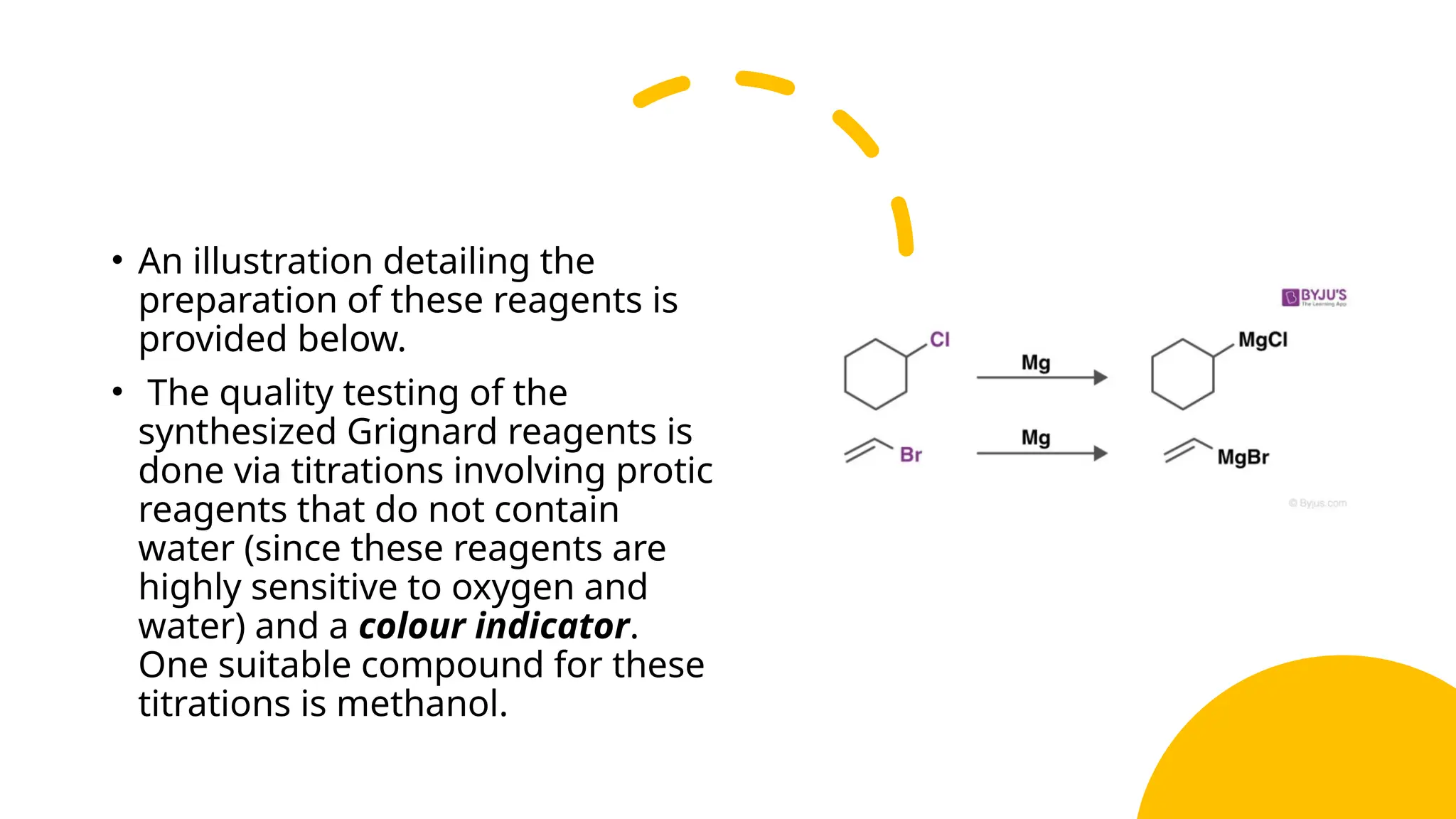
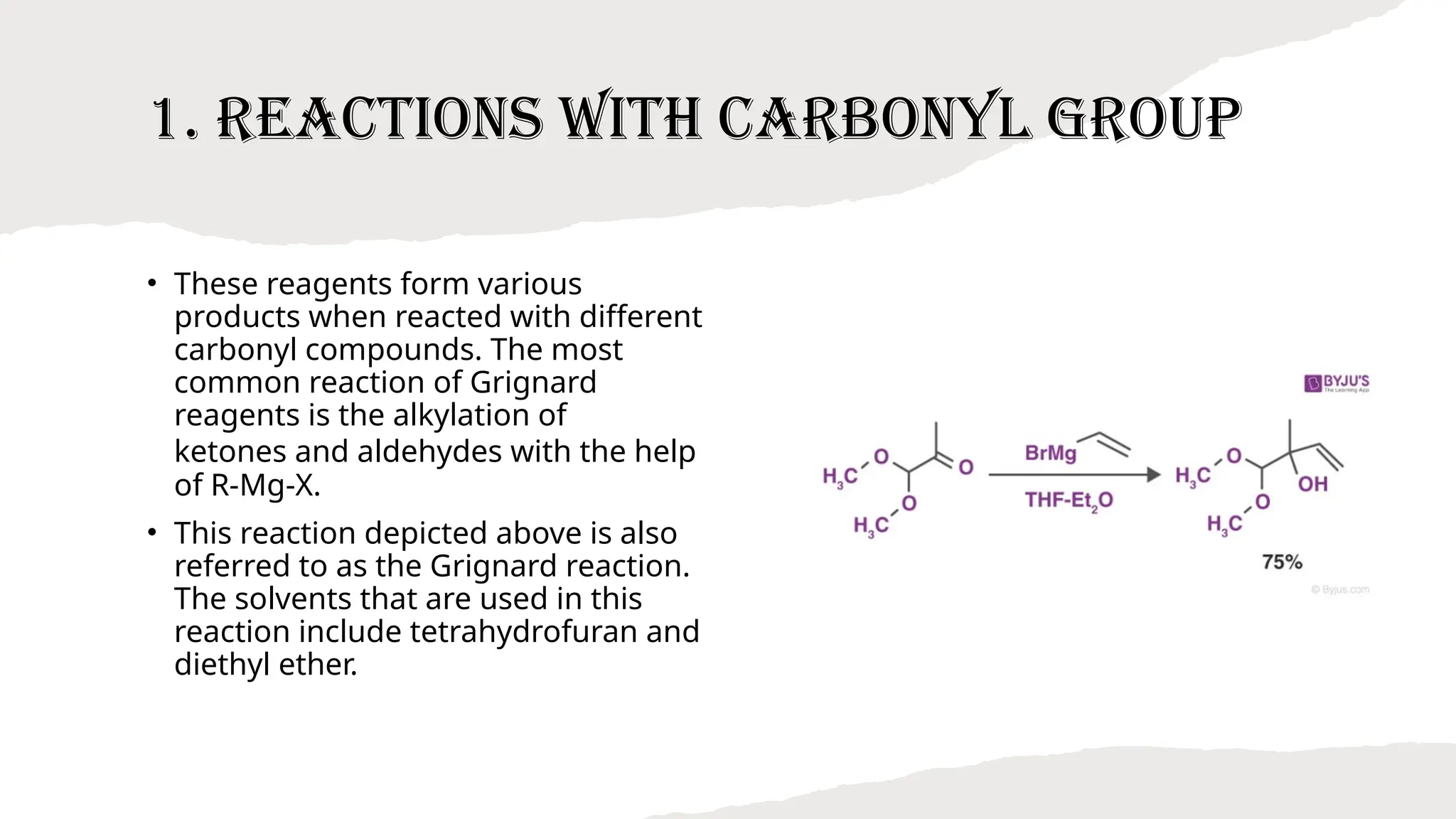
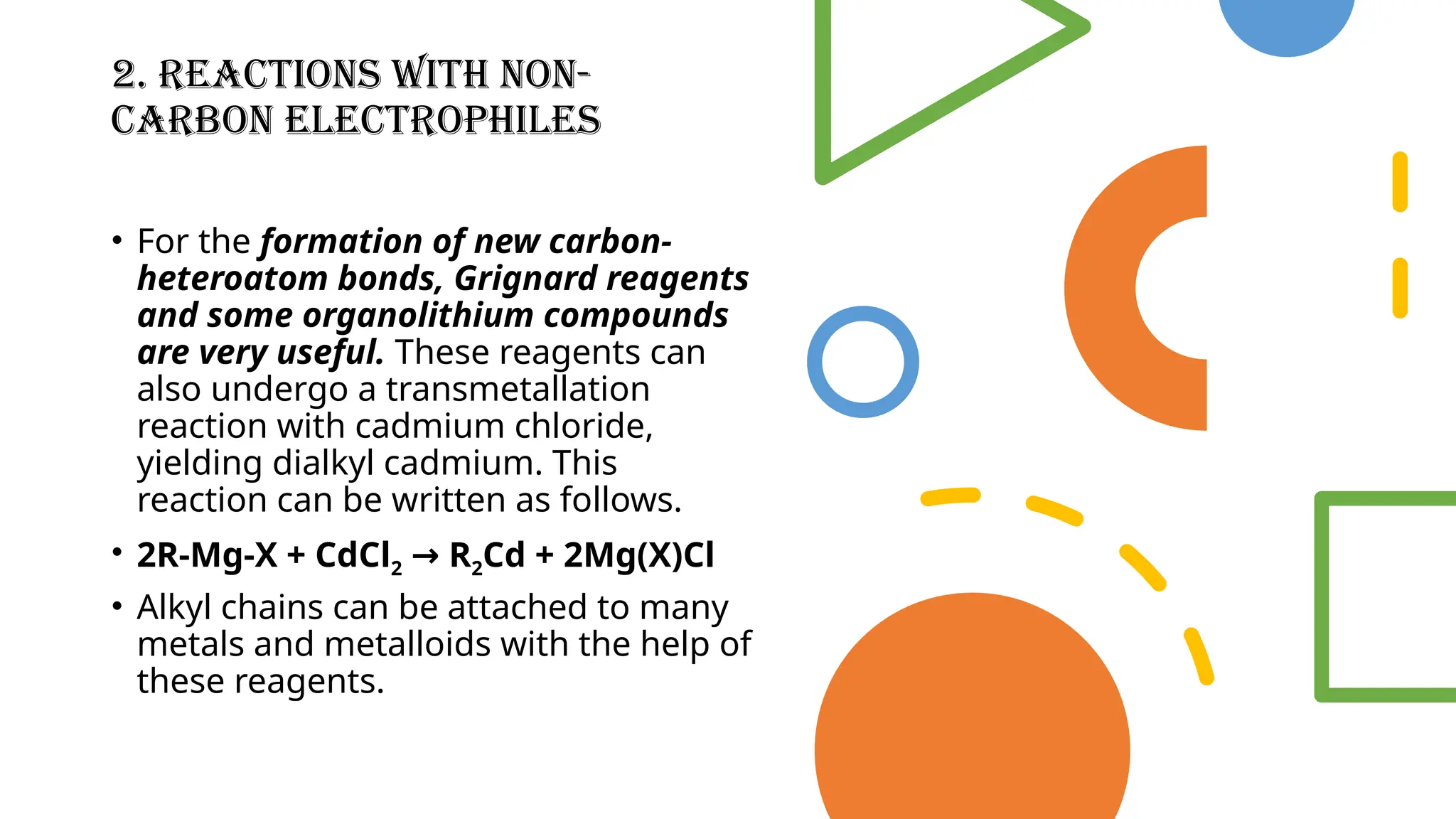
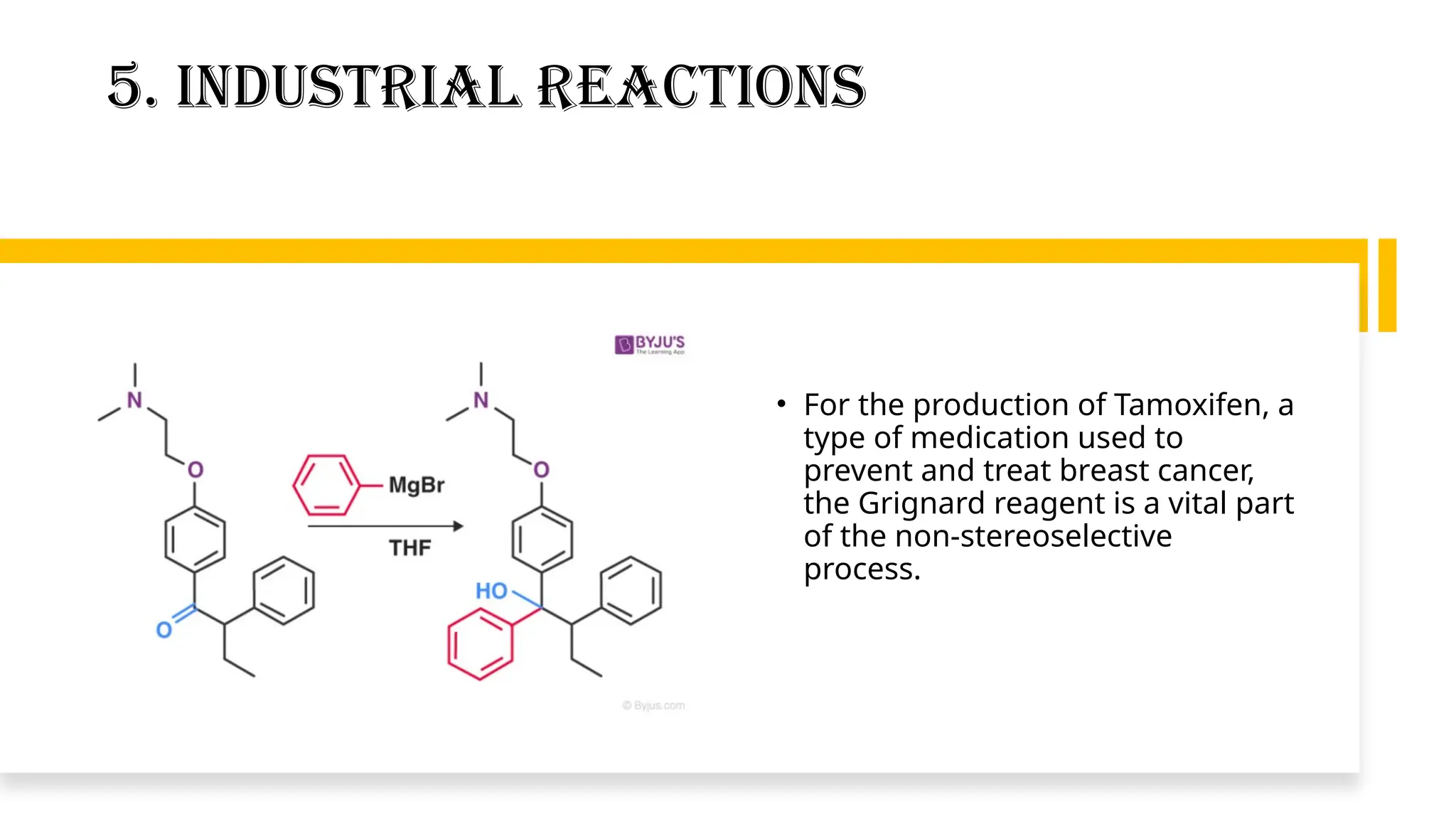
Grignard’s reagent is an organomagnesium compound, vital for organic synthesis, prepared by reacting aryl or alkyl halides with magnesium. Its reactions, particularly with carbonyl groups, allow for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds, making them essential for synthetic organic chemistry. The document also highlights the challenges in preparing Grignard reagents, emphasizing the need for anhydrous conditions and specific solvents to prevent decomposition.