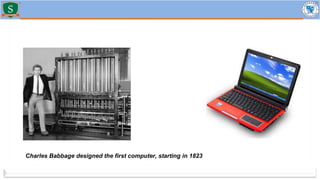
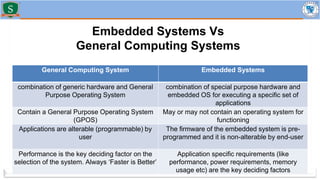
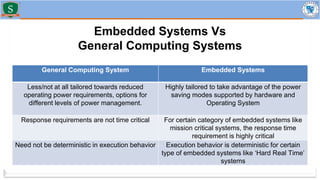
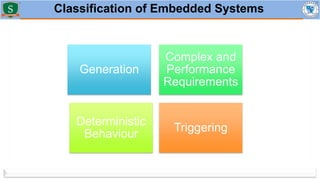
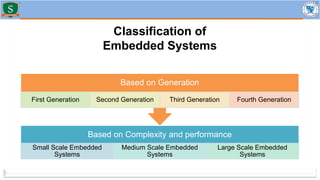
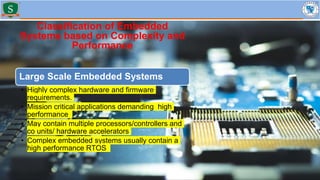
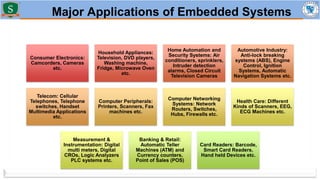
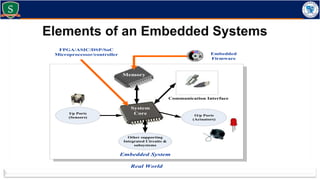
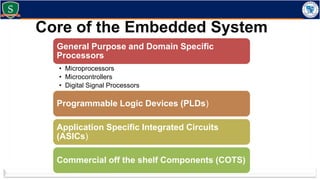
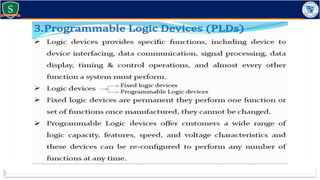
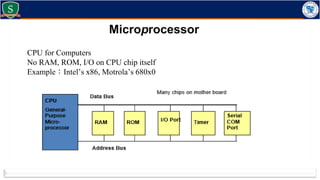
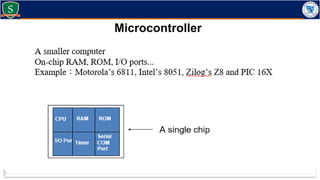
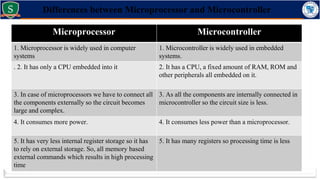
Embedded systems combine both hardware and firmware to perform specific functions. They are used in applications like smartphones, industrial equipment, medical devices, vehicles and more. Key elements include microprocessors or microcontrollers as the core, memory, and interfaces to sensors and actuators in the real world. Common types are small, medium and large-scale systems classified by their complexity, and generations from early 8-bit to modern systems-on-chip. Example applications span consumer electronics, industrial automation, automotive, networking and more. Sensors convert real-world inputs to electrical signals while actuators perform outputs like movement or displays.