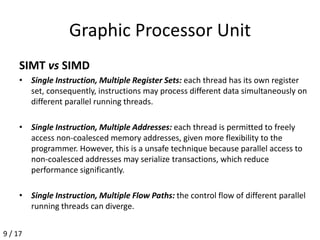
The document presents a methodology for predicting GPU performance using high-level application models, focusing on the behavior of applications when executed on GPUs. It outlines the objectives, related works, and details issues like data transfer, memory access, and branch divergence that impact GPU programming. The performance prediction engine will consider various factors, including branch divergence and memory access patterns, in its predictions.