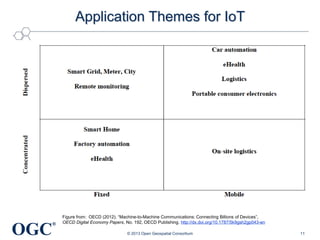
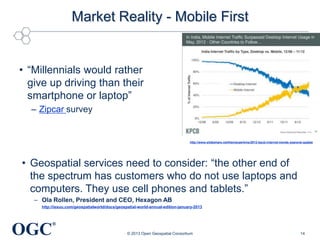
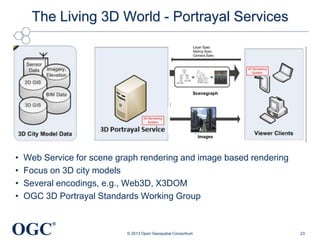
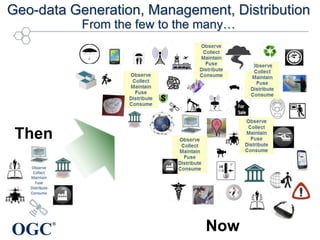
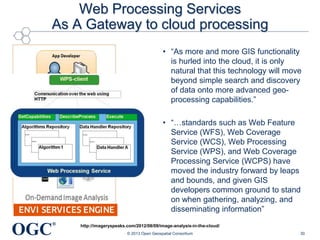
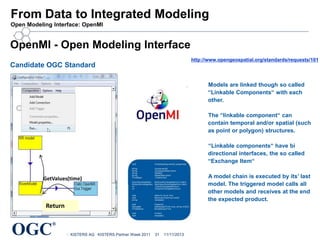
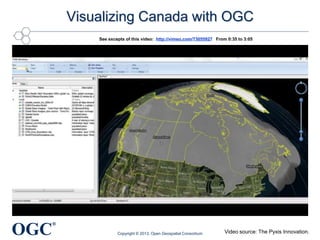
This document summarizes George Percivall's presentation on geospatial and geomatics trends at the 2013 TECTERRA Geomatics Showcase. Some of the key trends discussed include the power of location data and analytics, the rise of the Internet of Things and associated opportunities for geospatial processing and modeling, the mobile-first development landscape and standards like GeoPackage, opportunities in indoor mapping and modeling with IndoorGML, and advances in crowdsourced mapping, semantics, big data processing, and smart city applications. OGC standards play an important role in many of these emerging areas to support interoperability.