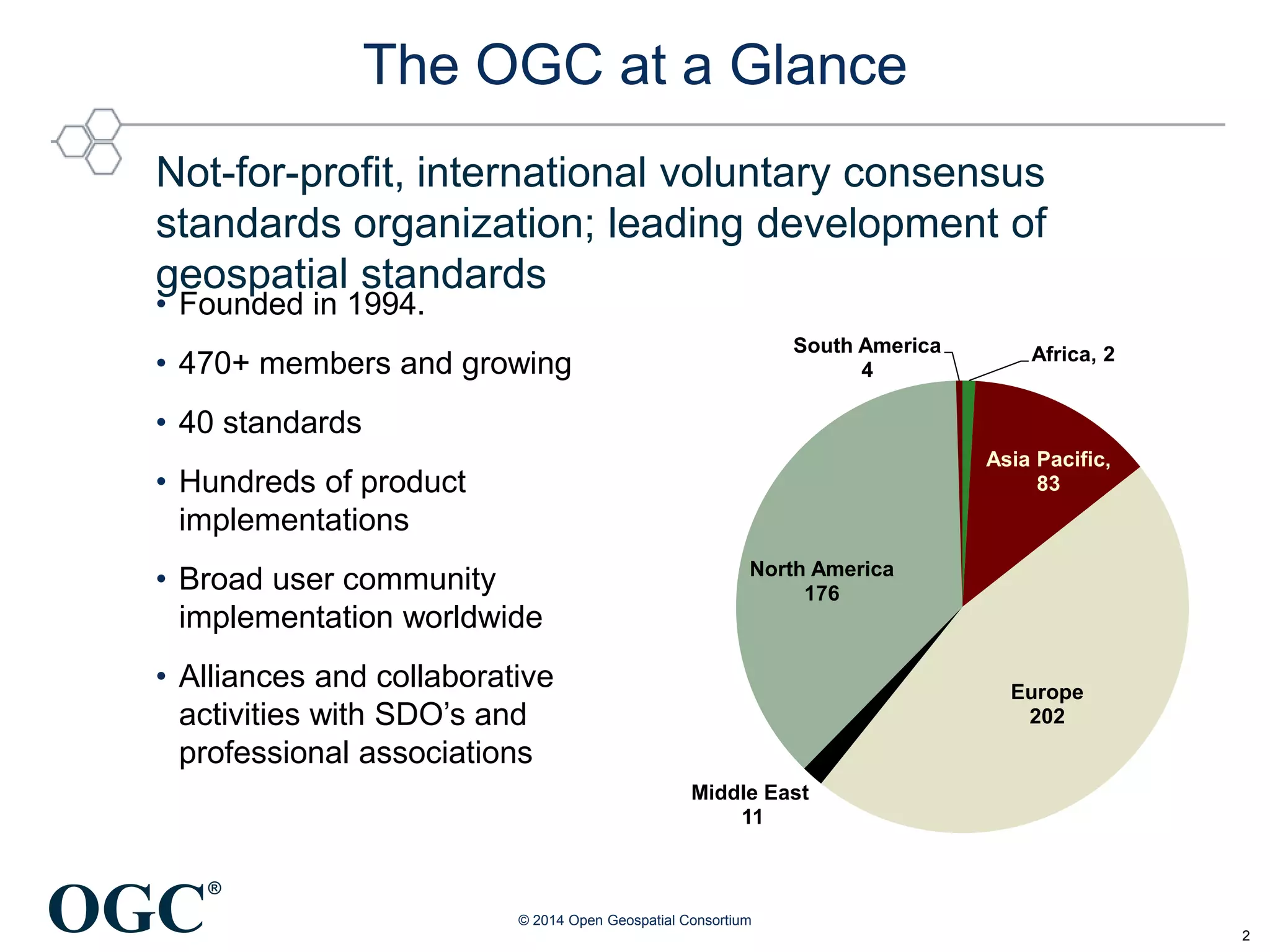
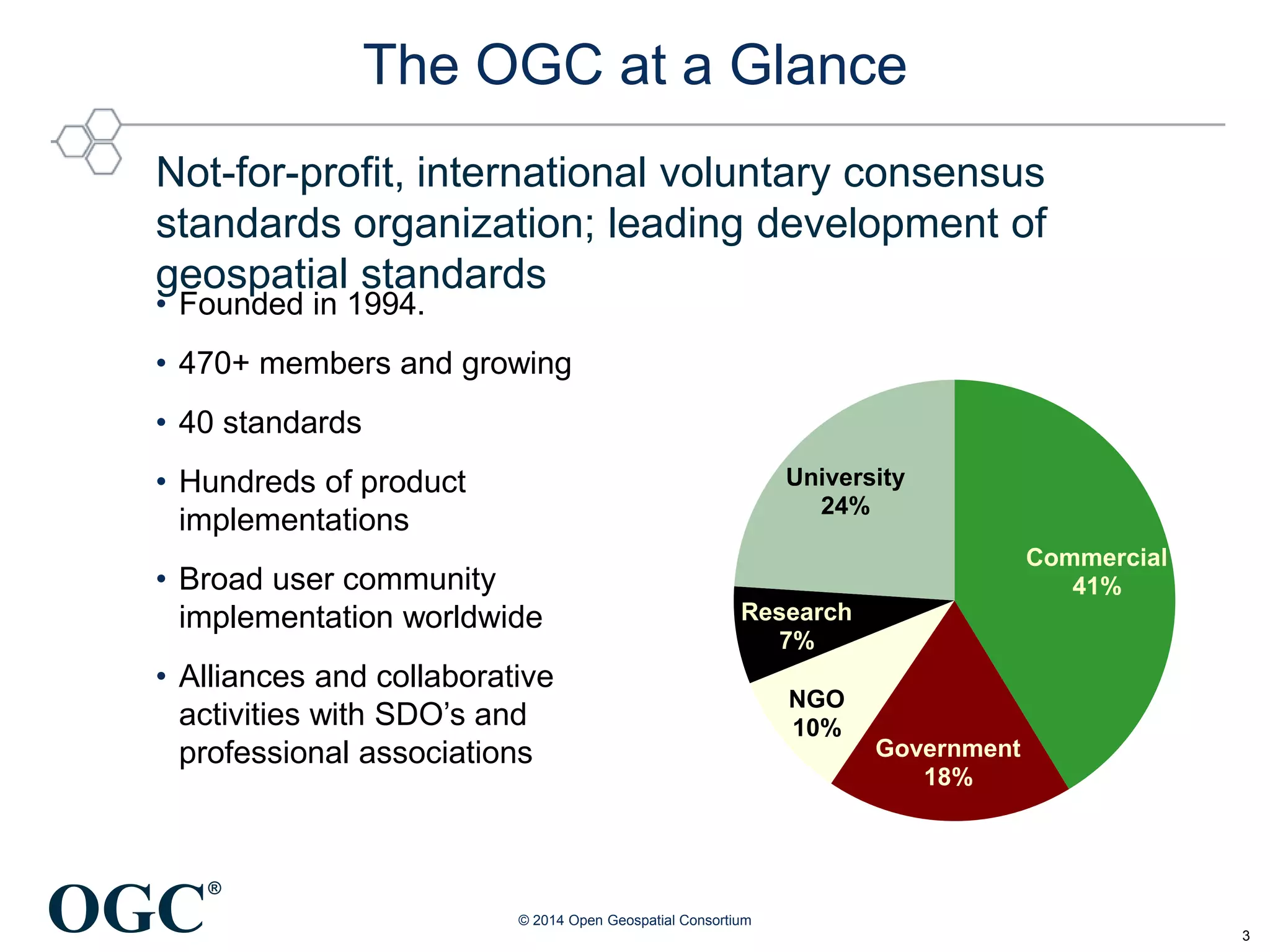
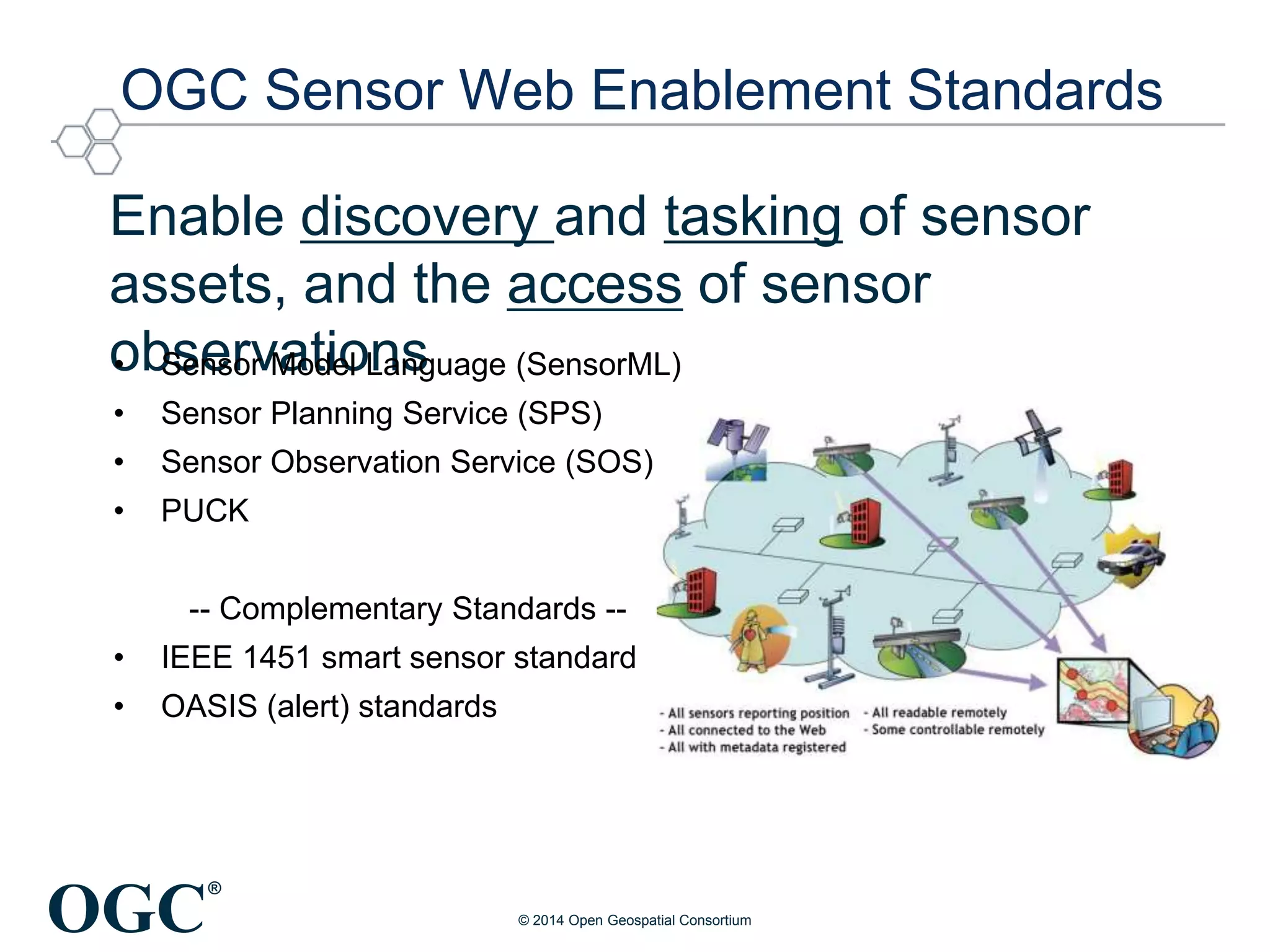
