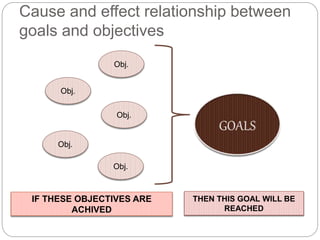
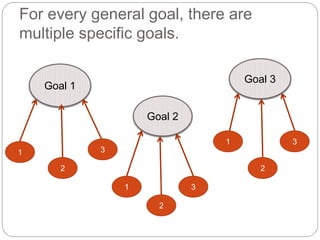
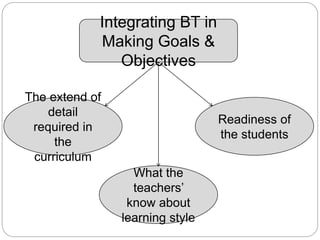
The document discusses goals and objectives for language curriculum design. It defines goals as general statements about what students should be able to do after completing a program, while objectives are more specific statements about the knowledge, behaviors, and skills students will have by the end of a course or program. The document provides examples of goals and objectives using different frameworks, emphasizes that objectives should directly support achieving goals, and recommends integrating Bloom's Taxonomy when formulating goals and objectives to ensure they address different learning domains.