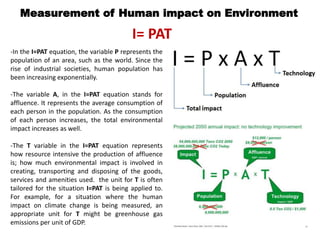
The document provides an extensive overview of environmental issues caused by human activities, outlining their causes, effects, and possible mitigation strategies. It discusses various global and local environmental challenges, including pollution, resource depletion, and biodiversity loss, particularly highlighting the significant issues faced by Bangladesh such as climate change and water pollution. It emphasizes the importance of collective action from individuals, governments, and organizations to address these pressing environmental concerns.