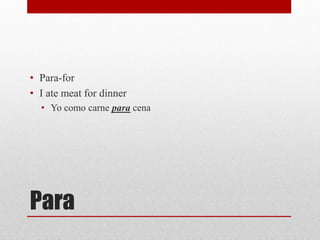
This document provides a table of contents and overview of various Spanish grammar topics including: nationalities, stem changers, indirect object pronouns, gustar, affirmative and negative words, superlatives, affirmative tu commands, irregular verbs, negative tu commands, reflexives, and sequencing events. It discusses rules, examples, and exceptions for each topic in 1-3 sentences per section.