
ii. Lactobacillus arobinosus and Enterococcus faecalis:
In the minimal media, Lactobacillus arobinosus and Enterococcus faecalis are able to grow together but not alone.
The synergistic relationship between E. faecalis and L. arobinosus occurs in which E. faecalis require folic acid
Direct Seeded Rice - Climate Smart Agriculture

Direct Seeded Rice - Climate Smart AgricultureInternational Food Policy Research Institute- South Asia Office
PPT on Direct Seeded Rice presented at the three-day 'Training and Validation Workshop on Modules of Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) Technologies in South Asia' workshop on April 22, 2024.
Pests of Storage_Identification_Dr.UPR.pdf

InIndia-post-harvestlosses-unscientificstorage,insects,rodents,micro-organismsetc.,accountforabout10percentoftotalfoodgrains
Graininfestation
Directdamage
Indirectly
•theexuviae,skin,deadinsects
•theirexcretawhichmakefoodunfitforhumanconsumption
About600speciesofinsectshavebeenassociatedwithstoredgrainproducts
100speciesofinsectpestsofstoredproductscauseeconomiclosses
EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...

Context. With a mass exceeding several 104 M⊙ and a rich and dense population of massive stars, supermassive young star clusters
represent the most massive star-forming environment that is dominated by the feedback from massive stars and gravitational interactions
among stars.
Aims. In this paper we present the Extended Westerlund 1 and 2 Open Clusters Survey (EWOCS) project, which aims to investigate
the influence of the starburst environment on the formation of stars and planets, and on the evolution of both low and high mass stars.
The primary targets of this project are Westerlund 1 and 2, the closest supermassive star clusters to the Sun.
Methods. The project is based primarily on recent observations conducted with the Chandra and JWST observatories. Specifically,
the Chandra survey of Westerlund 1 consists of 36 new ACIS-I observations, nearly co-pointed, for a total exposure time of 1 Msec.
Additionally, we included 8 archival Chandra/ACIS-S observations. This paper presents the resulting catalog of X-ray sources within
and around Westerlund 1. Sources were detected by combining various existing methods, and photon extraction and source validation
were carried out using the ACIS-Extract software.
Results. The EWOCS X-ray catalog comprises 5963 validated sources out of the 9420 initially provided to ACIS-Extract, reaching a
photon flux threshold of approximately 2 × 10−8 photons cm−2
s
−1
. The X-ray sources exhibit a highly concentrated spatial distribution,
with 1075 sources located within the central 1 arcmin. We have successfully detected X-ray emissions from 126 out of the 166 known
massive stars of the cluster, and we have collected over 71 000 photons from the magnetar CXO J164710.20-455217.
Authoring a personal GPT for your research and practice: How we created the Q...

Thematic analysis in qualitative research is a time-consuming and systematic task, typically done using teams. Team members must ground their activities on common understandings of the major concepts underlying the thematic analysis, and define criteria for its development. However, conceptual misunderstandings, equivocations, and lack of adherence to criteria are challenges to the quality and speed of this process. Given the distributed and uncertain nature of this process, we wondered if the tasks in thematic analysis could be supported by readily available artificial intelligence chatbots. Our early efforts point to potential benefits: not just saving time in the coding process but better adherence to criteria and grounding, by increasing triangulation between humans and artificial intelligence. This tutorial will provide a description and demonstration of the process we followed, as two academic researchers, to develop a custom ChatGPT to assist with qualitative coding in the thematic data analysis process of immersive learning accounts in a survey of the academic literature: QUAL-E Immersive Learning Thematic Analysis Helper. In the hands-on time, participants will try out QUAL-E and develop their ideas for their own qualitative coding ChatGPT. Participants that have the paid ChatGPT Plus subscription can create a draft of their assistants. The organizers will provide course materials and slide deck that participants will be able to utilize to continue development of their custom GPT. The paid subscription to ChatGPT Plus is not required to participate in this workshop, just for trying out personal GPTs during it.
Sexuality - Issues, Attitude and Behaviour - Applied Social Psychology - Psyc...

