This document provides an overview of key Google Analytics concepts including: how Google Analytics works by tracking users with JavaScript tags; metrics like pageviews, visits, and visitors; traffic sources; goals and funnels; profiles and filters; cookies and campaign tracking; ecommerce tracking; and custom visitor segmentation. It explains concepts in a straightforward way and provides examples to illustrate techniques like cross-domain tracking and event tracking.






![Pageviews, Visits and
Visitors [1]
pageview: is counted every time a page on your
site loads
visit (session): period of interaction between a
browser and a website. Closing the browser or
staying inactive for 30 minutes ends the visit.
visitor: is uniquely identified by a Google
Analytics cookie
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-7-320.jpg)
![Pageviews, Visits and
Visitors [2]
unique pageview: number of visits during which
page was viewed
absolute unique visitor: each visitor is counted
only once during the selected date range
new and returning visitor
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-8-320.jpg)
![Pageviews, Visits and
Visitors [3]
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-9-320.jpg)
![Time Metrics [1]
time on page (n) = timestamp (n+1) –
timestamp (n)
The time on page of the last page on a visit is
always 0, because there's not timestamp GA
can use to calculate the time.
time on site = sum(time on page) for a visit
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-10-320.jpg)
![Time Metrics [2]
avg. time on page = time on site / (pageviews –
exits)
pages with time on page 0 are excluded from the calculation
avg. time on site = sum(time on site) for all visits
/ visits
pages with time on page 0 are not excluded from the calculation
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-11-320.jpg)




![GA Accounts [1]
● One Google username:
● up to 25 GA accounts
● can be added as an administrator to an unlimited
number of GA accounts
● Administrators can:
● create filters, profiles, goals
● add users
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-16-320.jpg)
![GA Accounts [2]
● Users:
● read-only access to reports
● can be restricted to specific profiles
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-17-320.jpg)
![Profiles [1]
● Profile: set of rules that define what data is to
be included in the reports
● Examples:
● subdomains
● sections of a site
● filtered data (access control)
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-18-320.jpg)
![Profiles [2]
● The settings of a profile include:
● user access
● goals
● filters
Each domain has a unique tracking code number (property number)
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-19-320.jpg)





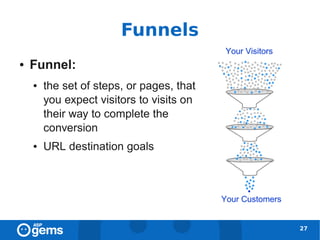
![Goals [1]
● Goal: website objetive
● Types:
● URL destination goal
– head match (/offer1/)
– exact match (/offer1/signup.html)
– regexp match (/.*/signup.html)
● Time on Site goal
● Pages/Visit goal
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-26-320.jpg)
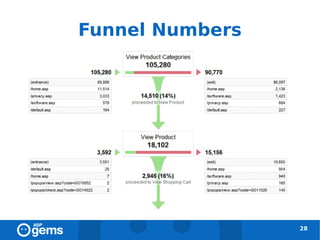
![Goals [2]
● Goal Value (optional): assign monetary value to
non-ecommerce goals
● During a visit:
● goal conversions => once
● e-commerce transactions => multiple times
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-29-320.jpg)

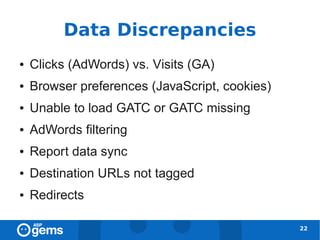
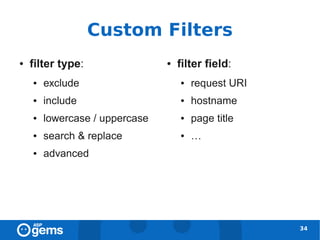
![Filters and Profiles [1]
● Filters are applied to profiles
● It is recommended to maintain an unfiltered
profile
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-31-320.jpg)
![Filters and Profiles [2]
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-32-320.jpg)