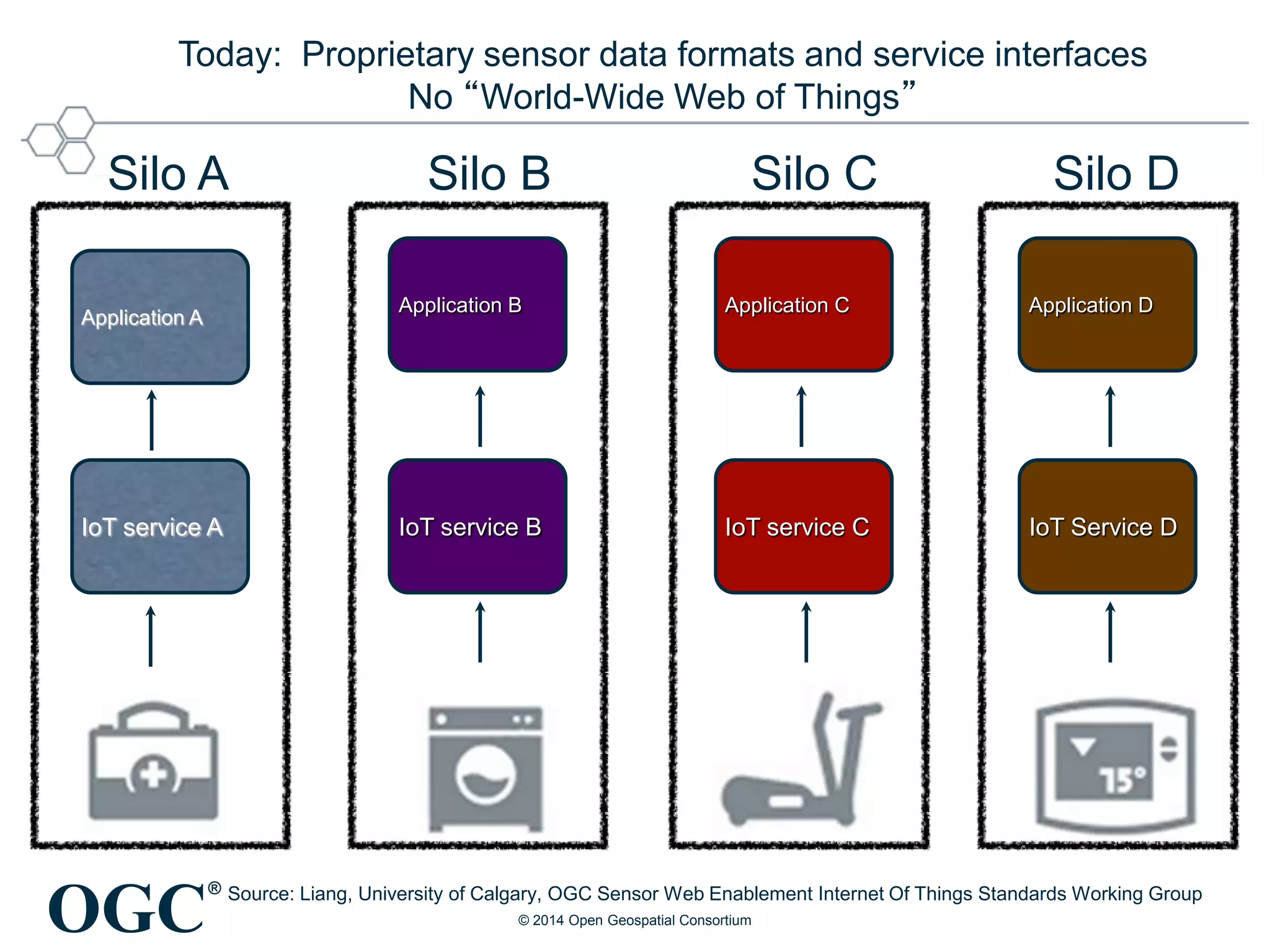
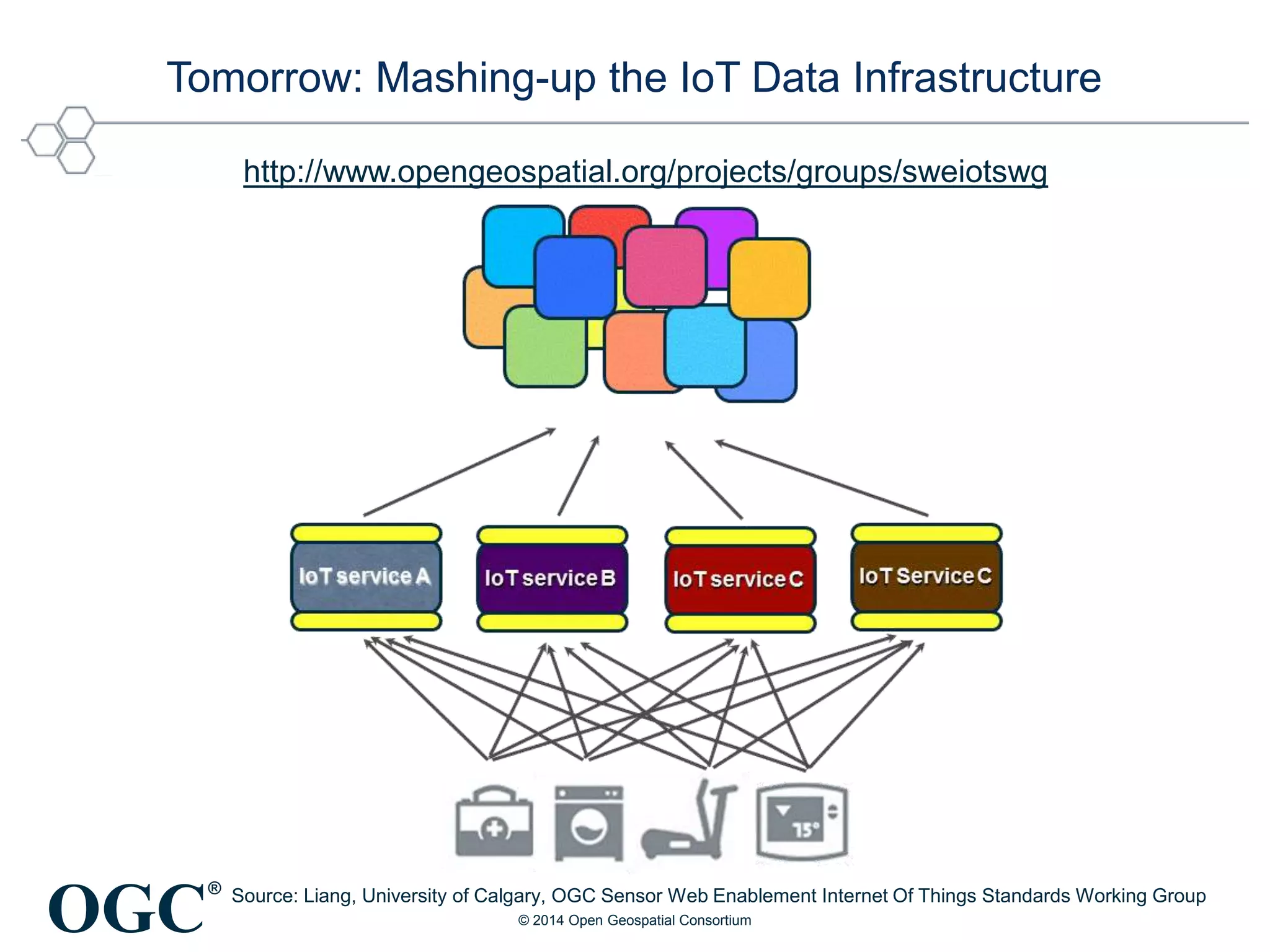
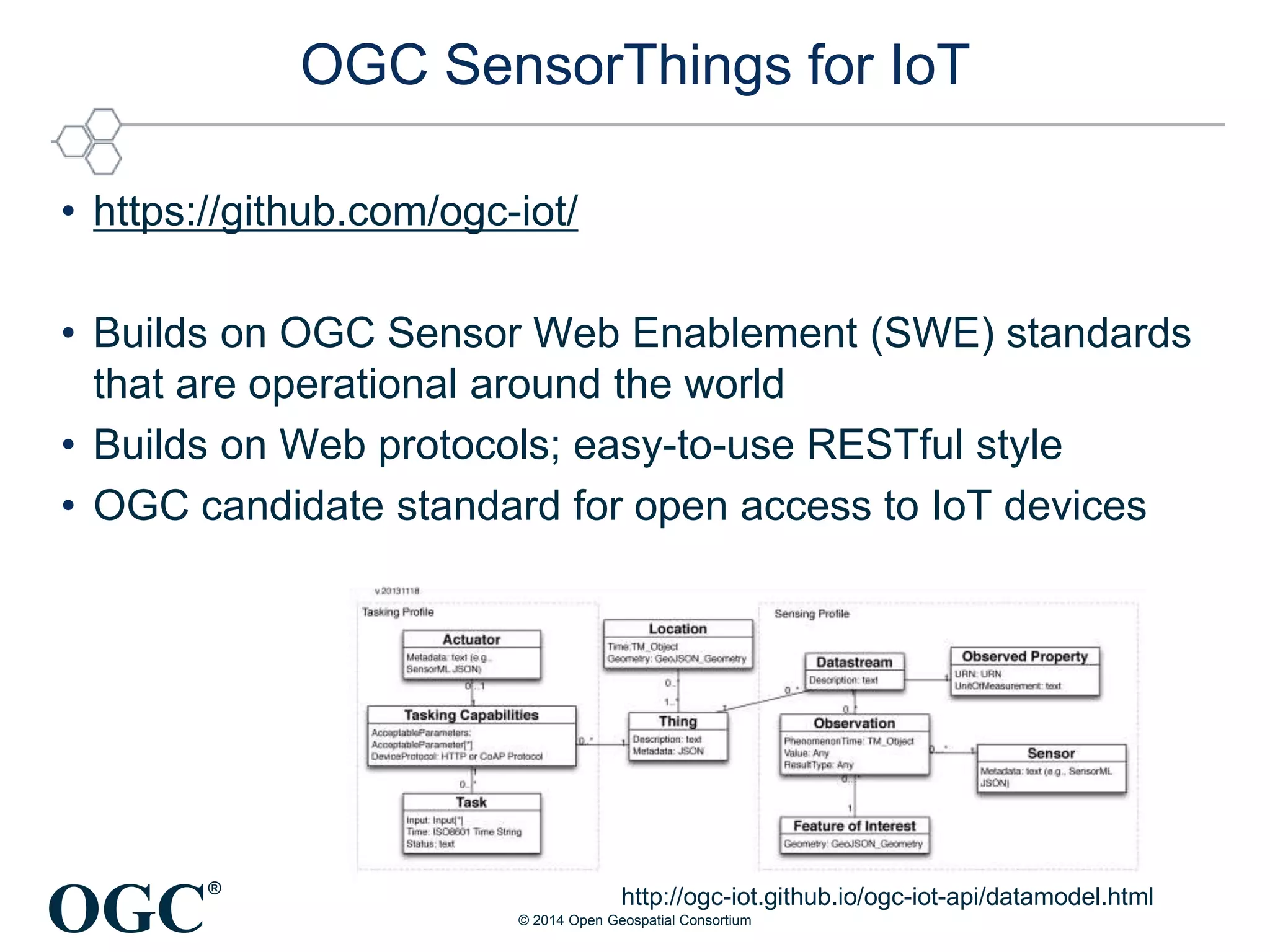
The Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) is a non-profit organization facilitating the development of geospatial standards, with over 470 members and 40 established standards since 1994. The document discusses the integration of IoT with geospatial data, highlighting its potential for enhanced situational awareness and data visualization through standardization. It emphasizes the arrival of IoT as accessible and practical, along with OGC's Sensor Web Enablement standards that support the discovery and tasking of sensor assets.