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
HUMAN EYE By-R.M Class 10 phy best digital notes.pdf

Class 10 human eye notes physics
Handwritten best quality
Farming systems analysis: what have we learnt?.pptx

Presentation given at the official farewell of Prof Ken Gillet at Wageningen on 13 June 2024
11.1 Role of physical biological in deterioration of grains.pdf

Storagedeteriorationisanyformoflossinquantityandqualityofbio-materials.
Themajorcausesofdeteriorationinstorage
•Physical
•Biological
•Mechanical
•Chemical
Storageonlypreservesquality.Itneverimprovesquality.
Itisadvisabletostartstoragewithqualityfoodproduct.Productwithinitialpoorqualityquicklydepreciates
CLASS 12th CHEMISTRY SOLID STATE ppt (Animated)

Description:
Dive into the fascinating realm of solid-state physics with our meticulously crafted online PowerPoint presentation. This immersive educational resource offers a comprehensive exploration of the fundamental concepts, theories, and applications within the realm of solid-state physics.
From crystalline structures to semiconductor devices, this presentation delves into the intricate principles governing the behavior of solids, providing clear explanations and illustrative examples to enhance understanding. Whether you're a student delving into the subject for the first time or a seasoned researcher seeking to deepen your knowledge, our presentation offers valuable insights and in-depth analyses to cater to various levels of expertise.
Key topics covered include:
Crystal Structures: Unravel the mysteries of crystalline arrangements and their significance in determining material properties.
Band Theory: Explore the electronic band structure of solids and understand how it influences their conductive properties.
Semiconductor Physics: Delve into the behavior of semiconductors, including doping, carrier transport, and device applications.
Magnetic Properties: Investigate the magnetic behavior of solids, including ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism, and ferrimagnetism.
Optical Properties: Examine the interaction of light with solids, including absorption, reflection, and transmission phenomena.
With visually engaging slides, informative content, and interactive elements, our online PowerPoint presentation serves as a valuable resource for students, educators, and enthusiasts alike, facilitating a deeper understanding of the captivating world of solid-state physics. Explore the intricacies of solid-state materials and unlock the secrets behind their remarkable properties with our comprehensive presentation.
The debris of the ‘last major merger’ is dynamically young

The Milky Way’s (MW) inner stellar halo contains an [Fe/H]-rich component with highly eccentric orbits, often referred to as the
‘last major merger.’ Hypotheses for the origin of this component include Gaia-Sausage/Enceladus (GSE), where the progenitor
collided with the MW proto-disc 8–11 Gyr ago, and the Virgo Radial Merger (VRM), where the progenitor collided with the
MW disc within the last 3 Gyr. These two scenarios make different predictions about observable structure in local phase space,
because the morphology of debris depends on how long it has had to phase mix. The recently identified phase-space folds in Gaia
DR3 have positive caustic velocities, making them fundamentally different than the phase-mixed chevrons found in simulations
at late times. Roughly 20 per cent of the stars in the prograde local stellar halo are associated with the observed caustics. Based
on a simple phase-mixing model, the observed number of caustics are consistent with a merger that occurred 1–2 Gyr ago.
We also compare the observed phase-space distribution to FIRE-2 Latte simulations of GSE-like mergers, using a quantitative
measurement of phase mixing (2D causticality). The observed local phase-space distribution best matches the simulated data
1–2 Gyr after collision, and certainly not later than 3 Gyr. This is further evidence that the progenitor of the ‘last major merger’
did not collide with the MW proto-disc at early times, as is thought for the GSE, but instead collided with the MW disc within
the last few Gyr, consistent with the body of work surrounding the VRM.
fermented food science of sauerkraut.pptx

This ppt contains the production of a fermented food name - sauerkraut
Alternate Wetting and Drying - Climate Smart Agriculture