![Cookies [1]
● Cookies are text files that describe a small
piece of information about a visitor or the
visitor's computer.
● Google Analytics:
● first-party cookies
● your site can uniquely but anonymously identify
individual visitors
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-35-320.jpg)
![Cookies [2]
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-36-320.jpg)
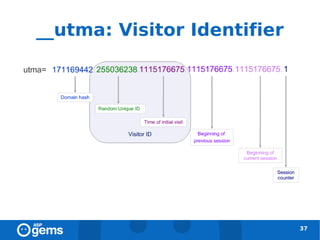

![__utmz: Campaign Values [1]
● The session number increments for every session during
which the campaign cookie gets overwritten.
● The campaign number increments every time you arrive at the
site by a different campaign or organic search, even if it is within
the same session.
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-39-320.jpg)
![__utmz: Campaign Values [2]
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-40-320.jpg)

![E-commerce Tracking [1]
● Enable e-commerce reporting in your website
profile
● Add the GATC
● Add some additional code to track each
transaction
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-42-320.jpg)
![E-commerce Tracking [2]
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-43-320.jpg)

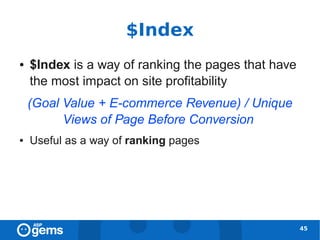
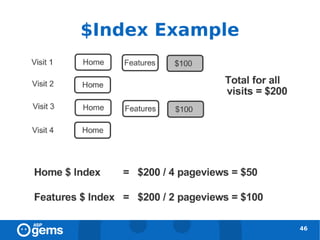
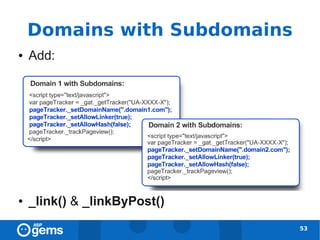
![Tracking across Domains [1]
● Add the following lines to the GATC on all
pages of both domains:
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-47-320.jpg)
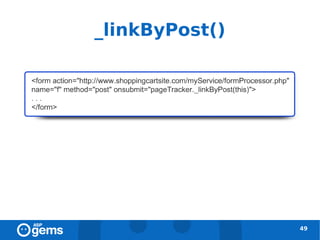
![Tracking across Domains [2]
● Add _link() to all links between domains:
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-48-320.jpg)





![Site Search Reports [1]
● Site Search Usage: compares performance of users
who use site search versus those who do not
● Site Search Terms: only includes visits where a
search is performed
– can compare metrics between internal search
queries
– useful for identifying new keywords
– can be combined with segmentation
● Search Refinement: View the keywords visitors used
to refine their original searches
57](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-57-320.jpg)
![Site Search Reports [2]
● Search Navigation: See where visitors who search on
a specific keyword go after viewing the search results
page
● Start Pages: Shows you where visitors begin using
the search function (useful to assess the effectiveness
of landing pages)
● Destination Pages
● Trending
58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-58-320.jpg)




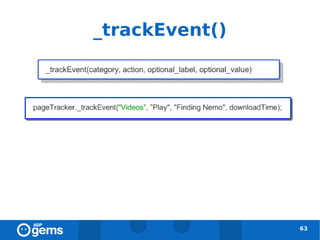

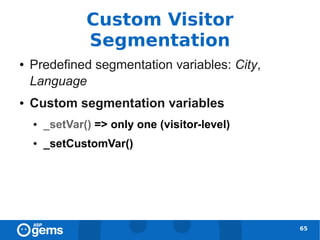
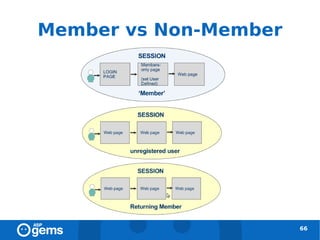
![_setVar() [deprecated]
● __utmv cookie
67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/googleanalyticsconcepts-100324094712-phpapp02/85/Google-Analytics-Concepts-67-320.jpg)


