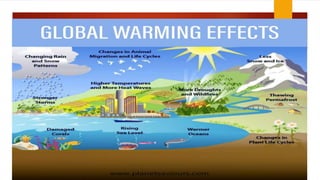
The document discusses greenhouse gases and global warming. It lists the group members and describes how burning fossil fuels increases carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere. This traps heat and warms the Earth's surface and lower atmosphere. It also notes that carbon dioxide levels have risen from 275 parts per million 100 years ago to over 375 parts per million currently. The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions is from burning fossil fuels for electricity, heat, and transportation. The effects of global warming include rising sea levels and temperatures.