Alternate Wetting and Drying - Climate Smart AgricultureInternational Food Policy Research Institute- South Asia Office
PPT on Alternate Wetting and Drying presented at the three-day 'Training and Validation Workshop on Modules of Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) Technologies in South Asia' workshop on April 22, 2024. Mending Clothing to Support Sustainable Fashion_CIMaR 2024.pdf

Ozturkcan, S., Berndt, A., & Angelakis, A. (2024). Mending clothing to support sustainable fashion. Presented at the 31st Annual Conference by the Consortium for International Marketing Research (CIMaR), 10-13 Jun 2024, University of Gävle, Sweden.
(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...

(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...Scintica Instrumentation
Targeting Hsp90 and its pathogen Orthologs with Tethered Inhibitors as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategy for cancer and infectious diseases with Dr. Timothy Haystead.Anti-Universe And Emergent Gravity and the Dark Universe

Recent theoretical progress indicates that spacetime and gravity emerge together from the entanglement structure of an underlying microscopic theory. These ideas are best understood in Anti-de Sitter space, where they rely on the area law for entanglement entropy. The extension to de Sitter space requires taking into account the entropy and temperature associated with the cosmological horizon. Using insights from string theory, black hole physics and quantum information theory we argue that the positive dark energy leads to a thermal volume law contribution to the entropy that overtakes the area law precisely at the cosmological horizon. Due to the competition between area and volume law entanglement the microscopic de Sitter states do not thermalise at sub-Hubble scales: they exhibit memory effects in the form of an entropy displacement caused by matter. The emergent laws of gravity contain an additional ‘dark’ gravitational force describing the ‘elastic’ response due to the entropy displacement. We derive an estimate of the strength of this extra force in terms of the baryonic mass, Newton’s constant and the Hubble acceleration scale a0 = cH0, and provide evidence for the fact that this additional ‘dark gravity force’ explains the observed phenomena in galaxies and clusters currently attributed to dark matter.
Recently uploaded (20)
MICROBIAL INTERACTION PPT/ MICROBIAL INTERACTION AND THEIR TYPES // PLANT MIC...

MICROBIAL INTERACTION PPT/ MICROBIAL INTERACTION AND THEIR TYPES // PLANT MIC...
EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...

EWOCS-I: The catalog of X-ray sources in Westerlund 1 from the Extended Weste...
Authoring a personal GPT for your research and practice: How we created the Q...

Authoring a personal GPT for your research and practice: How we created the Q...
Sexuality - Issues, Attitude and Behaviour - Applied Social Psychology - Psyc...

Sexuality - Issues, Attitude and Behaviour - Applied Social Psychology - Psyc...
HUMAN EYE By-R.M Class 10 phy best digital notes.pdf

HUMAN EYE By-R.M Class 10 phy best digital notes.pdf
Farming systems analysis: what have we learnt?.pptx

Farming systems analysis: what have we learnt?.pptx
Juaristi, Jon. - El canon espanol. El legado de la cultura española a la civi...

Juaristi, Jon. - El canon espanol. El legado de la cultura española a la civi...
11.1 Role of physical biological in deterioration of grains.pdf

11.1 Role of physical biological in deterioration of grains.pdf
The debris of the ‘last major merger’ is dynamically young

The debris of the ‘last major merger’ is dynamically young
Alternate Wetting and Drying - Climate Smart Agriculture

Alternate Wetting and Drying - Climate Smart Agriculture
Mending Clothing to Support Sustainable Fashion_CIMaR 2024.pdf

Mending Clothing to Support Sustainable Fashion_CIMaR 2024.pdf
Microbiology of Central Nervous System INFECTIONS.pdf

Microbiology of Central Nervous System INFECTIONS.pdf
(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...

(June 12, 2024) Webinar: Development of PET theranostics targeting the molecu...
Anti-Universe And Emergent Gravity and the Dark Universe

Anti-Universe And Emergent Gravity and the Dark Universe
Group 2 activity5
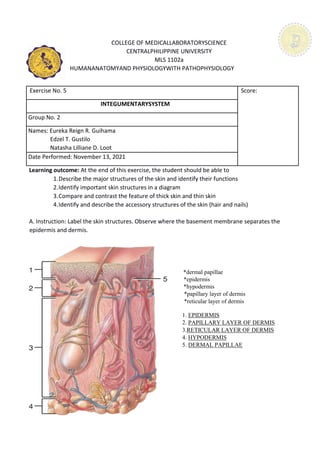
- 1. COLLEGE OF MEDICALLABORATORYSCIENCE CENTRALPHILIPPINE UNIVERSITY MLS 1102a HUMANANATOMYAND PHYSIOLOGYWITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Exercise No. 5 Score: INTEGUMENTARYSYSTEM Group No. 2 Names: Eureka Reign R. Guihama Edzel T. Gustilo Natasha Lilliane D. Loot Date Performed: November 13, 2021 Learning outcome: At the end of this exercise, the student should be able to 1.Describe the major structures of the skin and identify their functions 2.Identify important skin structures in a diagram 3.Compare and contrast the feature of thick skin and thin skin 4.Identify and describe the accessory structures of the skin (hair and nails) A. Instruction: Label the skin structures. Observe where the basement membrane separates the epidermis and dermis. *dermal papillae *epidermis *hypodermis *papillary layer of dermis *reticular layer of dermis 1. EPIDERMIS 2. PAPILLARY LAYER OF DERMIS 3.RETICULAR LAYER OF DERMIS 4. HYPODERMIS 5. DERMAL PAPILLAE
- 2. *apocrine *arrector pili *eccrine sweat gland *hair bulb *hair follicle *hair root *hair shaft *papilla of hair *sebaceous gland 1. HAIR SHAFT 2. HAIR ROOT 3. SEBACEOUS GLAND 4. ARRECTOR PILI 5. HAIR FOLLICLE 6. HAIR BULB 7. ECCRINE SWEAT GLAND 8. PAPILLA OF HAIR 9. APOCRINE
- 3. B. Describe the structure and function of the following parts of the skin: 1. Dermis The dermis is a fibrous structure composed of collagen, elastic tissue, and other extracellular components that includes vasculature, nerve endings, hair follicles, and glands. Also, dermis is a connective tissue layer sandwiched between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. Its role is to support and protect the skin and deeper layers, assist in thermoregulation, and aid in sensation. 2. Epidermis An epidermis is composed mainly of keratinocytes and it is the outermost layer of the skin. Its thickness varies depending on which part of the body it is located. Example on the eyelids it is thinner and is thickest on the palms and soles. Its function is to provide a waterproof barrier and create our skin tone. Also, it protects our body by keeping things that might be harmful to us and keeping the things our body needs to function properly. 3. Hypodermis The hypodermis is the subcutaneous layer lying below the dermis and it consists largely of fat. It contains the cells known as fibroblasts, adipose cells, connective tissue and larger nerves and blood cells. It provides the main structural support for the skin, as well as insulating the body from cold and aiding shock absorption. 4. Hair Root The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin. It is surrounded by the hair follicle which is also connected to a sebaceous gland. Each hair follicle is attached to a tiny muscle that can make the hair stand up. Its main function is the uptake of water and nutrients from the rhizosphere. 5. Hair Shaft It is formed of three layers: The medulla – the deepest layer of the hair shaft, only seen in large and thick hairs. The cortex – the middle layer of the hair shaft which provides the strength, color and texture of a hair fiber. The cuticle – the outer layer of the hair shaft is thin and colorless. The primary purpose for this is to trap a layer of air to add insulation. 6. Hair Follicle It is a stocking-like structure that contains cells and connective tissue and surrounds the root of a hair. It exists within the dermis and the epidermis, the two top layers of the skin. The hair follicle serves as an anchor for the hair shaft. 7. Sweat Gland Sweat glands are coiled tubular structures vital for regulating human body temperature. It consists of a secretory unit consisting of a base rolled into a glomerulum, and a duct that carries the sweat away. 8. Sebaceous Gland Sebaceous glands are usually attached to hair follicles and release a fatty substance, sebum, into the follicular duct and then to the surface of the skin.
- 4. 9.Arrector Pili This is a tiny muscle that attaches to the base of a hair follicle at one end and to dermal tissue on the other end. In order to generate heat when the body is cold, the arrector pili muscles contract all at once, causing the hair to "stand up straight" on the skin. It lies flat and prevents heat from being trapped by the layer of still air between the hairs. C. Discussion: 1. How does thin skin differ from thick skin? Explain briefly. In terms of people, one obvious difference between a thin and a thick skinned person is that people with thicker skin contains more adipose tissue which means there is more body fat making a person look bigger and its skin thicker that is why fat people could tolerate an environment with a lower temperature compared to those people who are thin-skinned. Talking about the parts of the body, the thinnest skin covers the eyelids and most of the body, except on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands where thick skin is present. Thick skin has no hair follicles or sebaceous glands, whereas thin skin does. Thick skin actually has a thinner dermis layer than thin skin, but is still thicker due to the stratum lucidum layer present in the epidermis which protects the area most common to damages. Stratum lucidum can be found only in thick skin not in thin skin.
- 5. D. Identify the nail structures on the diagram (a) *eponychium *free edge *lunula *nail body (b) *eponychium *free edge *hyponychium *lunula *nail root *nail body *nail matrix 1. FREE EDGE 2. NAIL BODY 3. LUNULA 4. EPONYCHIUM 5. NAIL MATRIX 6. NAIL ROOT 7. EPONYCHIUM 8. LUNULA 9. NAIL BODY 10. FREE EDGE 11. HYPONYCHIUM
- 6. E. Describe the structure of the following parts of the nail(s): 1. Free edge The end of the nail plate that is shaped during Manicure & Pedicure. It is made up of tightly packed, hard, keratinized epidermal cells. The nail plate leaves the end of the finger and forms a projection that is called the free edge. This is attached to the nail bed and appears as white. The function of the free edge is to protect the fingertip and the hyponychium. 2. Nail body It is also made up of tightly packed, hard, keratinized epidermal cells. It is found between the free edge and the lunula, just above the nail bed. It forms a back-support for picking up small objects with the fingers and protects the layer beneath it from germs to avoid infections. 3. Nail groove These are the grooves on the skin at the sides of the free edge, and the nail follows them as a guideline when it grows. 4. Lunula The white, half-moon shaped point where the matrix and nail bed meet. 5. Eponychium (Cuticle) The overlapping skin surrounding the nail. It is situated between the skin of the finger and the nail plate. It fuses these structures together and provides a waterproof barrier. Its job is to protect the matrix from being invaded by bacteria and physical damage. 6. Nail root This is also known as the germinal matrix. Its edge appears as a white crescent, known as the lunula. The root portion of this nail lies below the skin, underneath the nail, and extends several millimeters into the finger. It produces most of the volume of the nail and the nail bed. 7. Nail bed Referred also as the sterile matrix. It extends from the edge of the nail root, or lunula, to the hyponychium. The nail bed contains blood vessels, nerves, and melanocytes that produce melanin. As the root grows the nail, the nail streams down along the nail bed and adds material to the underside of the nail to make it thicker. When the nail grows properly, the nail bed is smooth, but if the nail doesn't grow correctly, the nail may split or develop ridges that aren't cosmetically attractive. 8. Hyponychium The hyponychium is the area between the free edge of the nail plate and the skin of the fingertip. It also provides a waterproof barrier.
- 7. 9. Nail fold The lateral nail fold overlaps the nail on the sides, helping to anchor the nail body and to protect the nail plate edges. The nail fold that meets the proximal end of the nail body forms the nail cuticle, also called the eponychium.